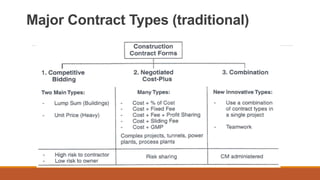
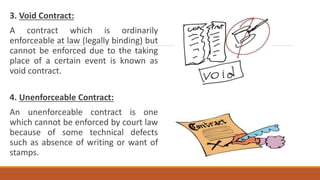
This document discusses different types of construction contracts. It defines a contract and describes lump sum and unit price contracts. Lump sum contracts involve a fixed total price for all work, while unit price contracts involve bidding based on units of work, with the total cost depending on actual quantities. The document also categorizes different types of contracts from a legal perspective, such as valid, voidable, void, unenforceable, illegal, and contingent contracts.