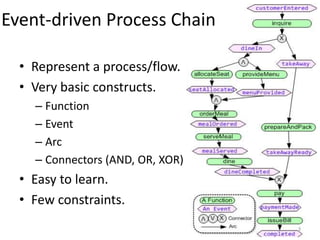
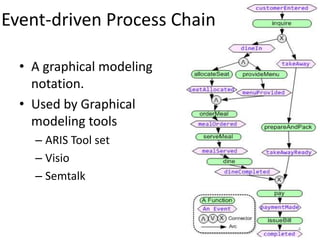
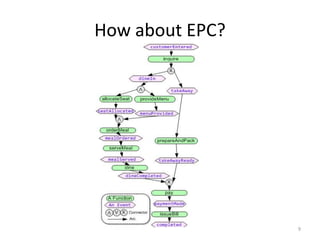
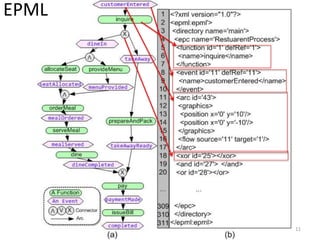
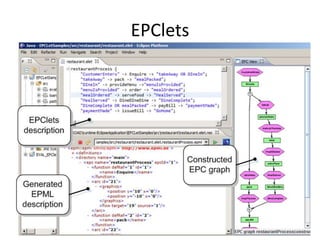
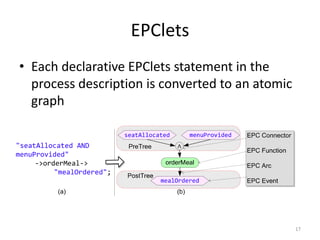
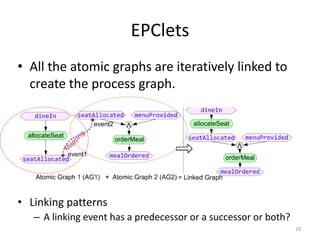
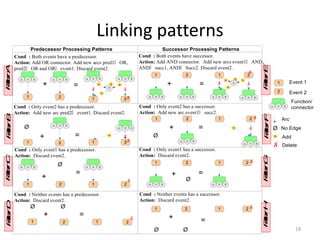
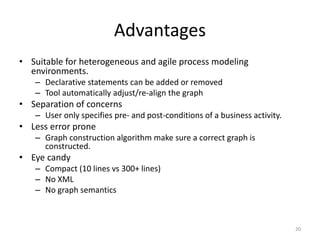
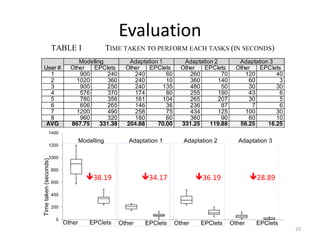
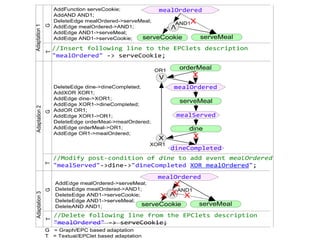
The document introduces EPClets, a lightweight textual language that can be used to augment event-driven process chains (EPC) modeling. EPClets allows users to specify the pre- and post-conditions of business activities declaratively, separating the process specification from the graph construction. An EPClets tool then automatically constructs the EPC graph based on the declarative rules. An evaluation showed that using EPClets reduced the time users spent repositioning graphs and was less error-prone compared to traditional graphical EPC modeling tools.