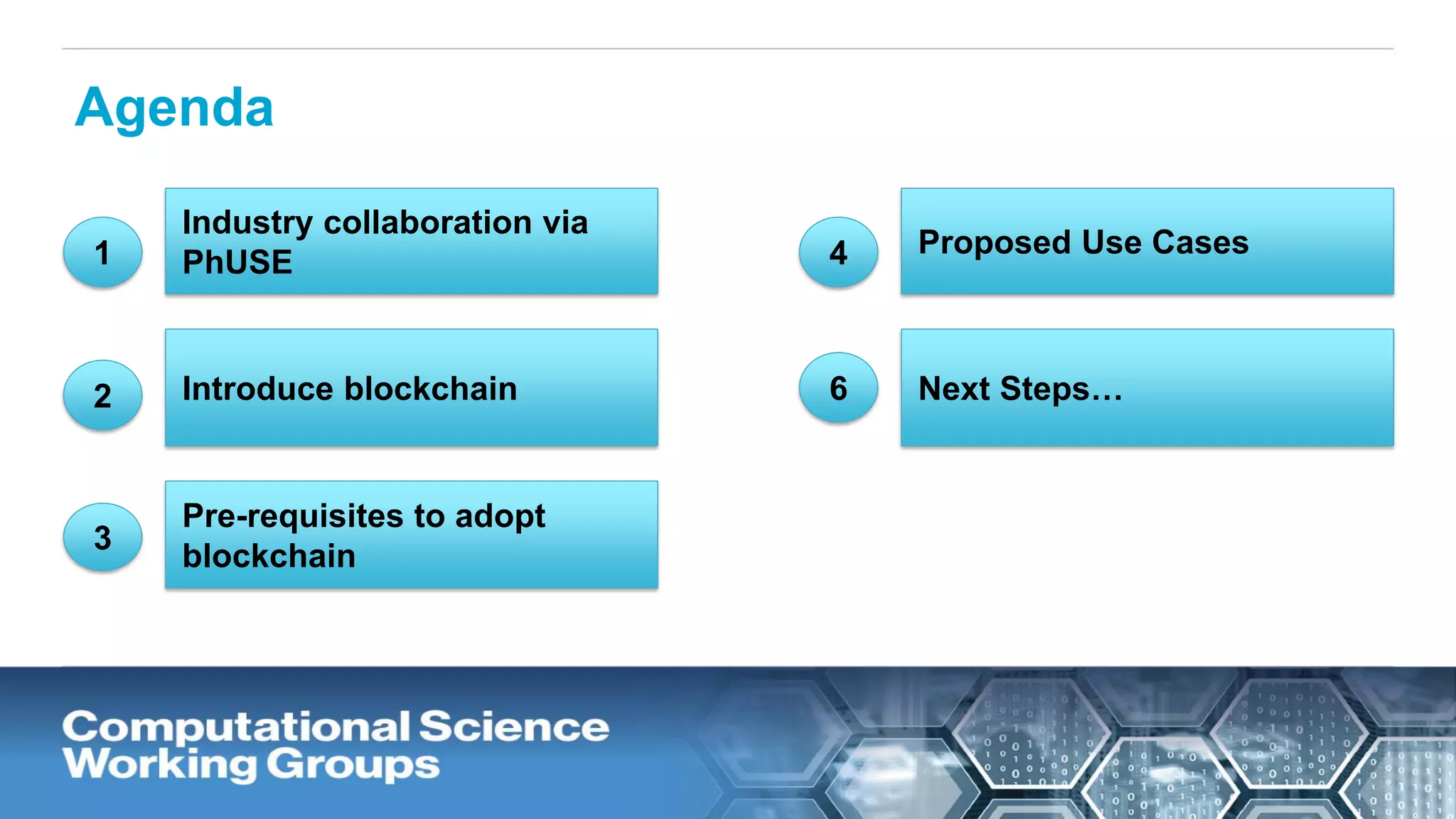
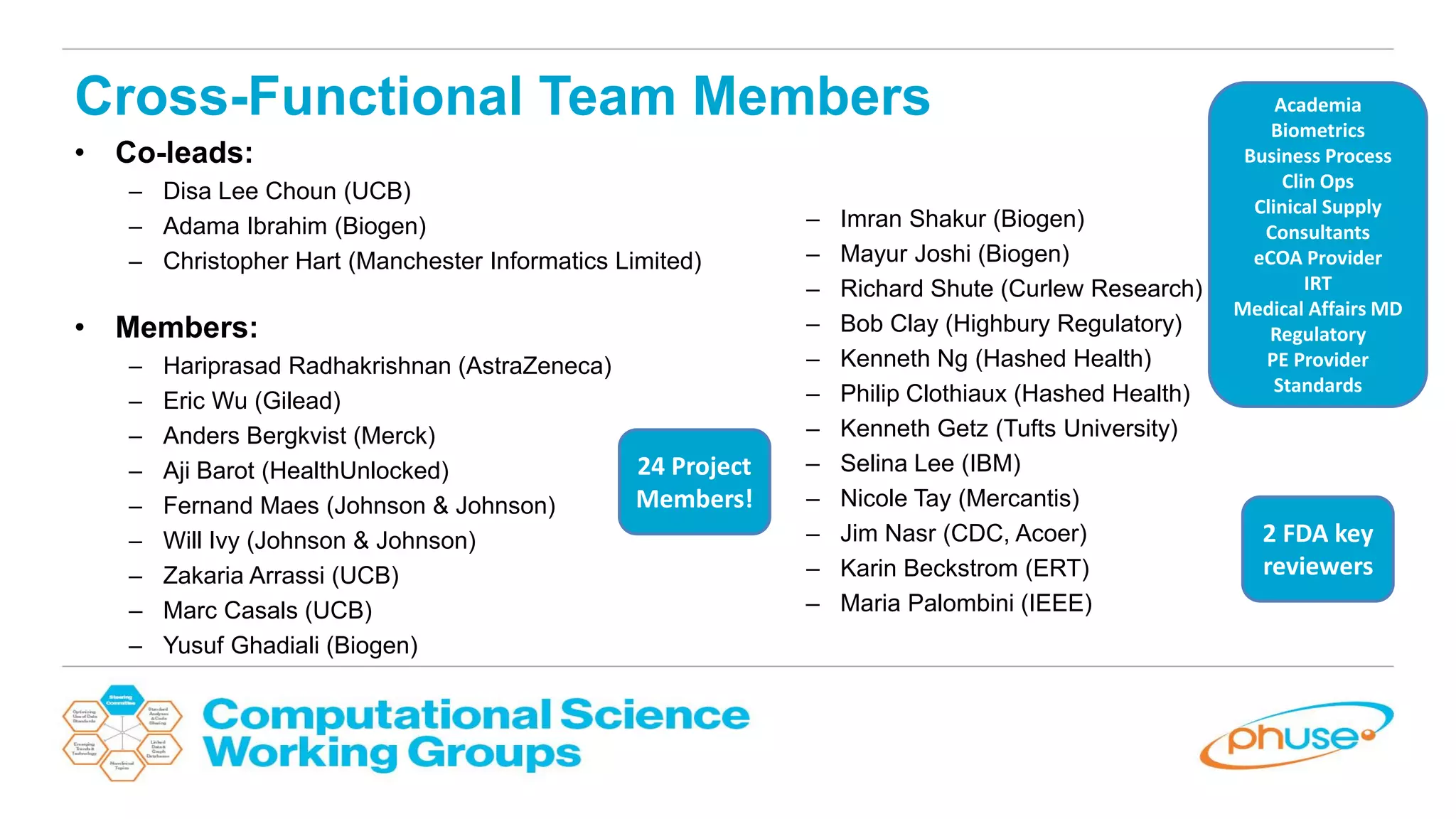
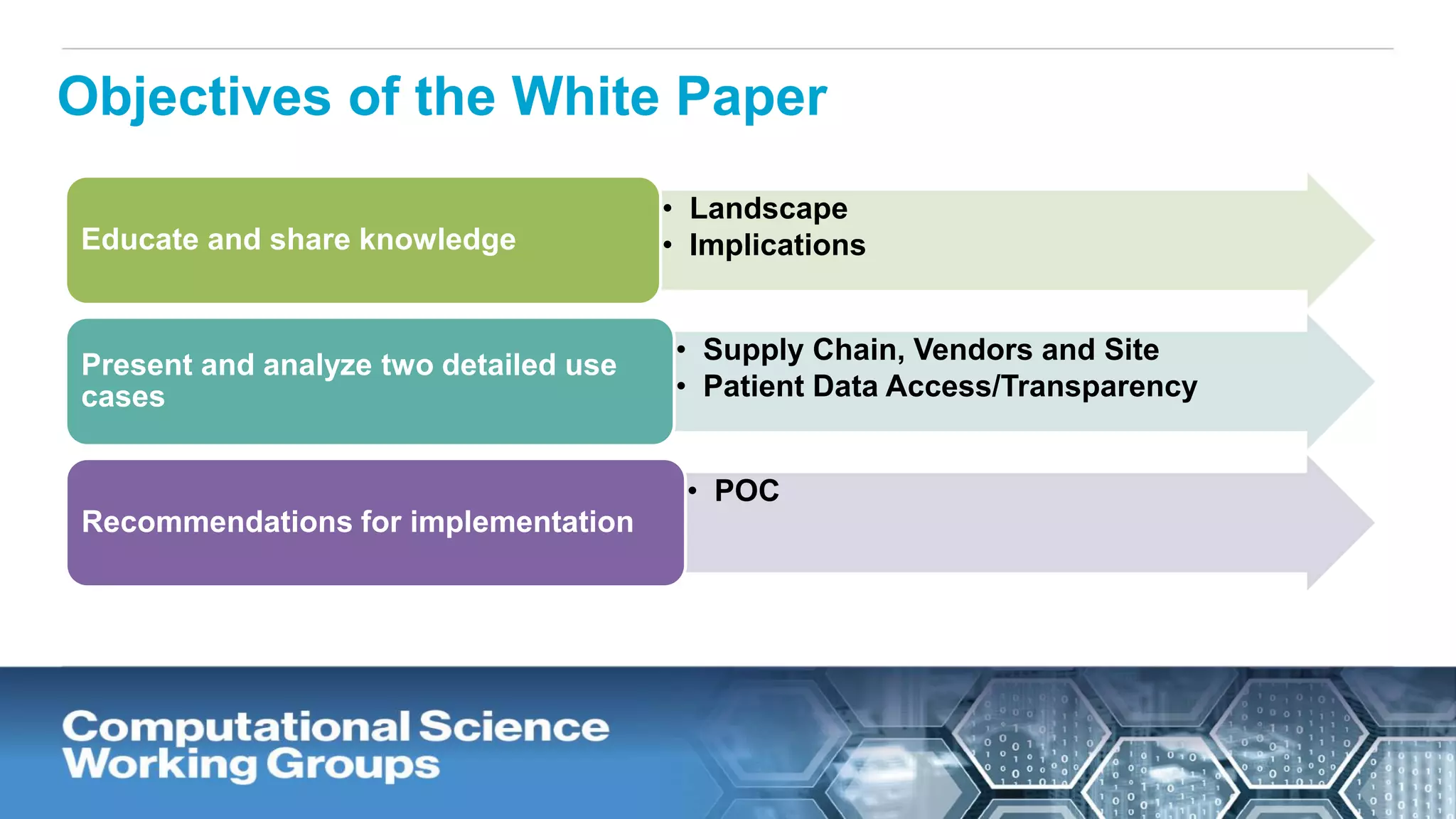
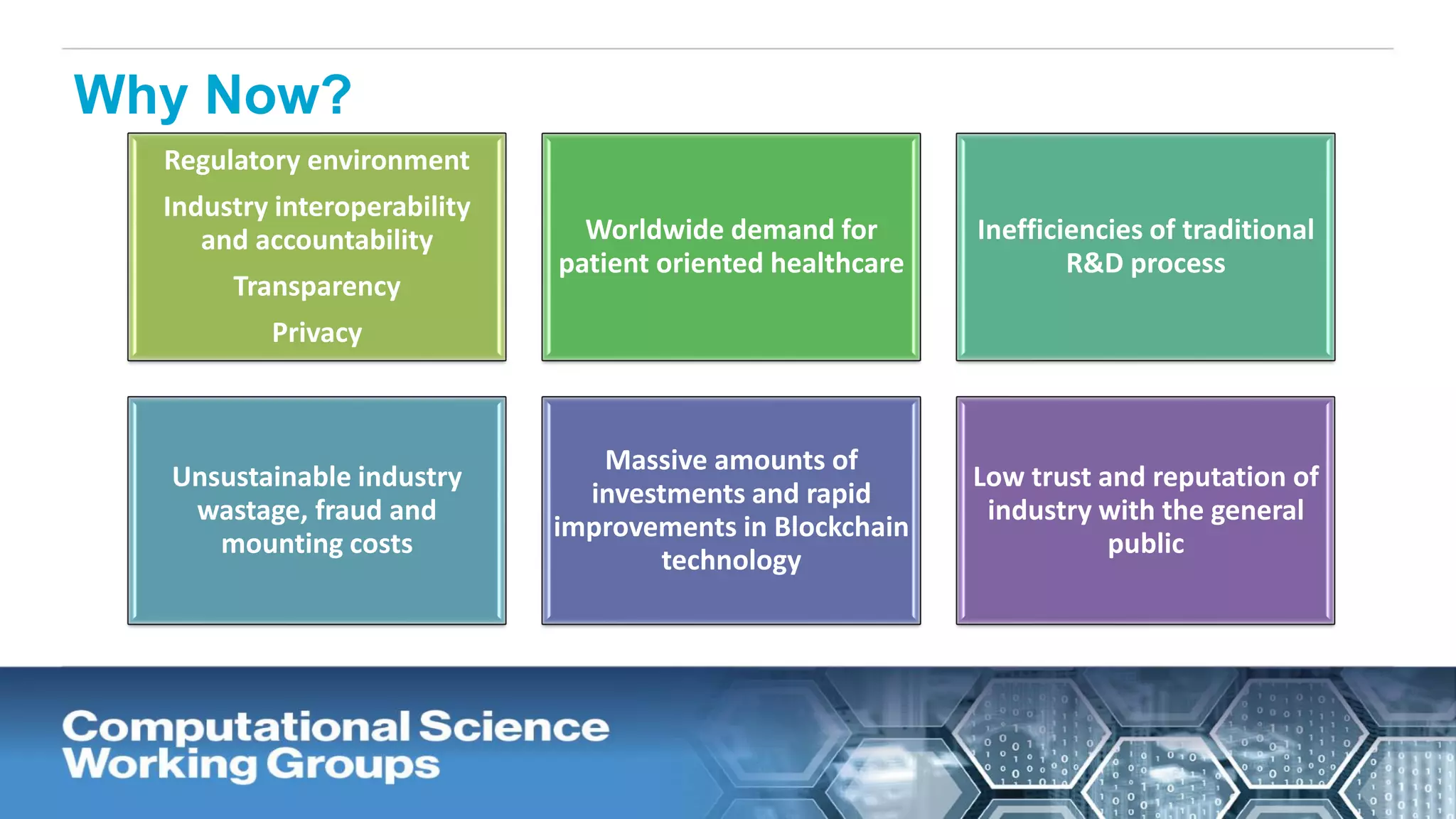
