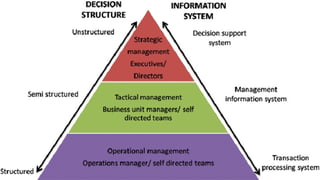
The document outlines the evolution of information systems, highlighting the development and functions of various types such as transaction processing systems (TPS), management information systems (MIS), and decision support systems (DSS). It discusses how these systems support different organizational levels and functions, from operational to strategic management. Additionally, it touches on mobile computing and knowledge management systems as modern advancements in the field.