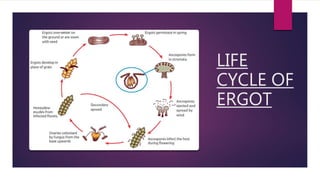
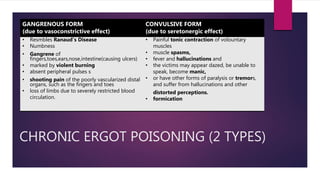
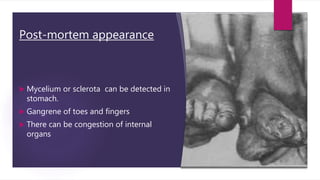
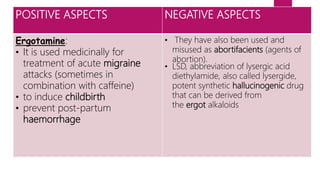
Ergot poisoning is caused by consuming grains contaminated with the parasitic fungus Claviceps purpurea, known as ergot. The fungus replaces grains with hard black sclerotia containing ergot alkaloids that act as vasoconstrictors or serotonin agonists. Historically, ergotism or "St. Anthony's Fire" was common from eating contaminated rye and caused either gangrenous or convulsive symptoms due to restricted blood flow or muscle spasms. Treatment focused on removing the alkaloids from the body since there is no antidote. While ergot alkaloids can be used to induce childbirth or treat migraines, they were also misused as abortifacients