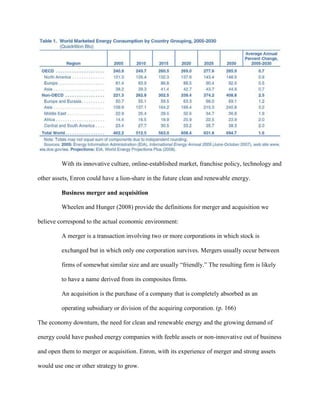
This document provides a SWOT analysis of Enron prior to its collapse in 2001. It identifies strengths such as Enron's human capital pool and competitive advantage in jet fuel sales after 9/11. Weaknesses included the failed board of directors, unethical practices, and a corporate culture that enabled fraud. Opportunities existed in growing clean energy markets and business expansion to Asia. Threats included increased competition, regulations, and the economic impacts of the subprime mortgage crisis. The analysis ultimately concludes that Enron's downfall was due to unethical internal practices rather than external forces.
![By Ngoie Joel Nshisso<br />International Business<br />Ph.D. program<br />Northcentral University<br />February 2010<br />Enron: SWOT analysis<br />Introduction<br />The public and literature world could not have know and write so intensely about Enron if it did not collapse and causing loses to partners, investors and all other stakeholders. If lose are one of the results in business, the way it happens matter to all people that have shares in the bankrupt companies.<br />Before presenting a SWOT analysis of Enron, a brief history will help to understand what was the place of this energy giant company in public and investors’ life.<br />In his report to congress, Mark (2002) presents the history of Enron as follow:<br />Formed in 1985 from a merger of Houston Natural Gas and Internorth, Enron Corp. was the first nationwide natural gas pipeline network. Over time, the firm’s business focus shifted from the regulated transportation of natural gas to unregulated energy trading markets. The guiding principle seems to have been that there was more money to be made in buying and selling financial contracts linked to the value of energy assets (and to other economic variables) than in actual ownership of physical assets.<br />Until late 2001, nearly all observers – including professional Wall Street analysts –regarded this transformation as an outstanding success. Enron’s reported annual revenues grew from under $10 billion in the early 1990s to $101 billion in 2000, ranking it seventh on the Fortune 500.<br />The unraveling began in August 2001, when CEO Jeffrey Skilling resigned for undisclosed reasons. On October 16, Enron reported its first quarterly loss in 4 years, CRS-2 taking a charge against earnings of $1 billion for poorly performing businesses. The reported third quarter loss was $618 million, versus a $292 million profit a year earlier.<br />On November 8, the company announced in a Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filing that it was restating its earnings since 1997 – reducing them by $586 million. The coup-de-grace came on November 28, when the major bond rating agencies downgraded Enron’s debt to below-investment-grade, or junk bond status. The company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on December 2, 2001. (pp. 1-2)<br />Bankruptcy is a combination of internal and external factors that did play against the company and prevented it to stay in business. The scanning of those factors is made in a mechanism called SWOT analysis. In the sections below, this mechanism will applied to Enron to try to understand how a marriage between them was the occasion to push the company out of business.<br />SWOT Analysis<br />The SWOT analysis describes the internal strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats of a company. Ferrell, Hartline, and Luc. (2006) define SWOT analysis as: <br />Basic, straightforward model that provides direction and serves as a basis for the development of marketing plans. It accomplishes this by assessing an organizations strengths (what an organization can do) and weaknesses (what an organization cannot do) in addition to opportunities (potential favorable conditions for an organization) and threats (potential unfavorable conditions for an organization). SWOT analysis is an important step in planning and its value is often underestimated despite the simplicity in creation. The role of SWOT analysis is to take the information from the environmental analysis and separate it into internal issues (strengths and weaknesses) and external issues (opportunities and threats). Once this is completed, SWOT analysis determines if the information indicates something that will assist the firm in accomplishing its objectives (a strength or opportunity), or if it indicates an obstacle that must be overcome or minimized to achieve desired results (weakness or threat).