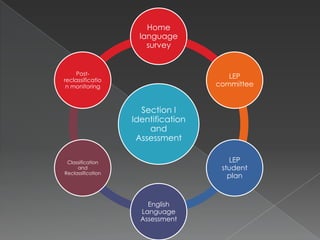
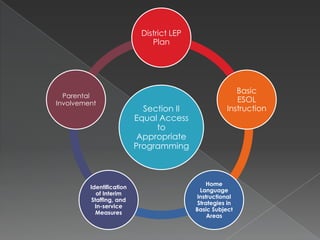
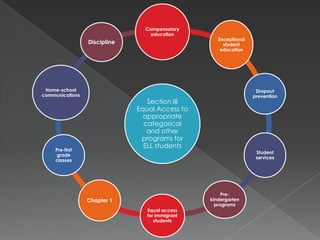
The ESOL Consent Decree was signed in 1990 as a settlement to ensure Florida provided equal education to limited English proficient (LEP) students. It establishes Florida's framework for complying with federal laws regarding English language learner (ELL) education. The Decree addresses identification and assessment of ELL students, equal access to programming, personnel qualifications, monitoring compliance, and evaluating outcomes to ensure equal opportunities for ELL students.