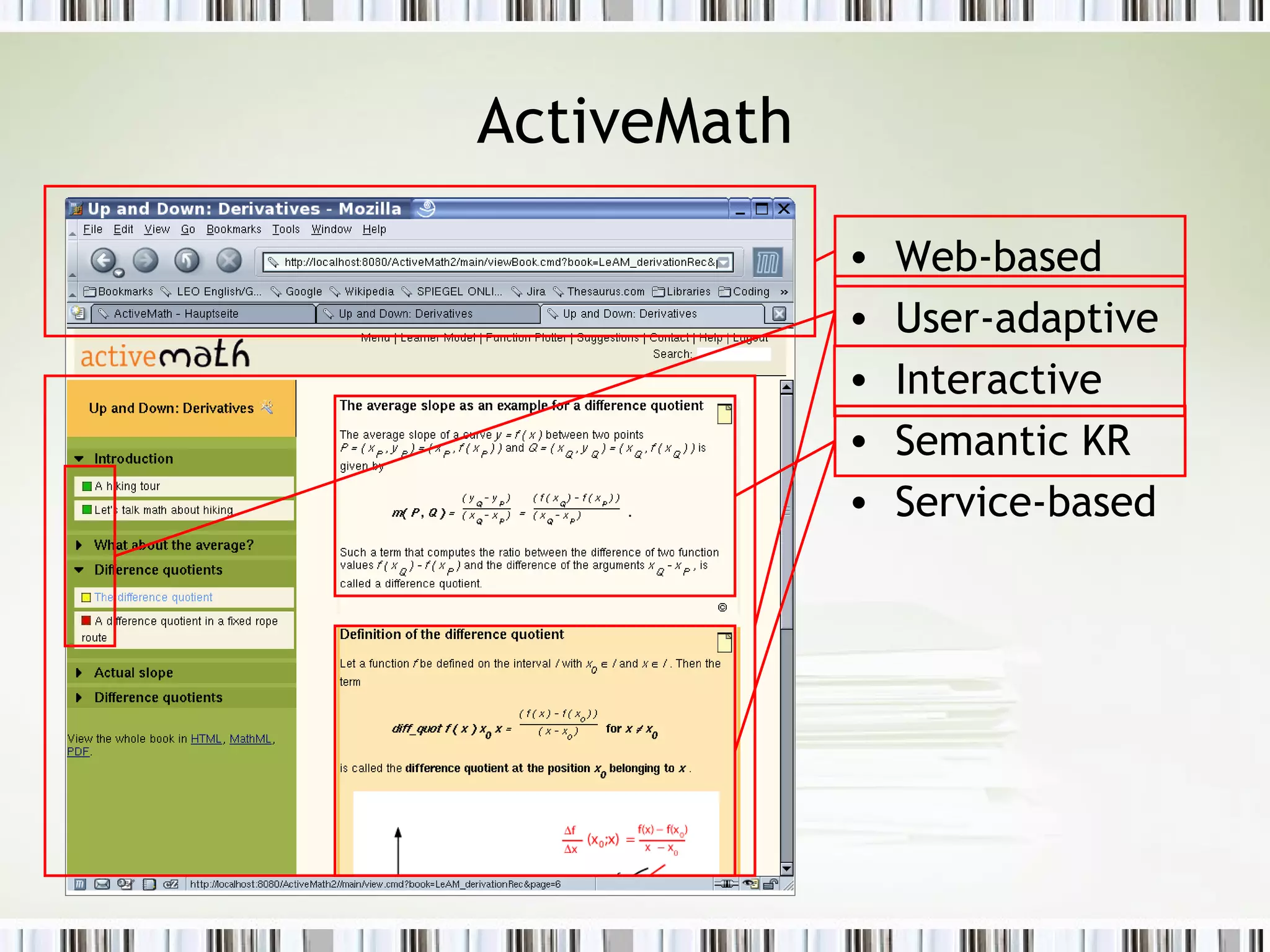
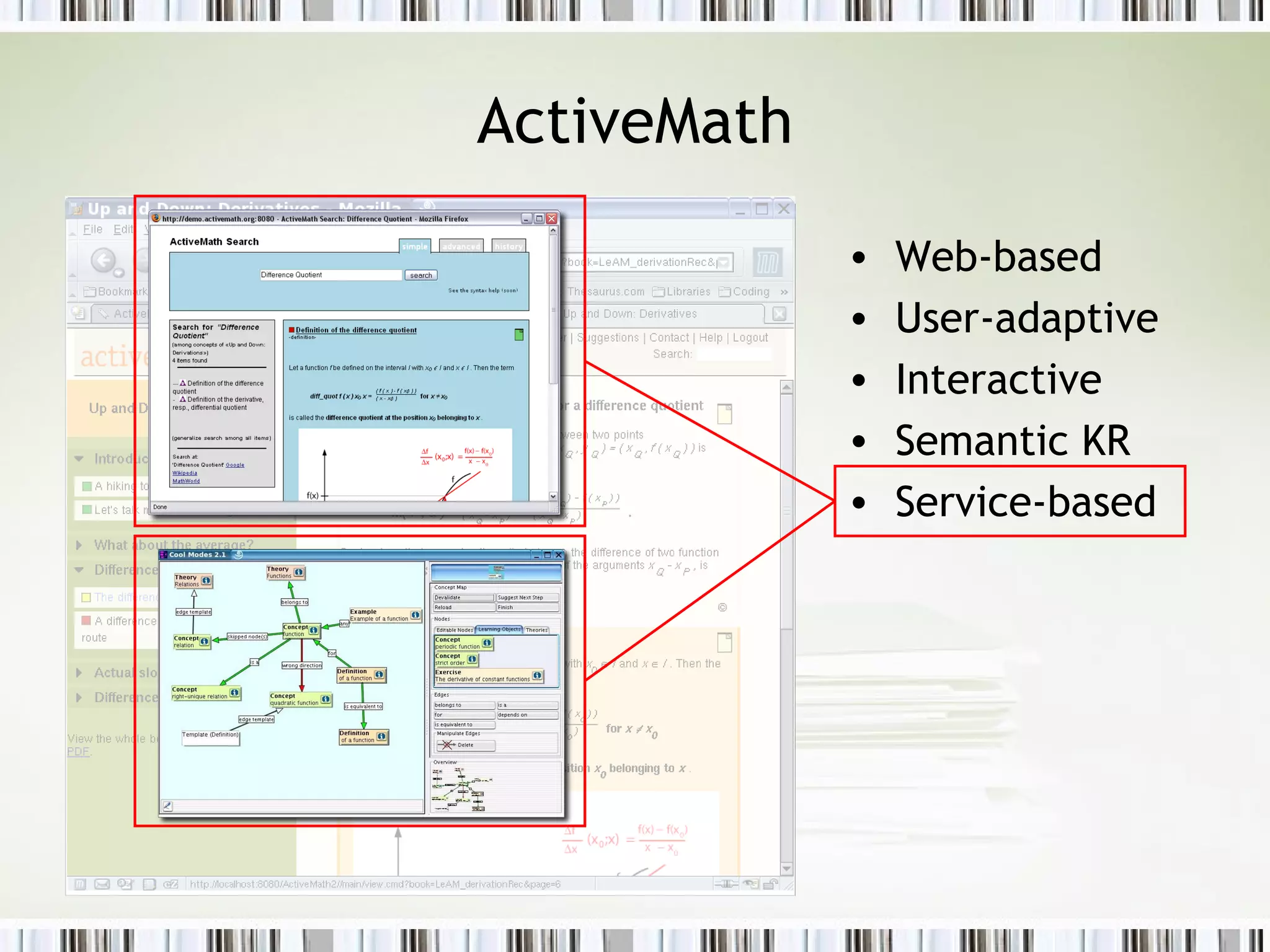
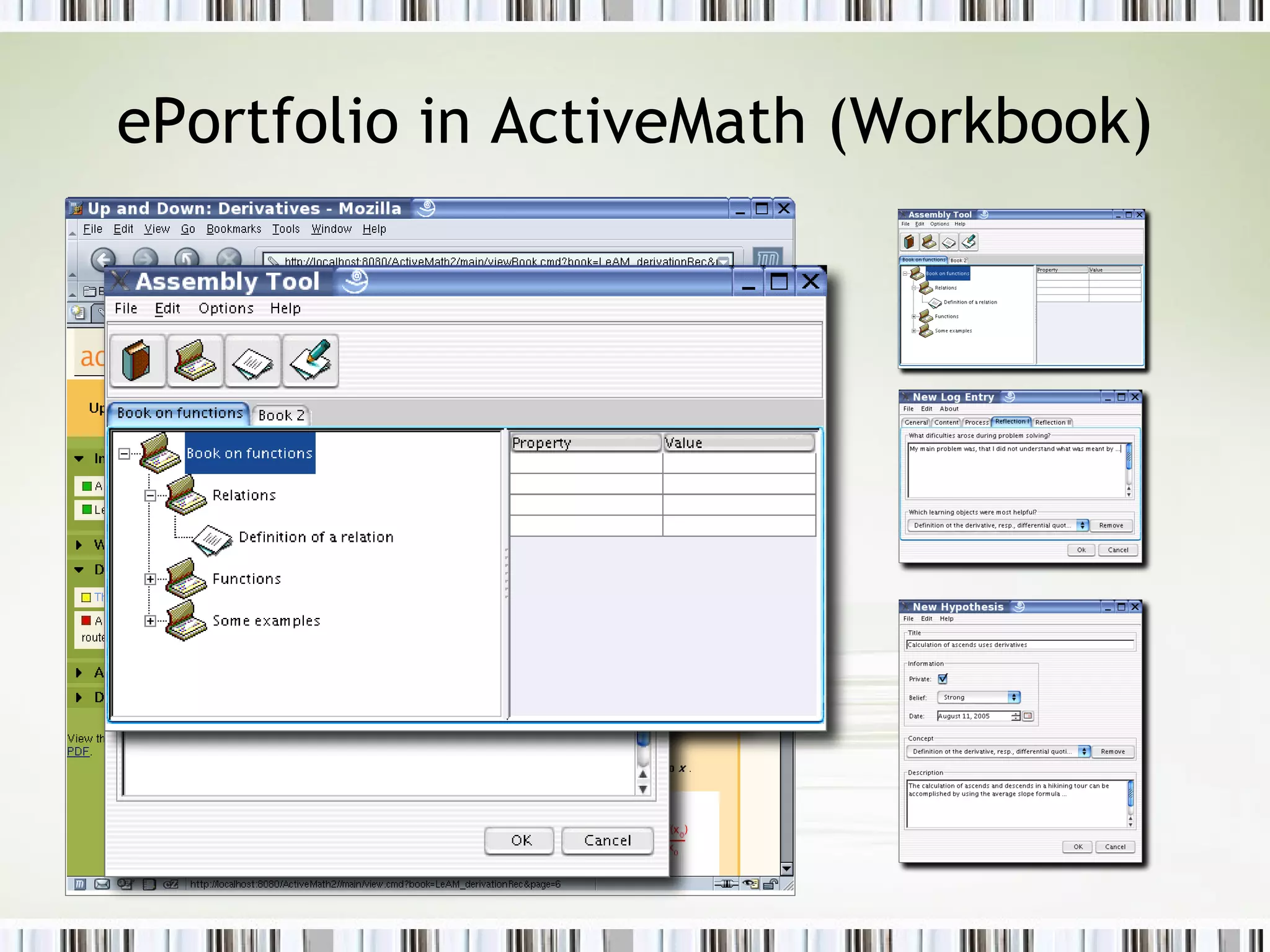
