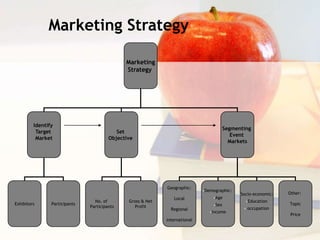
This document provides guidance on planning an event from concept to post-event. It discusses developing the event concept, choosing a location, developing the theme, creating invitations and promotional materials. It also covers budgeting, food and beverages, the event day checklist, post-event tasks like evaluation and cleanup. Appendices include templates like a site inspection checklist, layout diagram, production schedule, supplier checklist, and sponsorship information. The overall document aims to help event planners consider all essential aspects of holding a successful event.