This document discusses e-procurement and provides details about its objectives, key stakeholders, technical architecture, new processes, governance issues, current status, issues and challenges, and best practices. The main points are:
1. E-procurement aims to automate the entire procurement process online to reduce costs and cycle times, increase transparency and supplier participation, and eliminate corruption.
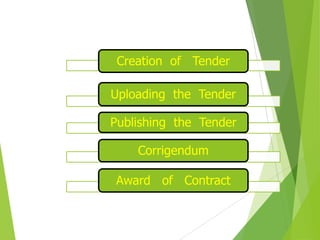
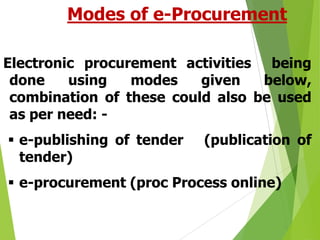
2. Key stakeholders in e-procurement include government ministries, central departments, and suppliers. The technical architecture allows for online publishing of tenders, bid submission, payments, and contract awards.
3. Global case studies show e-procurement can deliver substantial benefits through increased efficiency, competition, and transparency, but requires strong leadership, appropriate policy