<br />A close study of Enron shows that the company could be credited with the following SWOT facts:<br />Strengths<br />Marketing and value delivery<br />Enron did not become overnight an energy giant serving multitude of customers. Its success is a result of marketing and value delivery. Marketing helped Enron to identify and meet customer needs. As it is recognized by Kotler and Lane (2006), “Marketing involves satisfying consumers’ needs and wants. The task of any business is to deliver customer value at a profit. In a hypercompetitive economy with increasingly rational buyers faced with abundant choices, a company can win only by fine-tuning the value delivery process and choosing, providing and communicating superior value.” (p. 36)Human capital pool<br />Cynthia, Lyle, and James (2006) assert that “to gain competitive advantage, Human Resource managers must (a) help the organization develop human pool that has higher overall level of skills, abilities, and knowledge than competitors; and (b) ensure that the skills, abilities, and knowledge within the human capital pool are more closely aligned with the strategic objectives of the firm than is typical among competitors.” (p. 53)<br />Most companies engage in one or two lines of businesses. Enron was running after almost five different line of business: pipeline network, energy trading market, electricity and natural gas, pulp and paper and communications. All of them with different requirements on skills, equipments, and reporting methods. Enron succeeded to recruit and maintain employees from various educations an experience background. All point to believe that human capital pool was well organized and energized to accomplish the work without friction. <br />Competitive advantage on jet fuel sale after terrorist attack of September 11, 2001<br />One of the consequences of the terrorist attack on September 11, 2001 was economy disruption of the airline business. Any company that could offer securely commodity in this business gained competitive advantage. Sanders (2001) of market watch reported that:In the wake of the Sept. 11 terrorist attacks, one of the few places to buy or sell jet fuel was an online market maintained by Enron. <br />The attacks highlighted the Houston Company’s strength as a manager of risk during periods of heightened uncertainty. Through its trading centers, the company gives customers a way to hedge against volatility in oil, natural gas, and electricity markets, as well as other commodities. (¶ 1)<br />Innovative company<br />Directors and managers understood the place of innovation in the market that is increasingly affected by change. More importantly, they mastered the innovation diffusion process that Kotler and Lane (2006) describe as “the spread of new idea from its source of innovation or creation to its ultimate users or adopters.” (p. 659) <br />From the energy and natural gas transportation, Enron shifted to energy trading company. Coal, metals and steel, communications, pulp and paper were added to the line of business. Taking advantage of internet, Enron established a strong presence and operations online.<br />Weaknesses<br />On the path to its collapse, Enron showed the following weaknesses: <br />Failed board of directors<br />The question anyone did ask when the saga of Enron became known is where the board of directors was and why they did not see all that mess coming. Probably they were more interested and satisfied with profits. Nevertheless, beyond all analysis board of directors bears big responsibilities for not doing correctly their oversight. <br />The board of directors failed to carry out one or all of the following basic tasks described by Wheelen and Hunger (2008):<br />Monitor: by acting through its committees, a board of can keep abreast of developments inside and outside the corporation, bringing to management’s attention development it might have overlooked. A board should at least carry out this task.<br />Evaluate and influence: a board can examine management’s proposals, decisions, and actions; agree or disagree with them; give advice and offer suggestions; and outline alternative. More active boards perform this task in addition to monitoring.<br />Initiate and determine: A board can delineate a corporation’s mission and specify strategic options to its management. Only the most active boards take on this addition to the two previous ones. (p. 37)<br />Conflicts of interests<br />Even though at the time of Enron’s collapse the Sarbanes-Oxley Act was enacted yet, the Internal Revenue Service require corporation to adhere to the Conflict of Interest Policy to avoid wrong doing that can get it off the path. Panda (2005) who studied Enron failure noted that “For any corporation to be healthy and productive, it needs to be strong in four core areas: (a) financial capital in terms of investments and profits, (b) technological capital in terms of cutting-edge software and hardware, (c) human capital in terms of knowledge, expertise, and creativity and (d) social-spiritual capital in terms of ethics, relationships, meaning and purpose.” (¶ 30)<br />Unethical practices marked by conflict of interests may have been the front-runner cause to its collapse because it was like a cancer that ruined its infrastructure, its financial transactions, and its accounting practices.