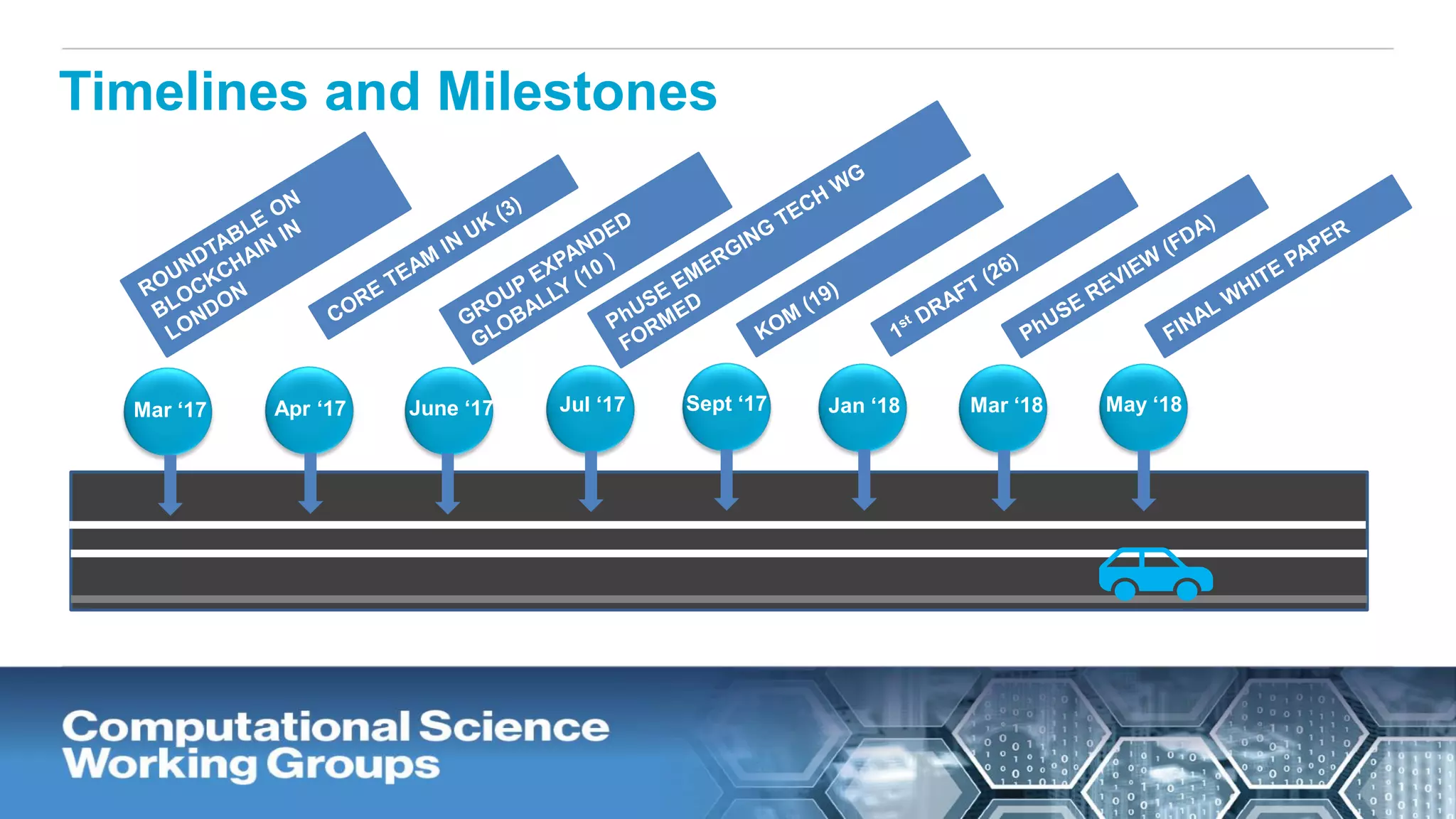
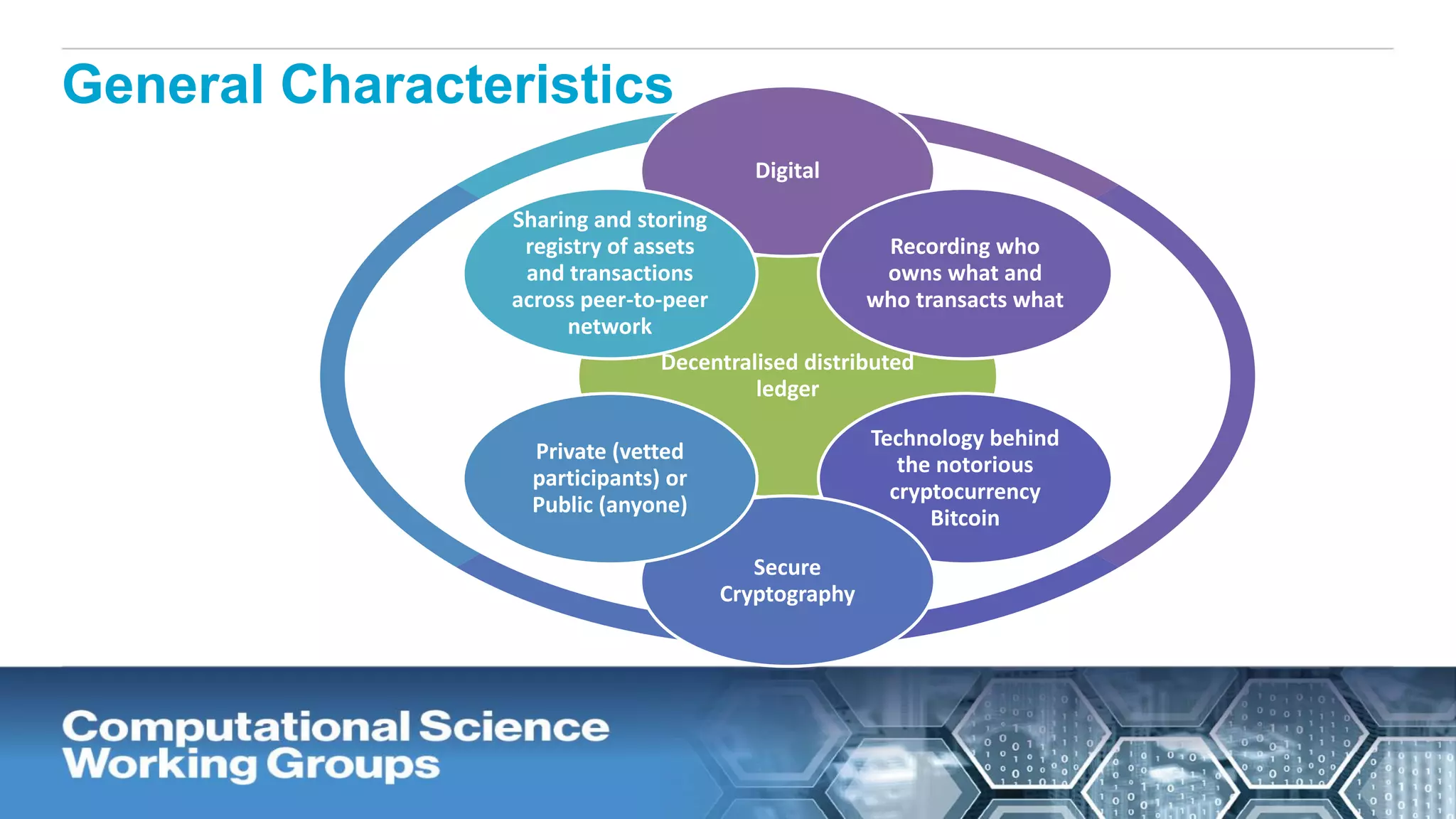
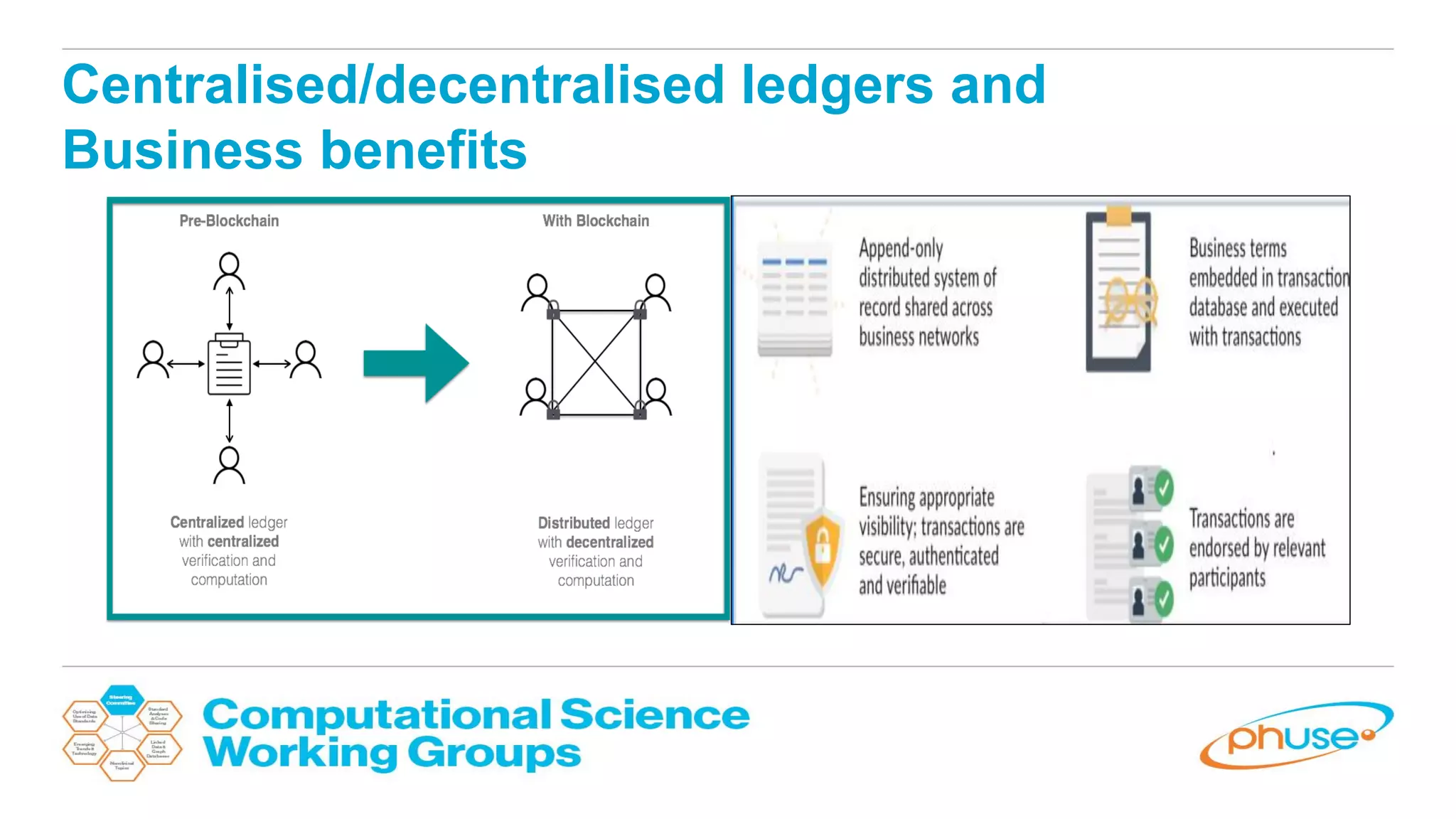
