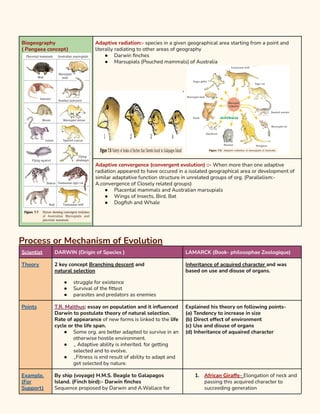
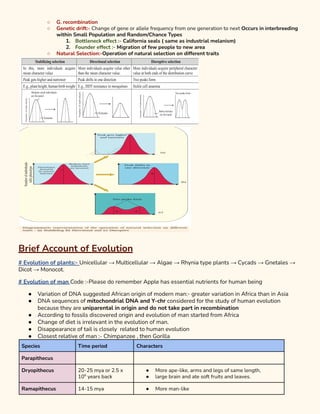
1. The document discusses evidence for evolution including paleontological, embryological, natural selection and adaptation, comparative anatomy, biogeography, and vestigial structures as evidence.
2. It describes the mechanisms of evolution including Darwin's theory of natural selection and Lamarck's theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics. Mutation, genetic drift, gene flow and natural selection can disrupt Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and drive evolution.
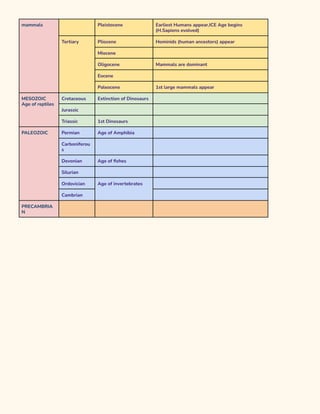
3. A timeline of human evolution is presented starting with early hominins like Australopithecus approximately 3-4 million years ago, through genus Homo species like H. habilis, H. erectus, H. heidelbergensis, H. neander