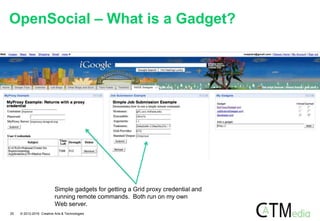
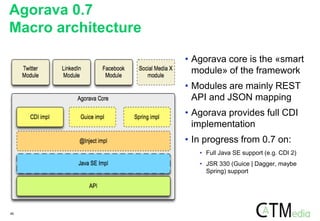
The document discusses the evolution and implementation of social media integration frameworks for Java, highlighting Agorava as a successor to earlier projects like Seam Social and its interaction with JSR 357. It critiques various open-source frameworks, notably Shindig and Spring Social, while exploring the challenges of standardizing social media APIs. The document concludes with a preview of an upcoming Agorava book and its project resources.















![18
1: {
2: "firstName": "John",
3: "lastName" : "Smith",
4: "age" : 25,
5: "address" :
6: {
7: "streetAddress": "21 2nd Street",
8: "city" : "New York",
9: "state" : "NY",
10: "postalCode" : "10021"
11: },
12: "phoneNumber":
13: [
14: {
15: "type" : "home",
16: "number": "212 555-1234"
17: },
18: {
19: "type" : "fax",
20: "number": "646 555-4567"
21: }
22: ]
23: }
JSON
•JavaScript Object
Notation: Data format
inspired by JavaScript. It
became a standard for
online services including
Social Media.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterprise20agorava-160221154433/85/Enterprise-2-0-with-Open-Source-Frameworks-like-Agorava-18-320.jpg)