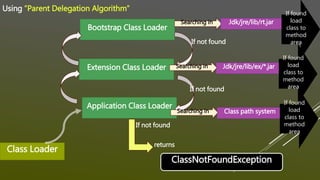
The document discusses the execution flow of the main() method inside the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It explains that the main() method acts as the initial entry point and starting point for program execution. When a Java class is run, the JVM loads the class and executes the main() method first. Any other methods in the class can only be executed if explicitly called from main(). It then provides answers to some common questions about the main() method, such as that it is user-defined but has a predefined syntax, and that the String array parameter allows passing runtime arguments to the program. Finally, it outlines the step-by-step process the JVM follows to load and execute a Java class containing a main() method


![WHY MAIN(-) METHOD
main(-) is a initial point
of a class Execution
JVM
Internal code
Example.java
Class Example {
public static void main(String[]
args)
{
System.out.println(“main
Block”);
}
Output :
main Block
If we create some
other method in a
class
static void m1()
{
System.out.println(“method 1
body”);
}
static void m2()
{
System.out.println(“method 2
body ”);
}
Then JVM only
execute main(-)
method’s logic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-3-320.jpg)
![WHY MAIN(-) METHOD(CONT’D)
JVM
Internal code
Example.java
Class Example {
public static void main(String[]
args)
{
System.out.println(“main Block”);
}
Output :
main Block
method 2 body
static void m1()
{
System.out.println(“method 1
body”);
}
If we want to execute
those method’s logics
then we must call these
methods from main(-)
method
m2();
static void m2()
{
System.out.println(“method 2
body ”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-4-320.jpg)
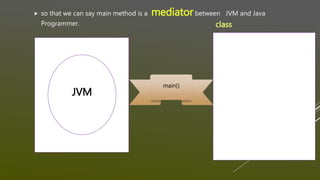

![QUES: IS MAIN METHOD IS USER DEFINED OR PREDEFINED
Ans:
main(-) method is User defined method with Predefined Syntax
Public static void main(String[] args)
{
}
given by : sun Public static void main(String[] args)
{
…………….
…………….
}
Complete logic is Programmer’s logic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-7-320.jpg)

![WHY MAIN() METHOD HAS STRING PARAMETER ARRAY ?
For reading runtime values from keyboard()
C:Windowssystem32cmd.exeC:_
Class Example {
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
String name=arg[0];
String addr =arg[1];
System.out.println(“name: ”+name);
System.out.println(“addr : ”+addr);
}
}
Compile
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.10240]
(c) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:Userssaurav>C:Userssaurav> javac Example.java
X[]-
C:Userssaurav>
Compiler
generate
Example.class
file in same
directoryC:Userssaurav> java Example sherlock NYsherlock NY
name :sherlock
addr : NY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-9-320.jpg)
![HOW JVM EXECUTE THIS “EXAMPLE1” JAVA CLASS
Class Example1 {
static int x=10;
static int y=20;
int a=30;
int b=40;
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
int p=50;
int q=60;
Eample1 e1=Example();
}
}
Example1.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-10-320.jpg)
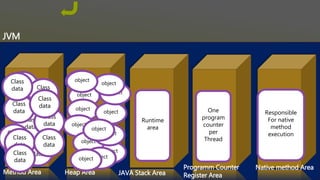
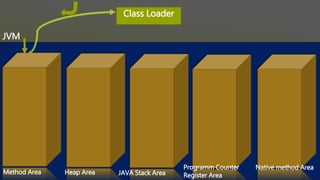
![Method Area Heap Area JAVA Stack Area
Programm Counter
Register Area
Native Area
Class Loader
If found, then load this class in method area by
creating java.lang.Class Object
x 0
y 0
a
b
main(s[]){ }
x = 10
y = 20
10
20p s v main(S args[])
args1010
p50
q60
length 0
1010
e12020
2020
a 30
b 40
Static variable
Linking
&
Execute
native
methods
uisng JNI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/executionflowofmainmethodinsidejvm-160531002415/85/Execution-flow-of-main-method-inside-jvm-15-320.jpg)

