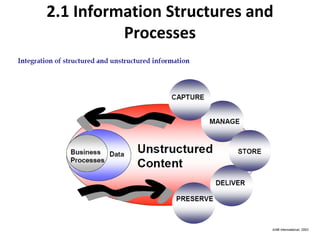
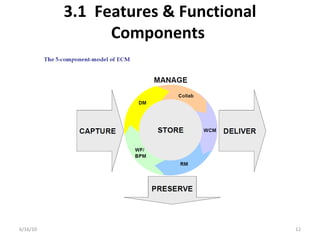
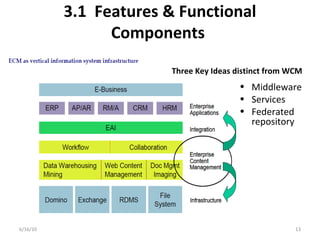
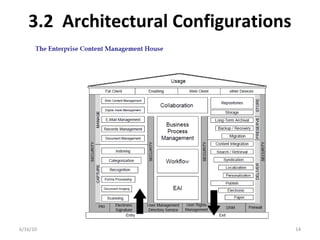
Enterprise content management (ECM) involves integrating technologies to store, access, and manage documents. It serves to create, manage, store, archive, share, and retrieve both structured and unstructured information. ECM provides benefits like compliance, efficiency, availability, and risk mitigation by supporting activities like document management, records management, collaboration, and workflow. Implementing an ECM system requires analyzing requirements, selecting a vendor solution, designing and testing the system, and evaluating it after deployment. Key challenges include balancing control with flexibility and ensuring usability for non-technical users.