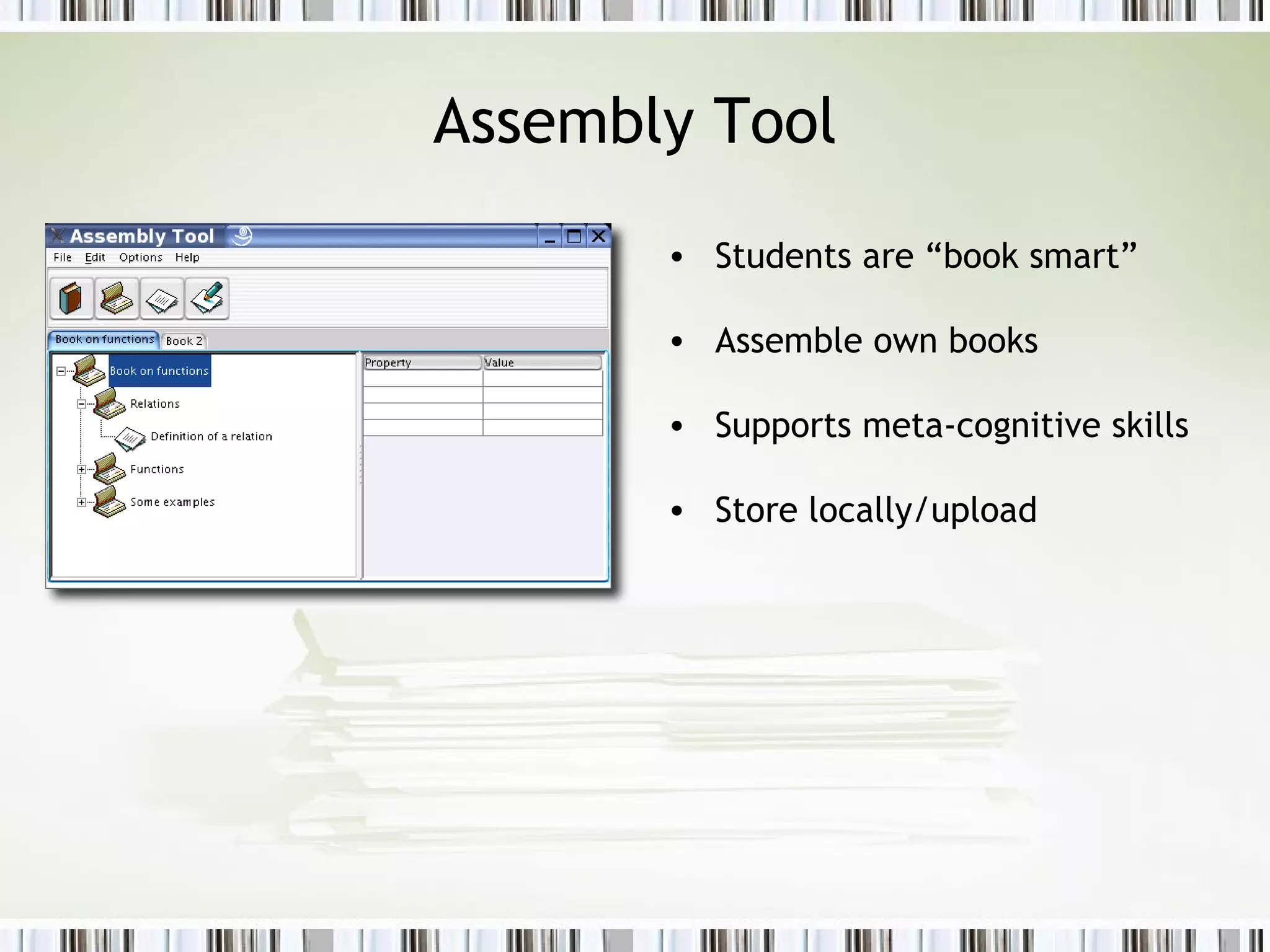
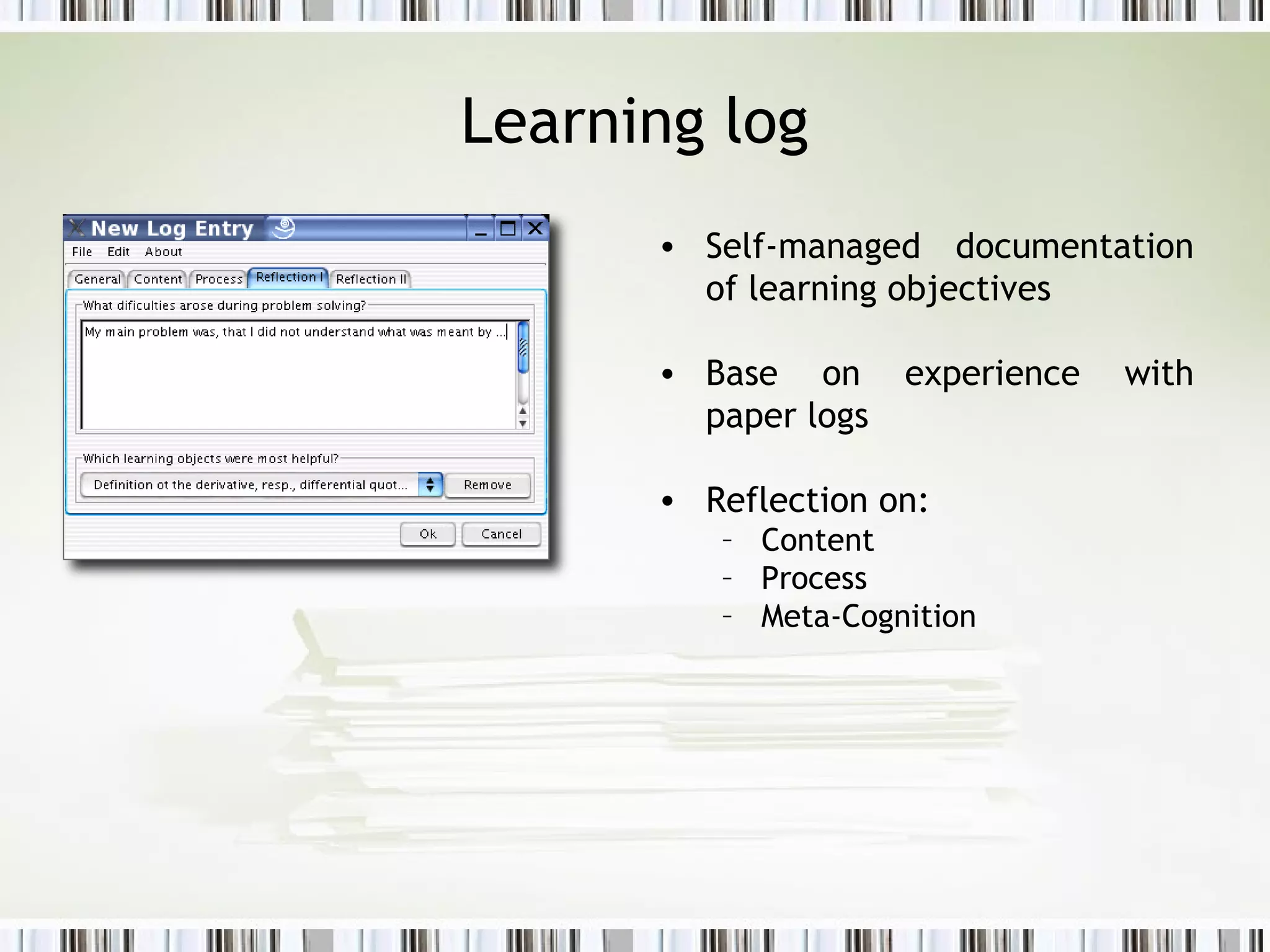
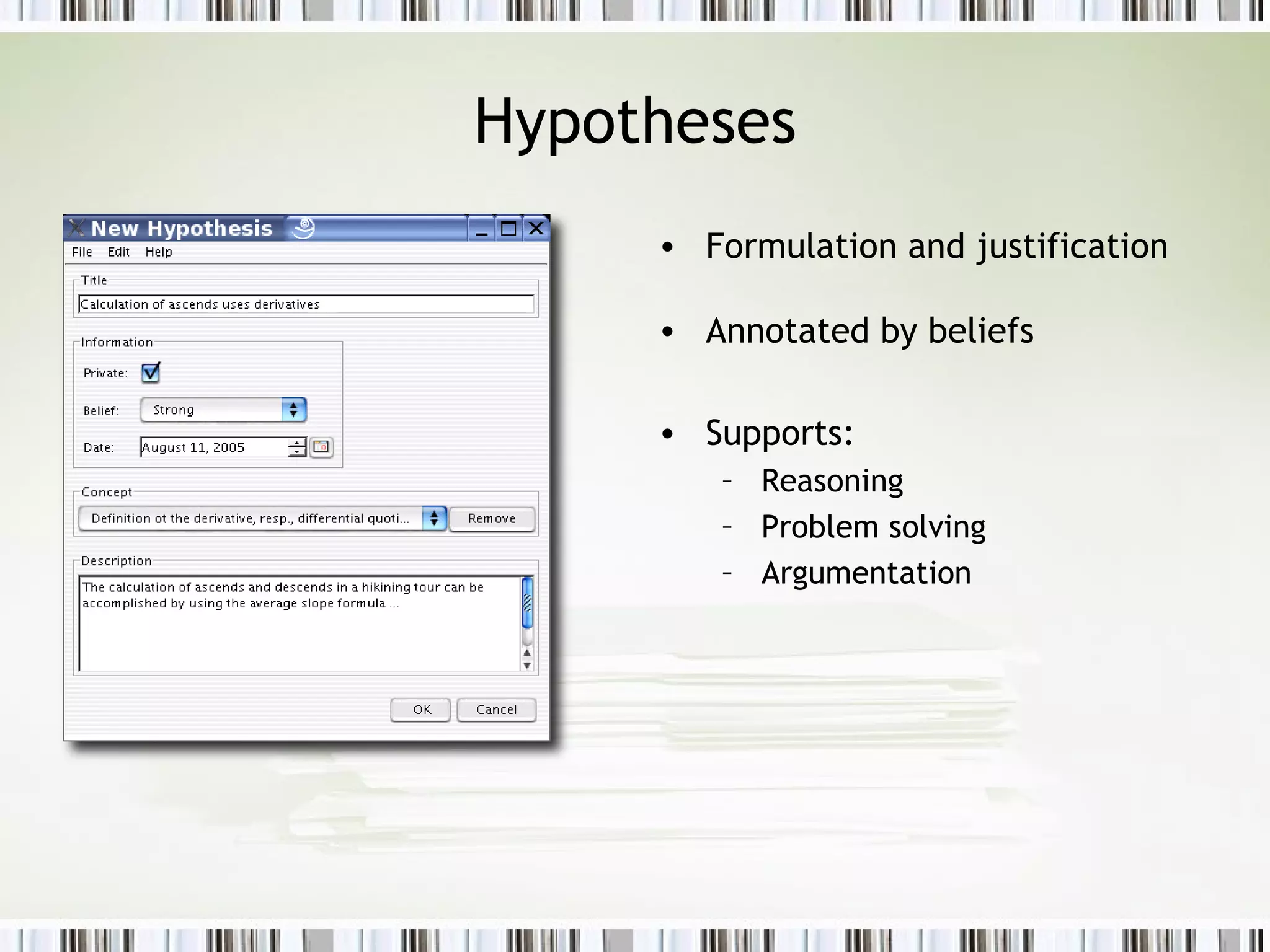
