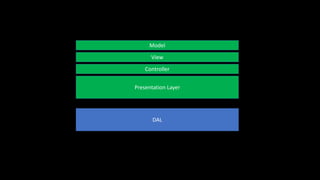
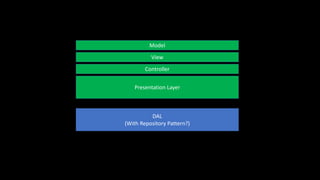
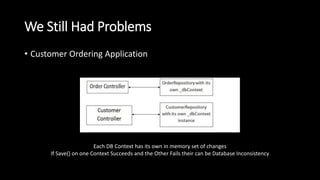
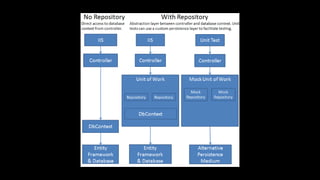
The document discusses issues with traditional ASP.NET application architectures and how the introduction of MVC helped address some problems. It then describes how the presenter implemented the Unit of Work pattern to help with testing and database consistency in their application. However, this implementation violated SOLID principles. The presenter improved the design by separating concerns into distinct layers and implementing generic repositories. This made the code more testable and decoupled from Entity Framework while better adhering to object-oriented design principles. In the end, the presenter advocates evaluating design patterns critically and continuously challenging accepted approaches.