<br />Unethical practices<br />Hearing and reports indicate that Enron kept accounting documents hidden and well manipulated with the complicity of its auditing company. Wheelen and Hunger (2008) wrote the following about Enron unethical practices:<br />Enron, in particular, has become infamous for the questionable actions of its top executives in the form (1) off-balance sheet partnerships used to hide the company’s deteriorating fiancés, (2) revenue from long-term contracts being spread over multiple years, (3) financial reports being falsified to inflate executive bonuses, and (4) manipulation of the electricity market – leading to California energy crisis. (p.63) <br />If someone would to pinpoint things that directly led to the downfall of Enron, it will be unethical practices <br />Corporate culture<br />One the good definition of corporate culture comes from Wheelen and Hunger (2008) who said:<br />Corporate culture is the collection of beliefs, expectations, and values learned and shared by a corporation‘s members and transmitted from one generation of employees to another. The corporate culture generally reflects the values of the founder(s) and the mission of the firm. It gives a company a sense of identity…Corporate culture shapes the behavior of people in a corporation. Because these cultures have a powerful influence on the behavior of people at all levels, they can strongly affect a corporation’s ability to shift its strategic direction. (p. 116)<br />The above definition makes it possible to believe that fraud and off-balance accounting were the artwork of the high-level managers. Because mid-level managers who were in charge of bookkeeping could not distort data without supervisor instruction or approval. The collapse unveiled the real culture of Enron that was until than presented as culture of innovation, success, and profits. <br />Opportunities<br />The market and the experience in business provided Enron with tremendous opportunities such as:<br />Supply of high quality energy<br />In their book Managerial economics, Keat and Young (2006) define supply as “quantities of a good or service that people are ready to sell at various prices within some given time period, other factors beside price held constant.” (p.53)<br />Enron was a worldwide leader in commodity sales and services. It marked and delivered energy in North America where the power volume increased for 90 percent and in Europe with an increase demand of natural gas volume over 250 percent. With its supremacy in energy and franchise business model, Enron could be serving today China and India whose emerging economy is in need of energy. <br />Clean energy<br />More and more the public claim for clean energy in order to reduce pollution of the environment. The United States, foreign governments, and international institutions like United Nations are adopting policies and incentives to push for research and production of renewable energy.<br />The market is even more interesting because, the demand of energy is growing as show in the table below:<br />With its innovative culture, online-established market, franchise policy, technology and other assets, Enron could have a lion-share in the future clean and renewable energy. <br />Business merger and acquisition<br />Wheelen and Hunger (2008) provide the definitions for merger and acquisition we believe correspond to the actual economic environment: <br />A merger is a transaction involving two or more corporations in which stock is exchanged but in which only one corporation survives. Mergers usually occur between firms of somewhat similar size and are usually “friendly.” The resulting firm is likely to have a name derived from its composites firms.<br />An acquisition is the purchase of a company that is completely absorbed as an operating subsidiary or division of the acquiring corporation. (p. 166) <br />The economy downturn, the need for clean and renewable energy and the growing demand of energy could have pushed energy companies with feeble assets or non-innovative out of business and open them to merger or acquisition. Enron, with its experience of merger and strong assets would use one or other strategy to grow. <br />Market development in Asian region<br />As part of functional strategy, Wheelen and Hunger (2008) recommend as marketing strategy, the market development for “a company or business unit can (1) capture a larger share of an existing market for current products through market saturation and market penetration or (2) develop new markets for current products.” (p. 190)<br />The 21st century has seen the emergence of Chine and India as big energy consumers. These two nations are desperately need energy to keep their industries operational. Enron could have had a tremendous opportunity to tape in these two giants markets to capture a large share whether through franchising, licensing, joint ventures, or acquisitions in these two specific countries. <br />Threats<br />The external business and global environment presented the following threats to Enron:<br />Competition<br />Justin, Carlos, and William (2003) discovered that “frequently, entrepreneurs ignore the reality of competition for their new ventures, believing that the market place contains no close substitute or that their success will not attract other entrepreneurs.” (p. 233)<br /> There are hundreds of energy companies in the United States with ambitions to gain a big share of the energy market whether with new technology or cheap price. They are all aggressively involved in research and development. One of the way they learn about competitor