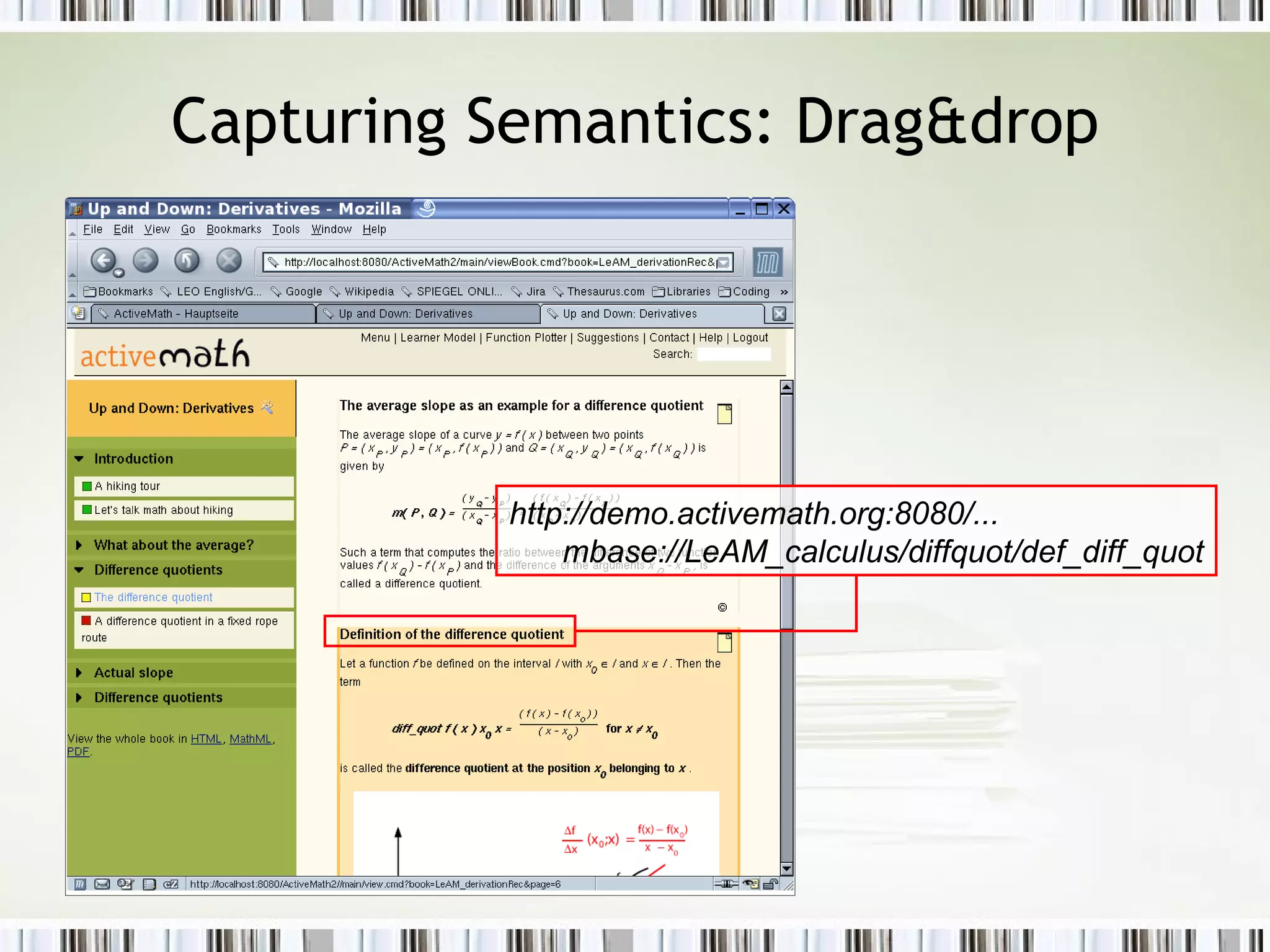
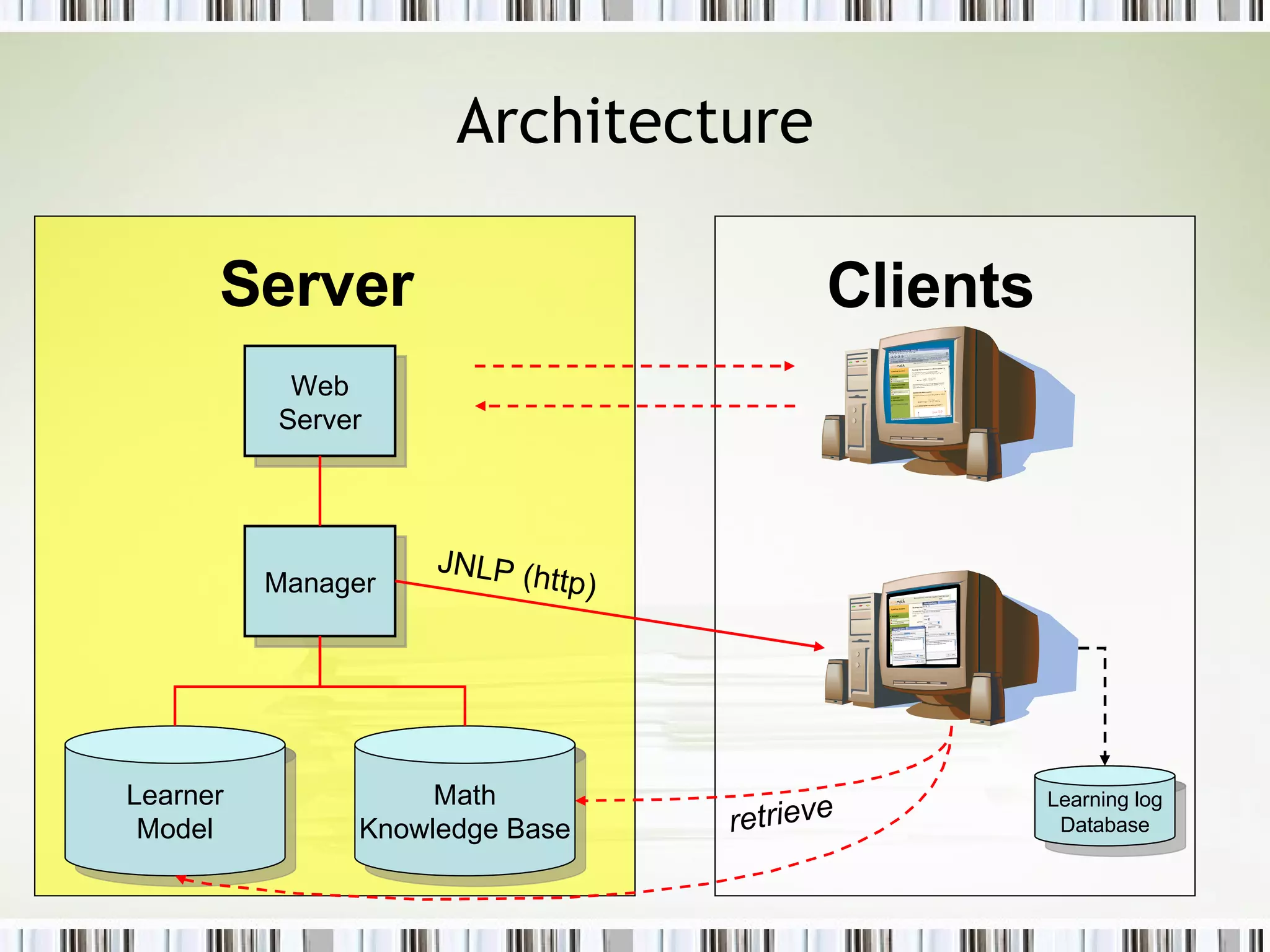
The document discusses using an ePortfolio called the ActiveMath Workbook to capture student learning and reflection within the ActiveMath learning environment. The Workbook allows students to assemble their own books, maintain a learning log, and formulate hypotheses with annotated beliefs. Semantics are captured through the Workbook's structure, questions, and ability to relate entries to learning objects. The architecture involves a math knowledge base, learner model server, and clients connected to a web and database server. Future work includes more evaluation and enhancing collaboration and interaction with ActiveMath services.