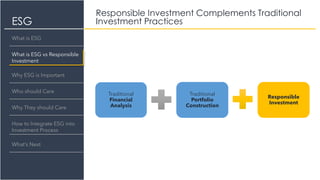
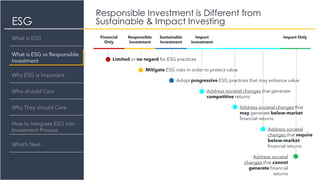
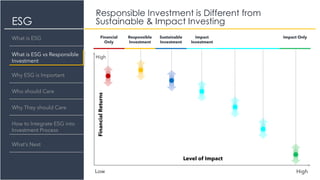
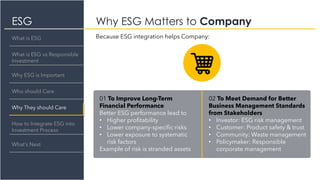
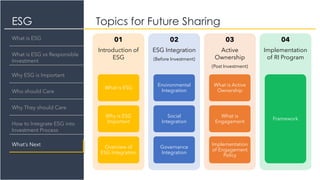
The document provides an overview of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors, emphasizing their significance in responsible investment for achieving sustainable financial growth. It outlines how ESG considerations can improve investment returns and mitigate risks, urging various stakeholders, including investment firms and policymakers, to integrate these factors into their processes. The document also discusses the differences between responsible investment, sustainable investing, and impact investing, and offers guidance on integrating ESG into investment practices.