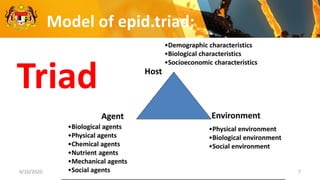
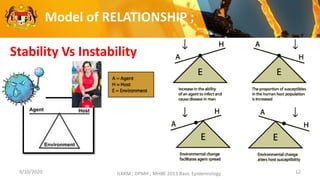
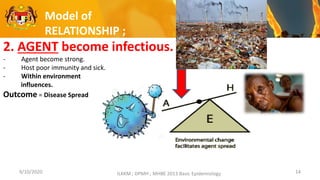
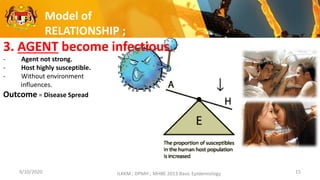
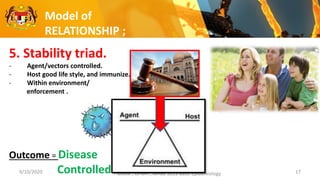
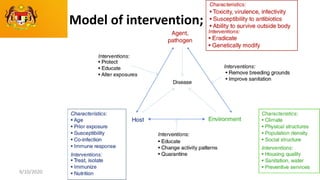
This document discusses the epidemiology triad and basic epidemiology. It begins with learning outcomes which are to describe the epidemiology triad, interpret the relationship between host, agent and environment, and discuss intervention concepts related to these. It then provides definitions and models of the triad and relationships between components. Specifically, it models how disease spreads under different conditions of agent strength, host susceptibility and environmental/enforcement influences. It also models intervention strategies related to the environment like housing standards and to the host like immunization and behavior modification. Overall, the document presents foundational epidemiological concepts through defining the triad components and modeling their interactions and interventions.