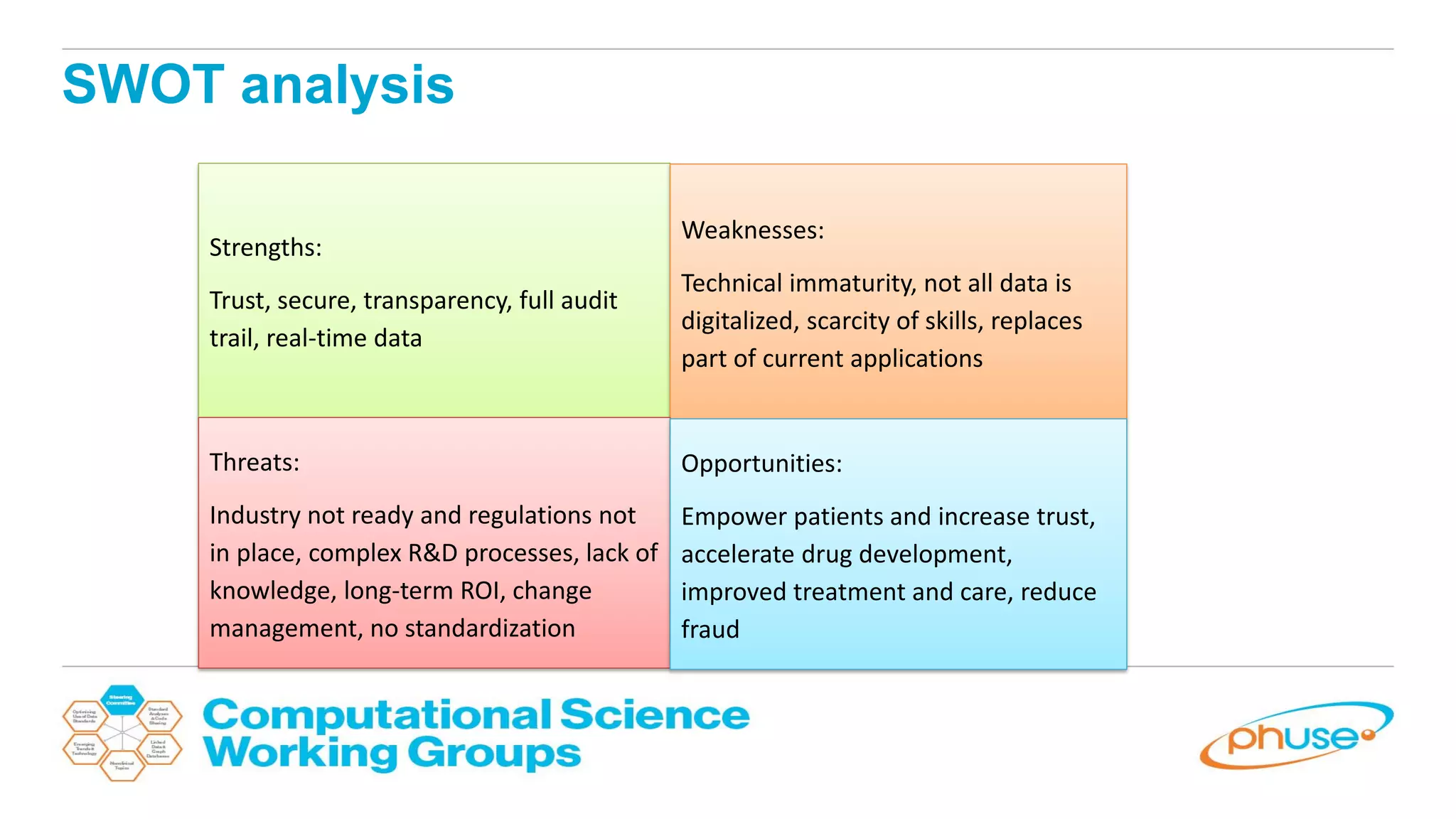
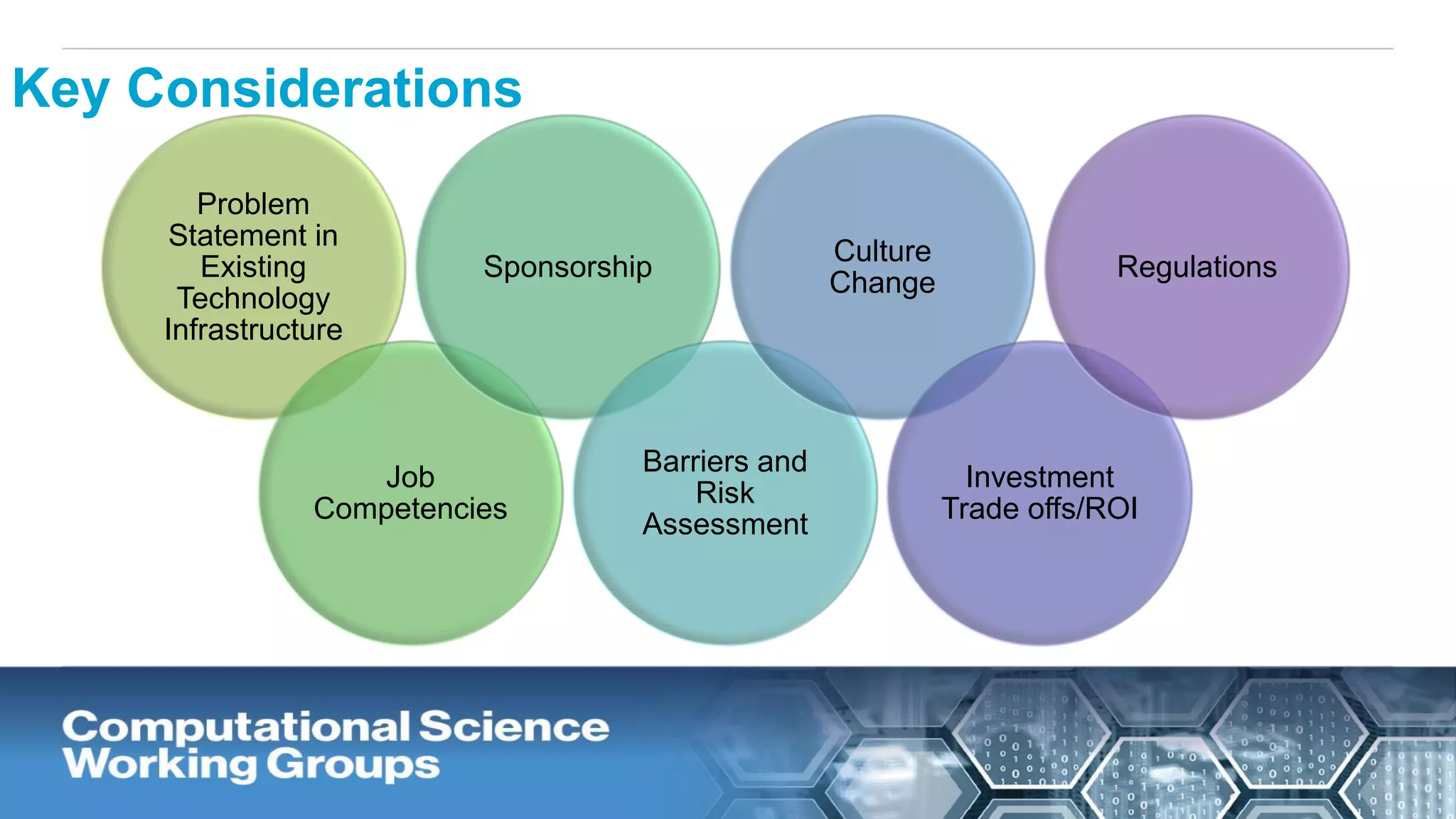
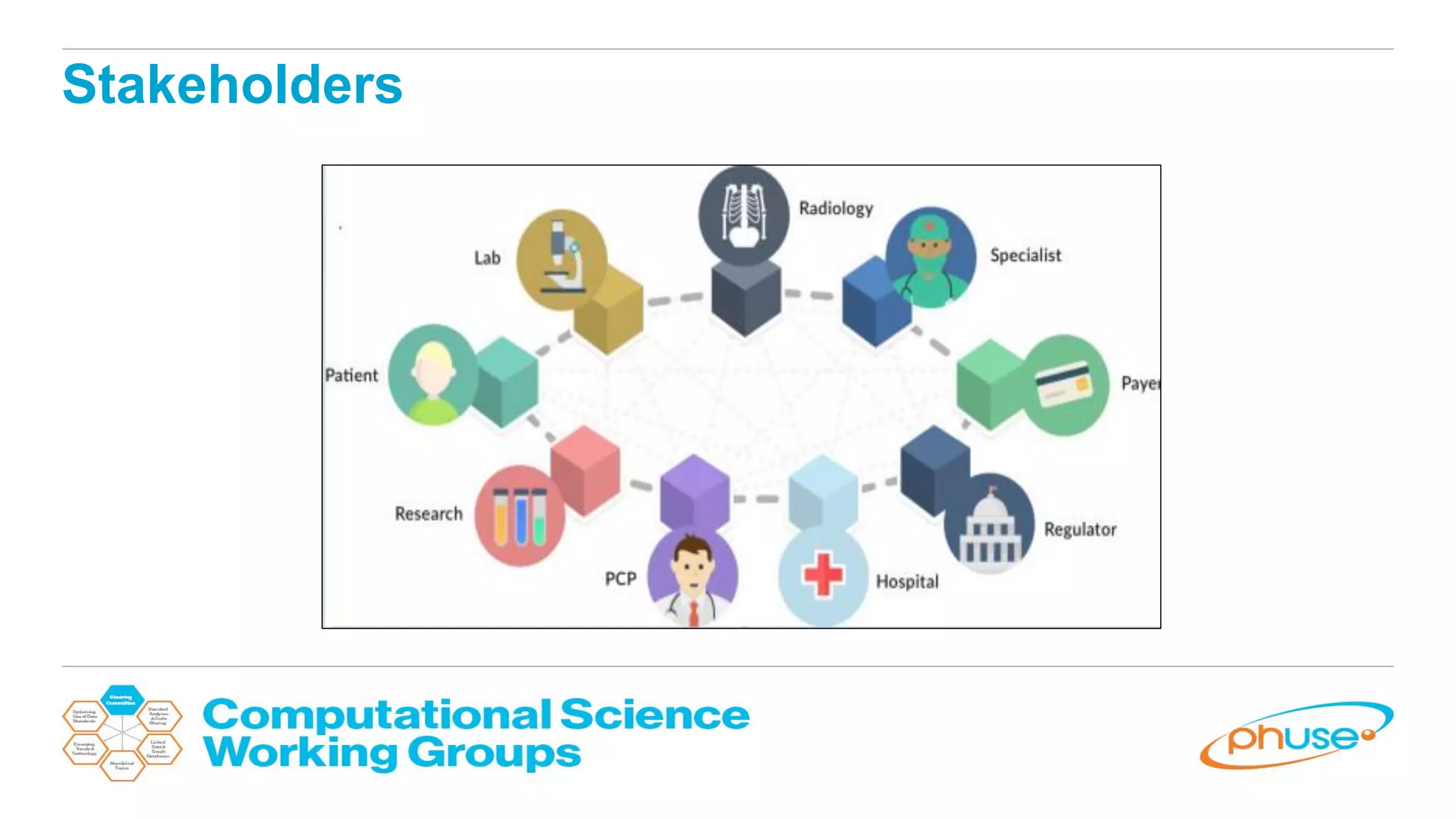
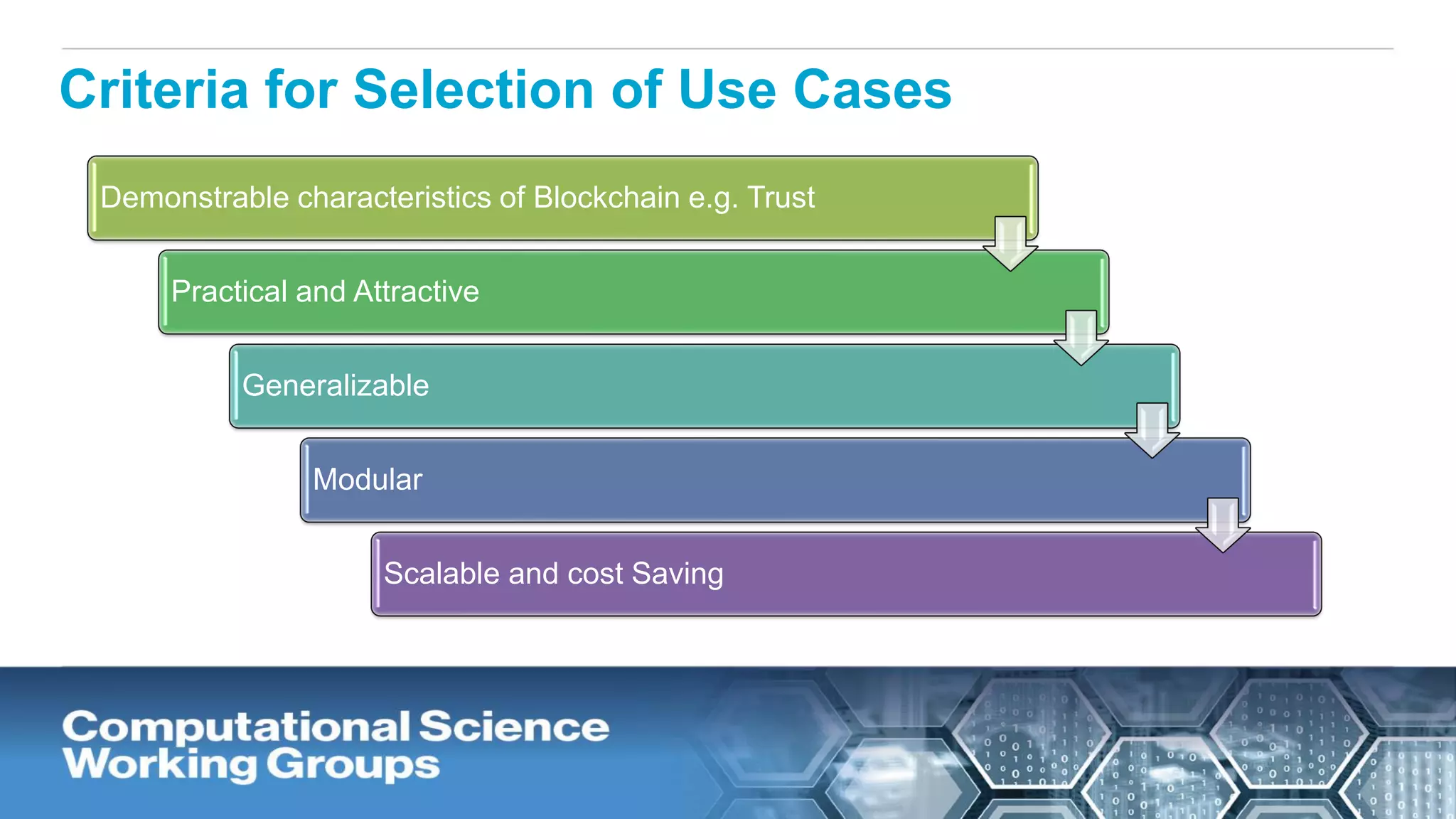
