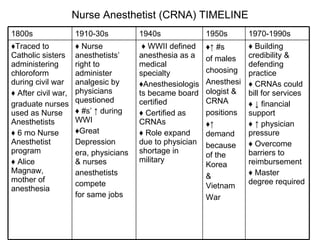
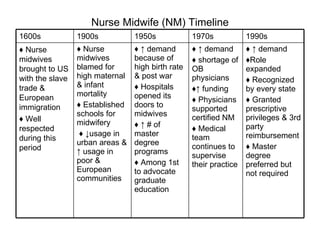
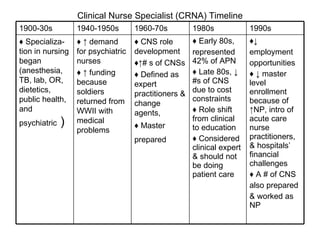
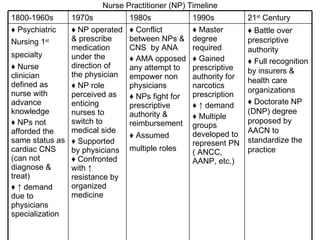
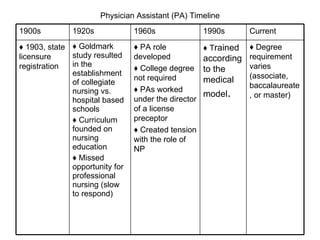
The document provides a timeline and overview of the evolution of several advanced practice nursing roles from the 1800s to present day, including nurse anesthetists, nurse midwives, clinical nurse specialists, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants. It traces the development of these roles in response to societal needs and pressures from organized medicine. Key events included establishing educational standards, gaining prescriptive authority, and fighting for reimbursement and full recognition of their scope of practice. Resistance from physicians occurred when nursing roles competed for similar jobs or responsibilities.