The document provides an in-depth overview of Java, including its history, principles, usage, and basic syntax. It explains key Java features such as object-oriented programming, portability, high performance, and the significance of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Additionally, it covers Java installation, fundamental data types, control statements, methods, classes, and offers a simple 'Hello World' exercise as a practical introduction.















![Variables
• type identifier [=value];
- boolean status;
- int i = 0;
- int d = 66, e, f = 1410;
‣ declare three ints and initialize d and f.
- String name;
- Date today = new Date();
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-16-320.jpg)





![Methods
• [modifiers] return_type method_name([parameterType parameterName, …]) {
method body;
[return result]
}
• public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello World!”);
// without return!
}
• long getMax(int a, int b) {
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-22-320.jpg)
![Classes
• Top-level class
- [modifiers] class CLASS_NAME { //the file name should be CLASS_NAME.java
// Class members (variables, methods, classes)
}
• Inner class
- class Foo { // Top-level class
class Bar { // Inner class
}
}
• Local class
- class Foo {
void bar() {
class Foobar {// Local class within a method
}
}
}
• Initialization
- Foo foo = new Foo();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-23-320.jpg)

![Interfaces
• Interface (Animal.java)
- interface Animal {
public void eat();
public void sleep();
}
• Implements (Cat.java)
- public class Cat implements Animal{
String name;
public Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(name + “ eats");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println(name + “sleeps");
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Cat cat = new Cat(“Barney”);
cat.eat();
cat.sleep();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-25-320.jpg)
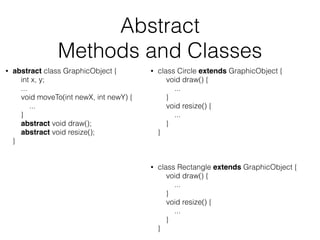
![Java File Structure
[package _________] // package directory name (com.zebardast.java.tutorials)
[import _________]
[import _________]
[import _________]
[public] class CLASS_NAME { //File Name should be CLASS_NAME.java
//class members
}
class Foo {
//class members
}
class Bar {
//class members
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-27-320.jpg)
![Simple Exercise
Hello Word!
• Create HelloWorldApp.java:
- public class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!"); // Print the string to the console.
}
}
• Compile:
- $ javac HelloWorldApp.java
• Run:
- $ java HelloWorldApp
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mjmfd1svicaxodosdwbg-signature-20f2778232a45aa451929d2911be83c6c8661dd5a561b5d80dcb42b24dda3828-poli-141211130900-conversion-gate02/85/Java-for-beginners-28-320.jpg)