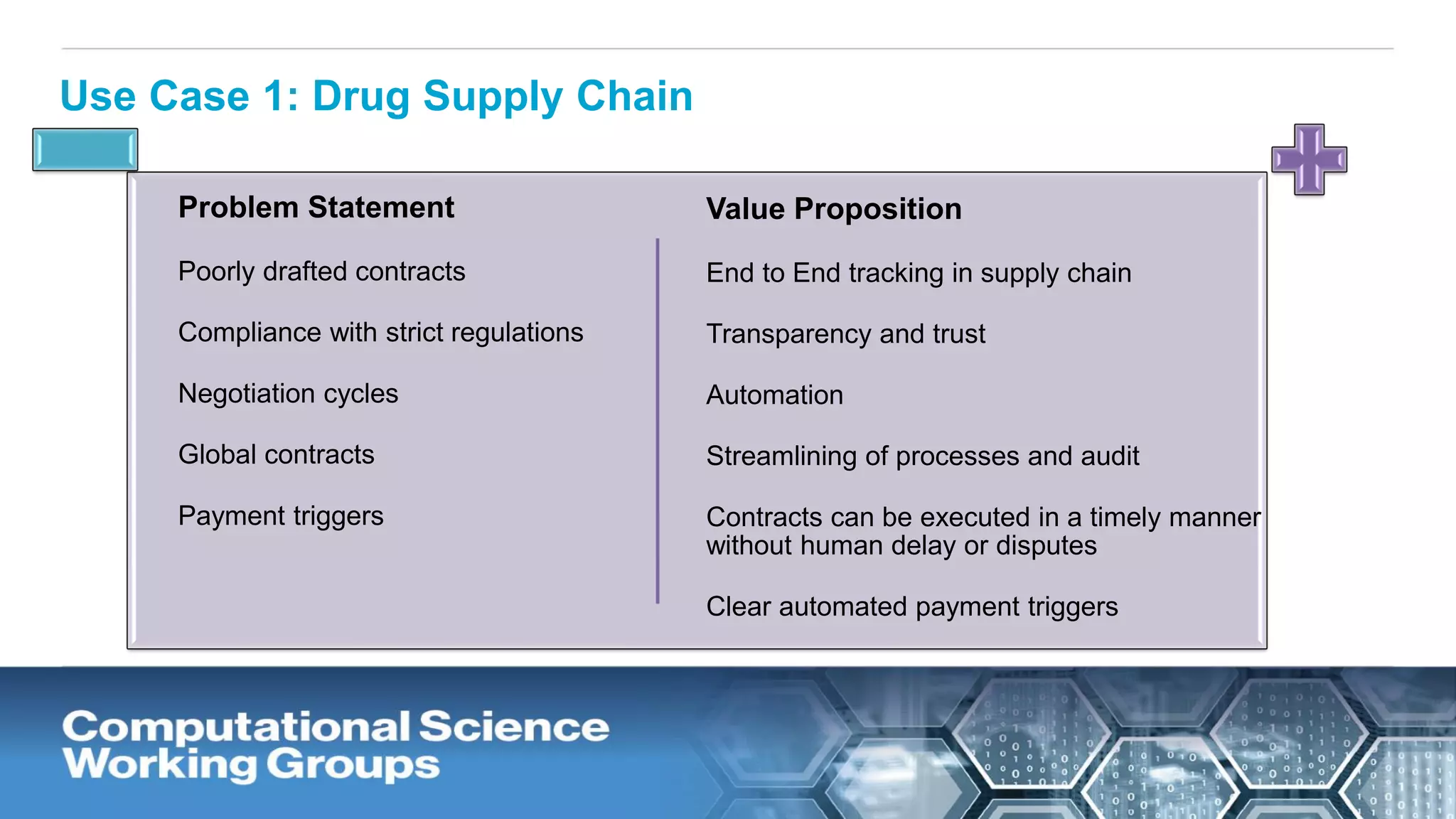
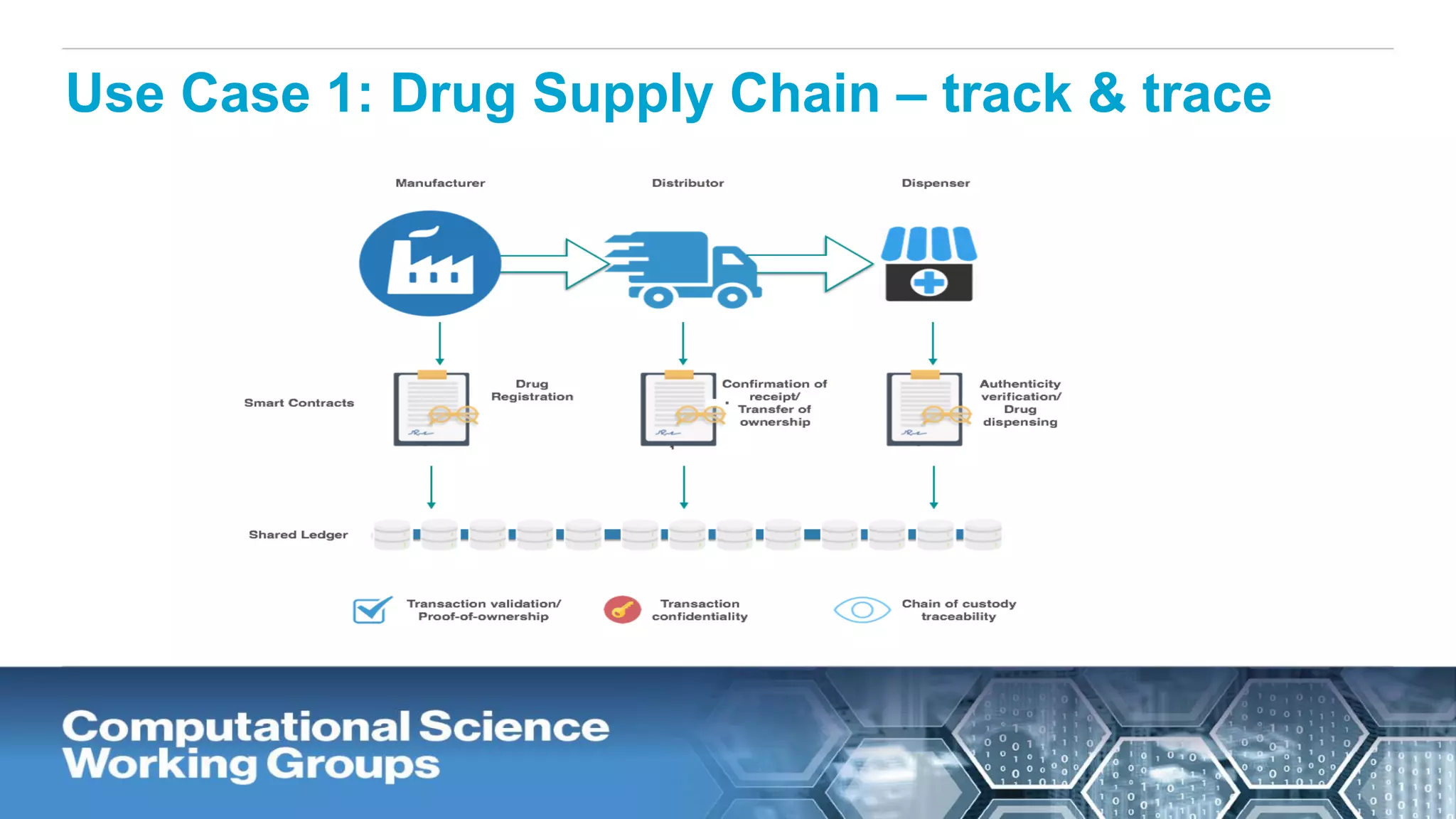
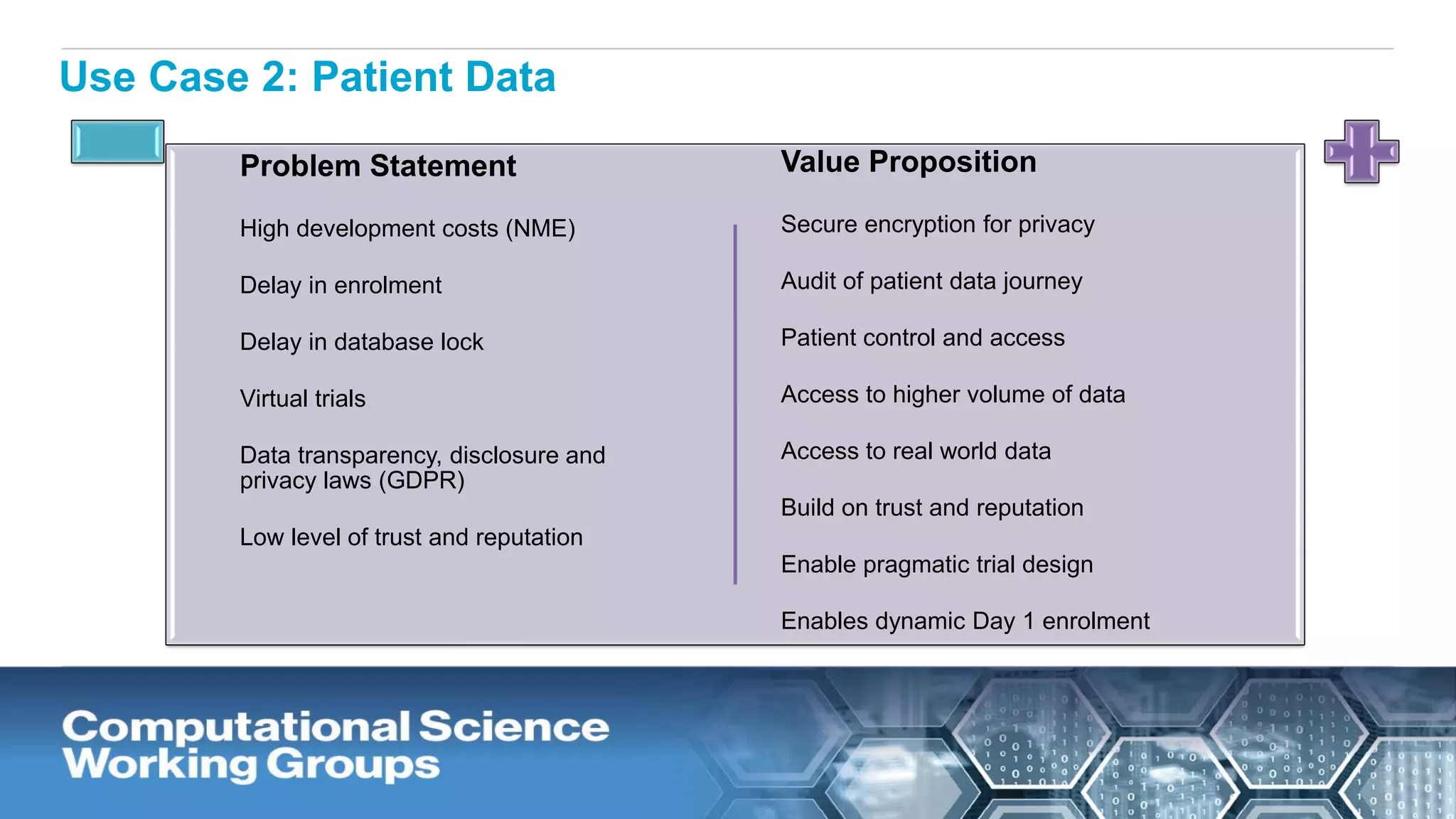
