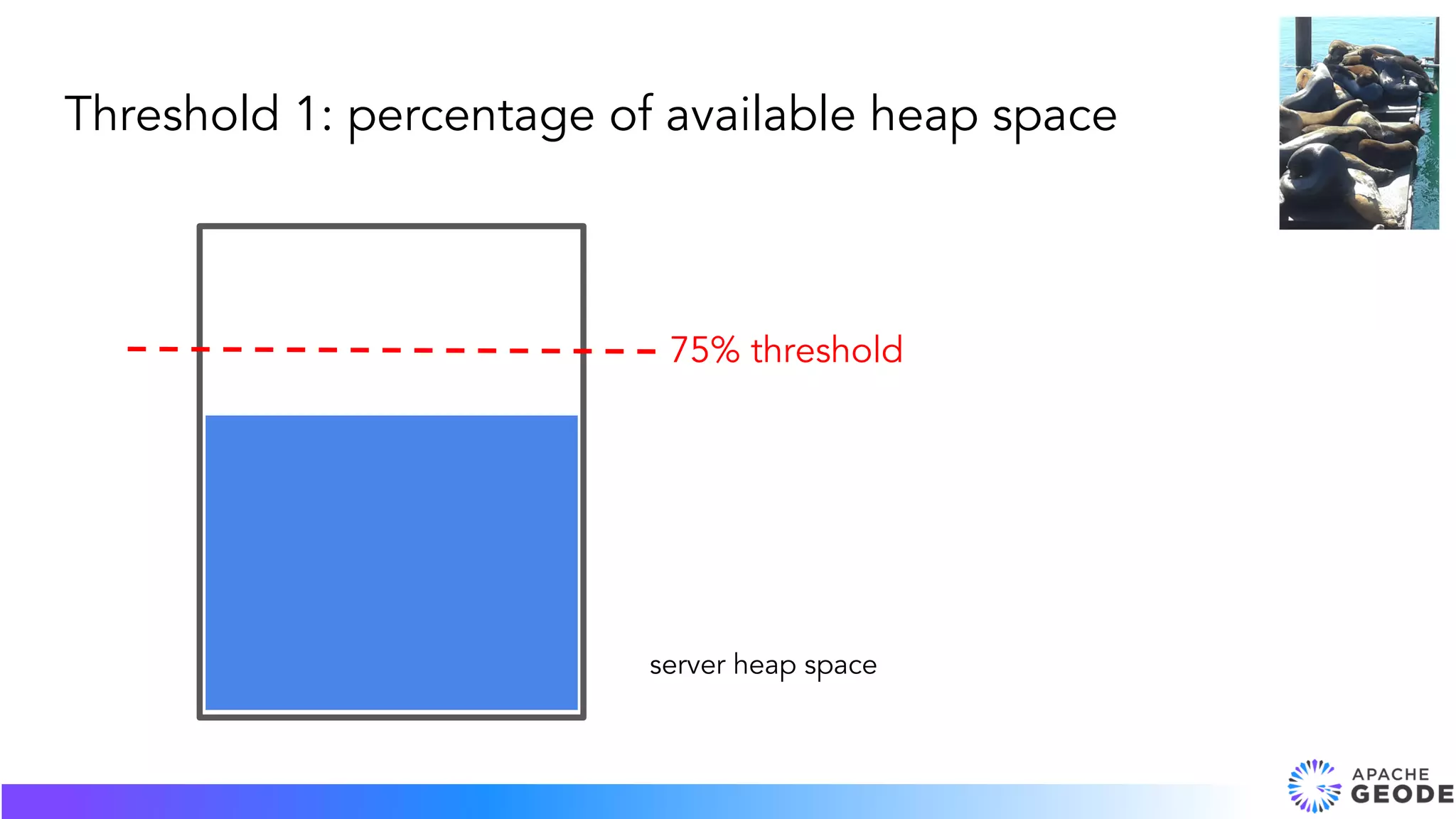
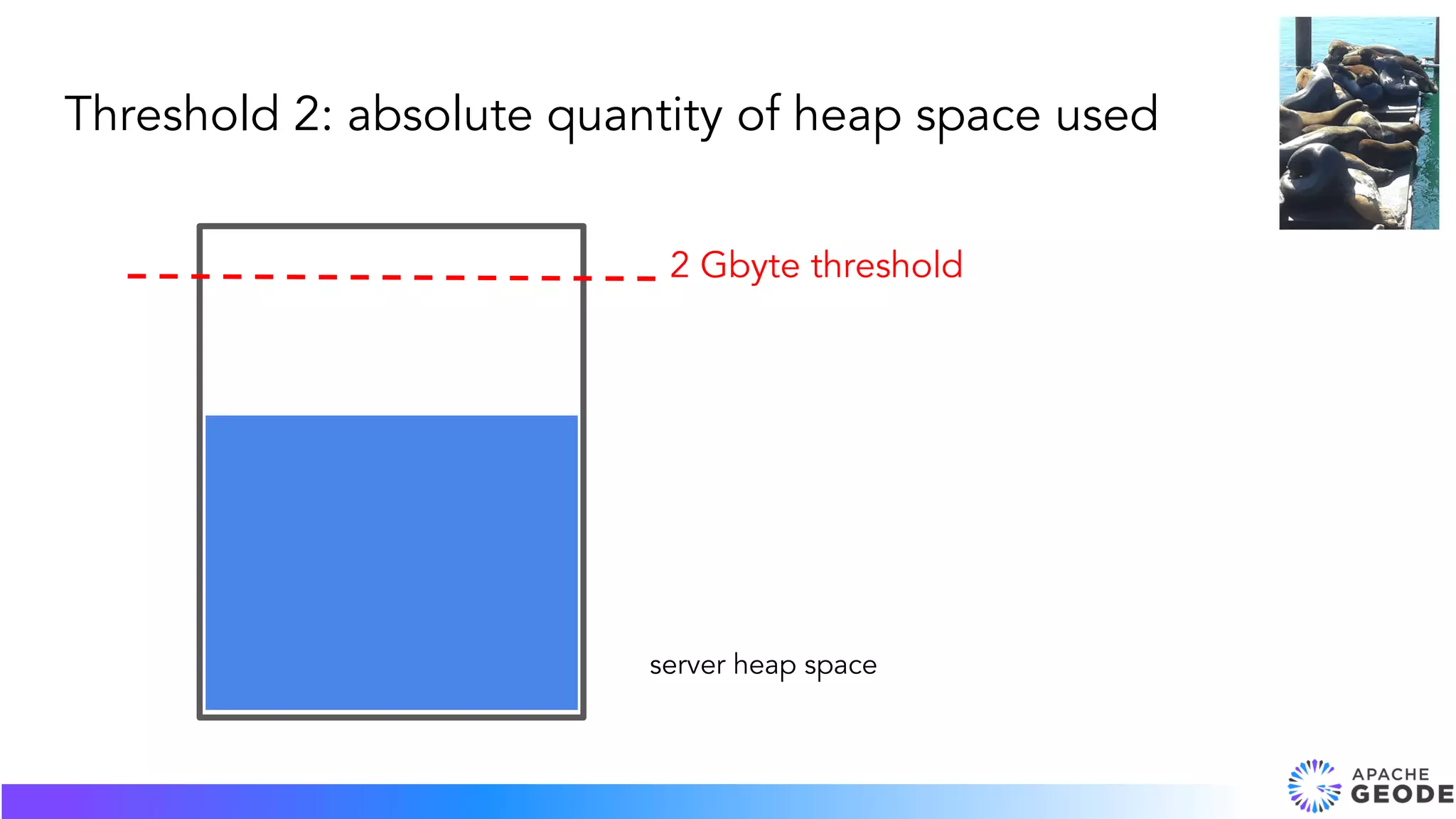
The document discusses overflow, expiration, and eviction in the context of memory management. It covers expiration concepts such as time to live (TTL) and idle timeout, including use cases and examples in Apache Geode. Additionally, it addresses eviction actions to manage heap memory usage and maintain performance by removing less recently used entries.