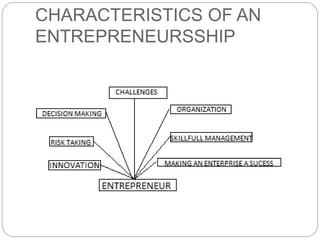
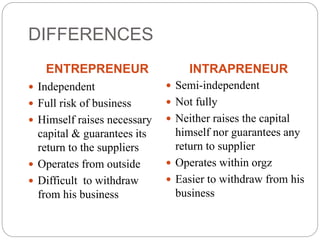
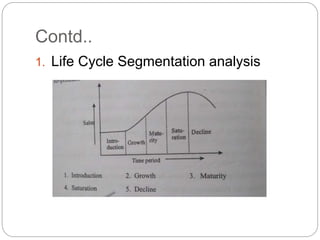
The document outlines the evolution, characteristics, and types of entrepreneurs, as well as the process and importance of project feasibility analysis in entrepreneurship. It discusses various barriers to entrepreneurship and the role of entrepreneurs in economic development, along with methods for identifying and evaluating business opportunities. Finally, it covers the different aspects of market, technical, financial, and social feasibility studies essential for assessing new business projects.