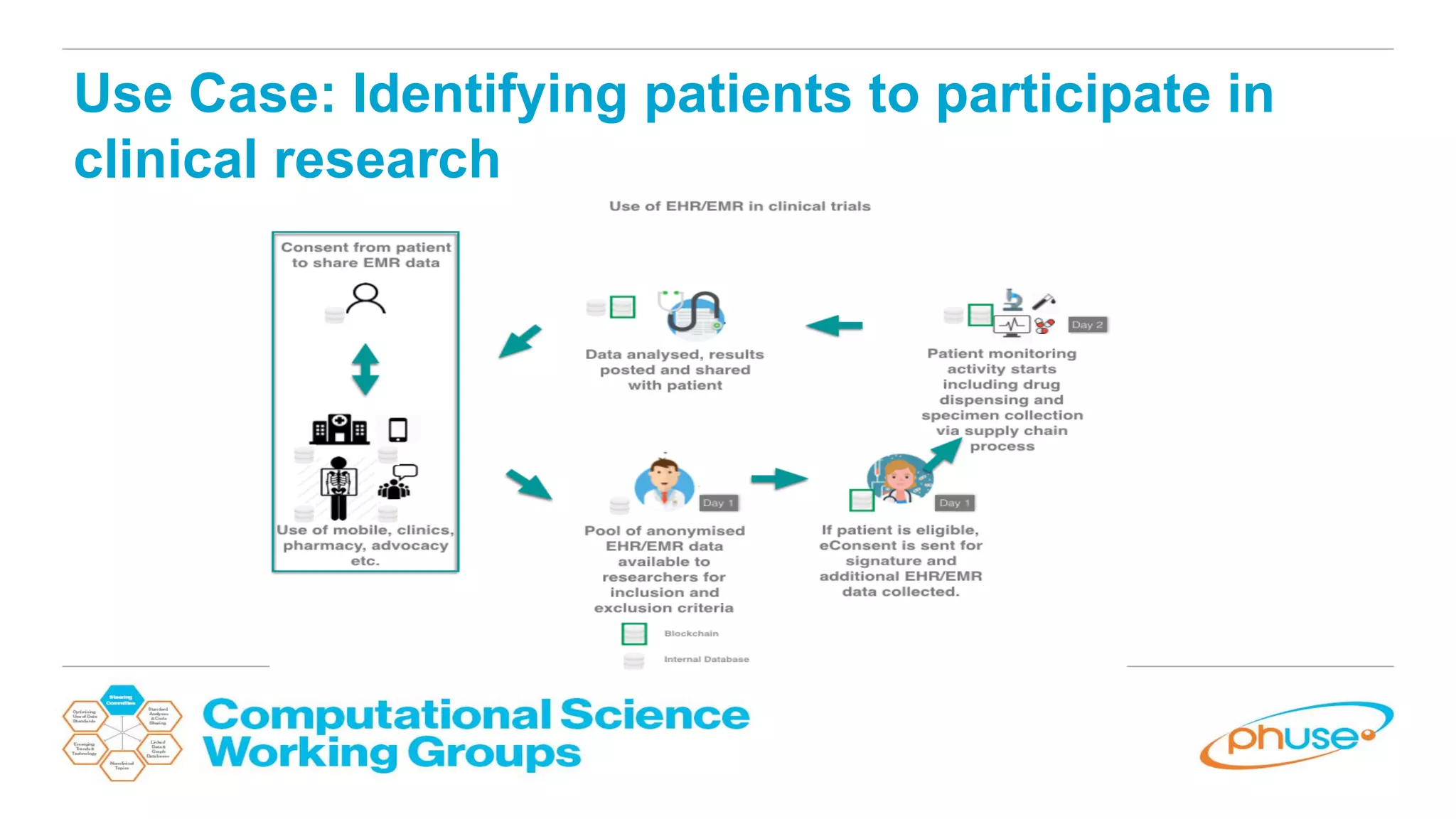
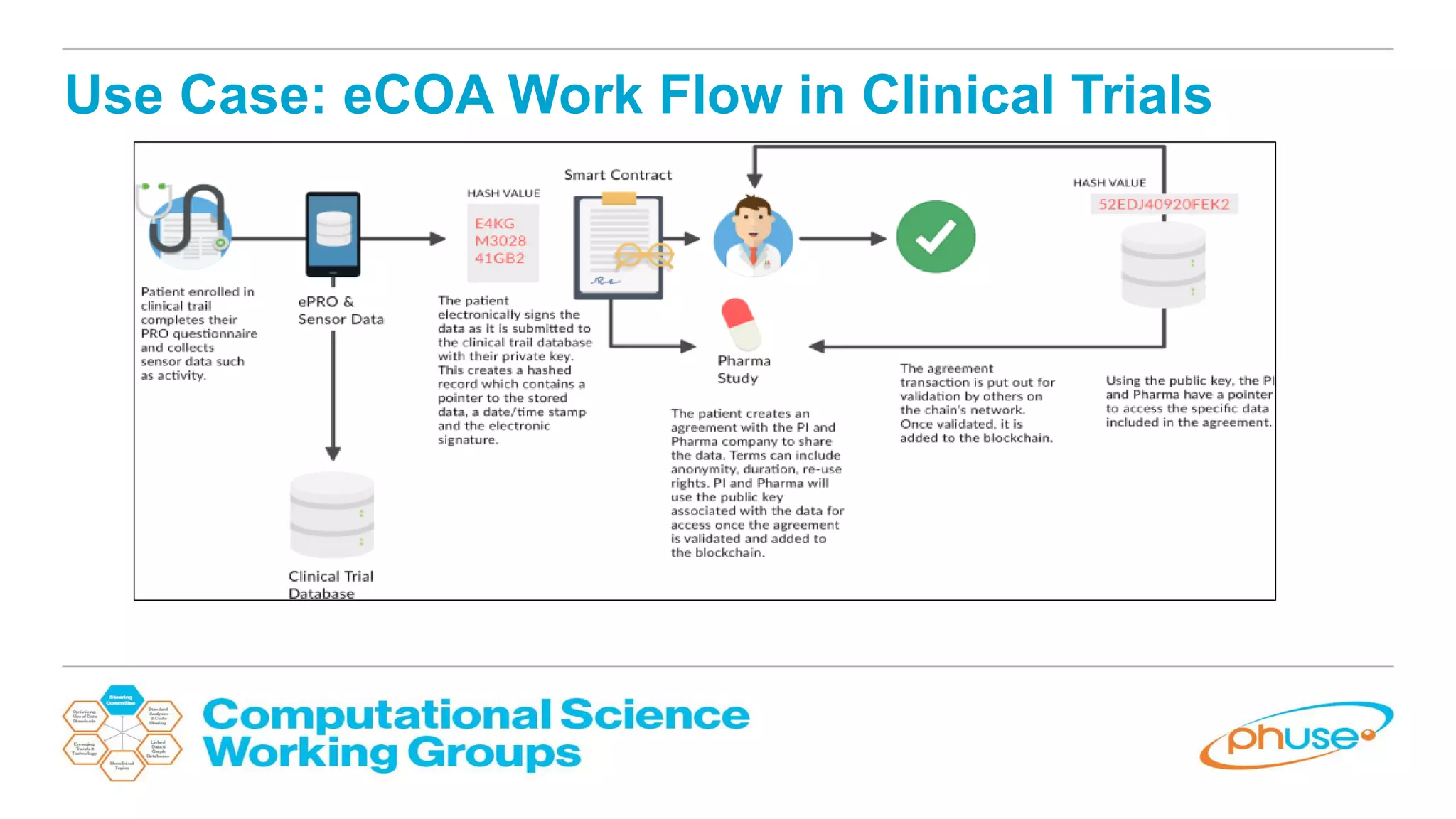
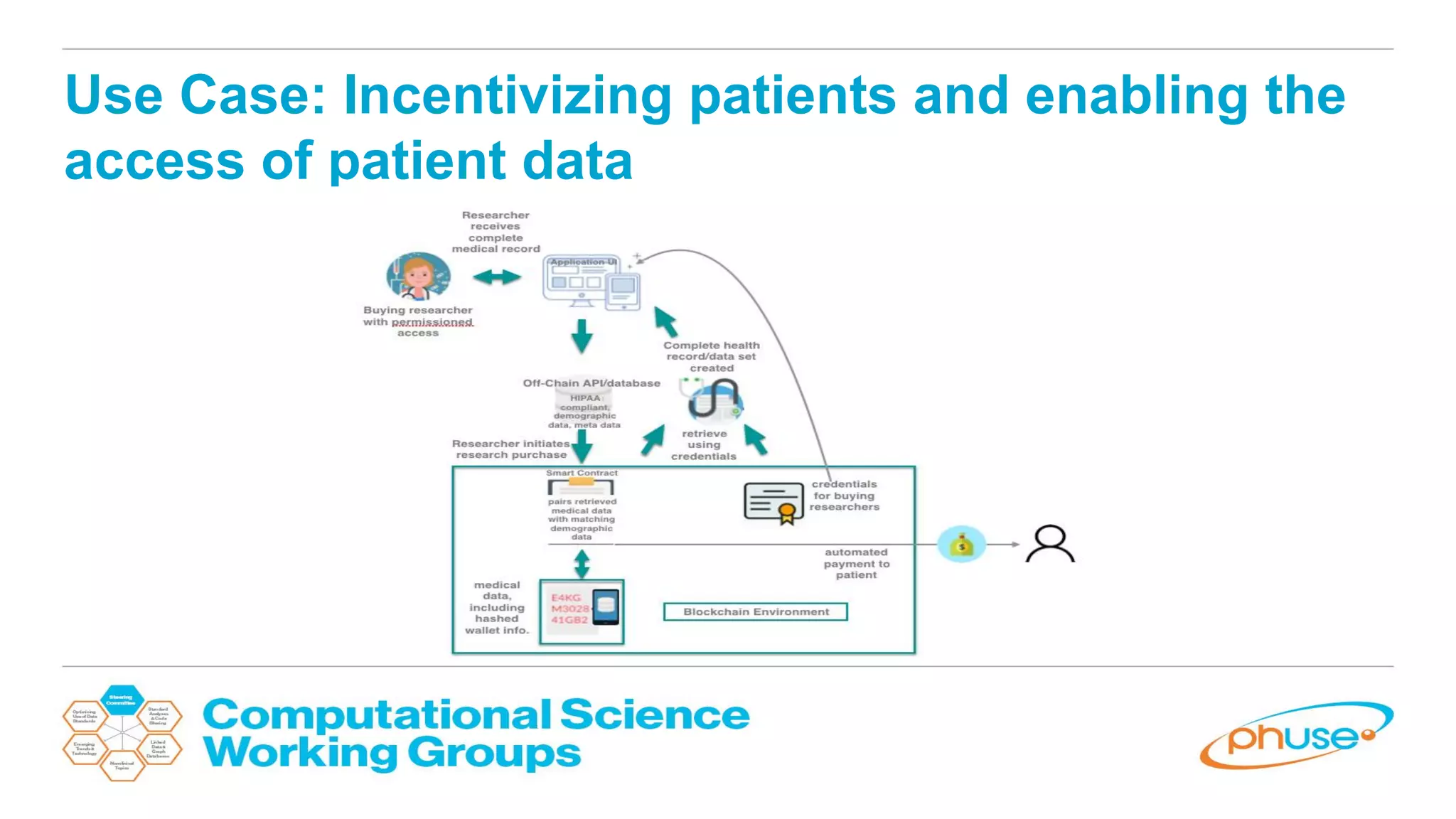
The document discusses the potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors by enhancing transparency, trust, and efficiency. It outlines the formation of a collaborative initiative involving various industry stakeholders to explore blockchain's applications, such as drug supply chain tracking and patient data management. Key considerations for adoption include regulatory readiness, infrastructure challenges, and the need for industry consensus on standards and practices.