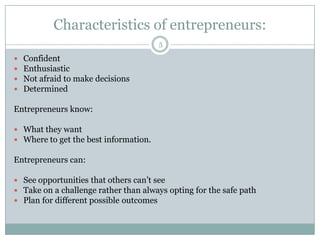
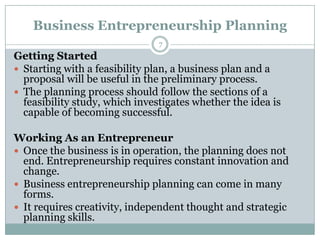
This document defines entrepreneurship and discusses the characteristics of entrepreneurs. It states that entrepreneurship involves assembling resources like finance, business skills, and innovations to transform new ideas into economic goods. Entrepreneurship is described as a process of innovation, creation of new ventures, and is aided by collaborative networks. The document outlines that entrepreneurs are innovators who recognize opportunities, organize operations to exploit opportunities, and take on the risks of starting a business. Common traits of entrepreneurs include confidence, enthusiasm, decision-making ability, and determination. The importance of entrepreneurship is discussed as turning innovations into demand, providing employment, and contributing to wealth, self-sufficiency, and research. The document concludes with sections on business entrepreneurship