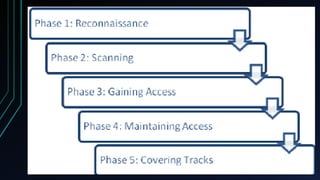
The document discusses ethical hacking and how it has evolved over time. It begins by defining hacking and explaining how hackers originally exploited telephone systems to make free calls. It then describes how hacking migrated to computers in the 1980s and became illegal with laws passed in 1986. The document outlines the different types of hackers and phases of a typical hack, including reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, and covering tracks. It also provides examples of commonly used hacking tools like Nmap, Nessus, and Kismet. In closing, it discusses both the advantages and disadvantages of hacking, and considers the future scope of ethical hacking.