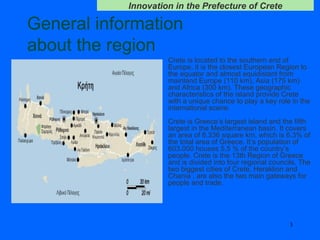
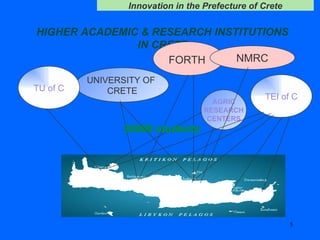
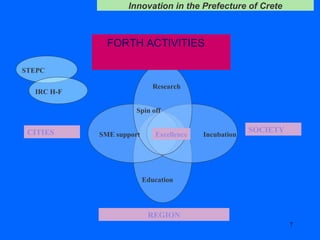
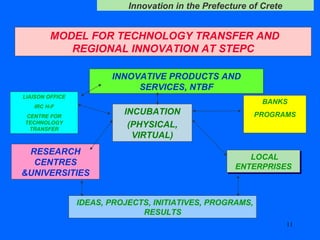
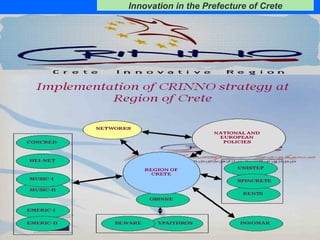
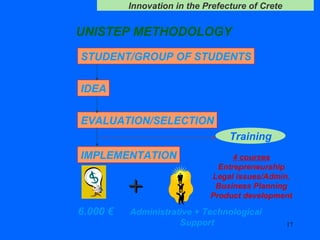
The document discusses innovation challenges and opportunities in the region of Crete, Greece. It provides details on the higher education and research institutions in Crete and describes some of their activities. It also presents a SWOT analysis of the region and discusses some successful examples of technology transfer and regional innovation projects.