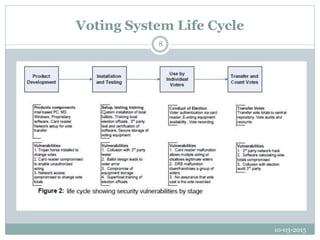
This document discusses e-voting and associated risks. It begins by defining electronic voting as a system where election data is primarily recorded, stored, and processed digitally. It notes that e-voting could increase voter turnout and support democracy, while also opening new markets. However, barriers include a lack of standards, difficulty changing laws, high costs, and security and reliability concerns. The document outlines security risks like denial of service attacks and malware infecting voting machines. It provides details on how early internet voting systems worked and the life cycle of voting systems. Finally, it concludes that e-voting is an emerging issue with open questions that requires further experimentation and security expertise.