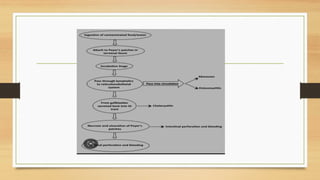
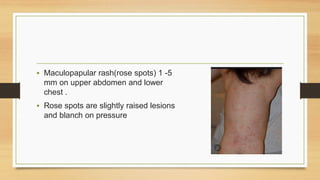
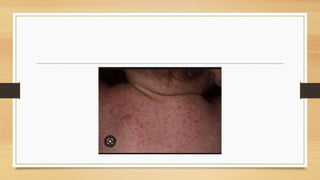
This document discusses typhoid fever, caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria. It is characterized by prolonged fever and can cause intestinal bleeding or perforation. Infection occurs through ingestion of contaminated food, water, or contact with infected humans or animals. Diagnosis involves blood or bone marrow cultures. Treatment consists of antibiotics like chloramphenicol or fluoroquinolones for 2 weeks. Prevention focuses on handwashing, sanitation, safe food/water handling, and vaccination.