is to go to their website, read news, follow stock evolution, attract employees from the competitor with good pay…if Enron was still in business he could be facing fierce competition from other energy companies that by the way took opportunity of its bankruptcy to gain the abandoned and deceived market. <br />Regulation<br />Keat and Young (2006) consider regulation as “action that includes changes in taxes, labor law rules, minimum wages, and price controls.” (p. 468) <br />National and international regulations on greenhouse gas reduction to curb global warming would have been a major threat to Enron. One of the major regulations that could affect Enron on its European business is the Kyoto protocol. <br />Subprime mortgage crisis<br />The economic recession has been triggered by subprime mortgage crisis characterized by mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures. The negative effect of foreclosures is the reduction of energy and natural gas consumption as commodities.<br />Enron was an energy wholesaler and retailer whose revenues depended on house’s consumption. As the foreclosure hit the nation, Enron could have seen its profits decline because of the economic recession. <br />Terrorist threats <br />Threats of terrorist attacks in the American soil or American interest abroad affect initiatives and investments. Enron line of business is one of the targets of terrorist threats. <br />Another negative effect of terrorism threats is the cost of risk assessment “based on a combination of workplace vulnerabilities, the potential of a recognized threat occurring and the anticipated consequences” (Fisher, Schoenfeldt and Shaw 2006, p. 635)<br />Strategy for continued growth<br />We noted that energy demand is deemed to grow substantially for the forecast provided by the energy information administration (EIA), the emergence of China and India as producer and consumer in the global economy. We also mentioned the demand of clean energy leading to new technology in which government and international organizations have pledged to invest billions of dollars opening opportunities for innovative businesses to compete for financing or grants and comprehensive regulations. All these trends provide a way for growth to any company in the energy business.<br />What could have been Enron strategy to grow?<br />We mentioned early the innovative character of Enron that flowing from exhaustible human capital. We also indicate the experience of Enron in merger and business line expansion.<br />These assets helped Enron to focus in energy and natural gas transportation. They also provided way to develop energy trading markets, communications, and pulp and paper businesses. <br />Enron was already practicing concentration and diversification growth strategies that had the capability to provide long-term profits and maturity in all lines of operations. What were missing in the Enron growth strategies and that could prevent its melt-down are the enforcement of code of ethics and absence of social responsibilities. <br />Conclusion<br />The SWOT analysis performed above helped to identify, among many, strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats faced by Enron. As this analysis provides internal and external environment factors that the company had to deal with, the important question is to determine the forces leading to the collapse of an apparent wealthy company like Enron. <br />External events are to be ruled out as causes presiding to the debacle of the American energy giant Enron. To outside agents took the company by surprise or as prepared plan to push the company out of business. The death of Enron comes from inside of its own actions and practices. Its officers and board of directors may have been caught in their own nets.<br />Enron had knowledgeable employees that may had perform Michael Porter’s five forces model to “determine the relative attractiveness of an industry and includes buyer power, supplier power, threat of substitute products or services, threat of new entrants and rivalry among competitors” (Baltazan & Phillips 2008, pp. 17-18). It can be also possible that SWOT analysis was carried out and highlighted the breach of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), of code of ethics, corporate culture, the risk to deceive shareholders and being one day caught by government’s agencies but officers and board of directors chose to ignore the warnings. Doing so, they turned away from growth strategies in place and decide a death sentence that took their investments and of many others into the grave. <br />References <br />Baltzan, P., & Phillips, A. (2008). Business driven information systems (4th ed.). The McGraw-Hill companies, (Original work published 2007)<br />Energy information administration. (2008, June). Report #:DOE/EIA-0484(2008). In World market energy consumption by country grouping, 2005-2030. Retrieved February 29, 2009, from Energy information administration Web site: http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/ieo/pdf/table1.pdf<br />Fisher, C. D., Schoenfeldt, L. F., & Shaw, J. B. (2006). Human resource management (6th ed.). 222 Berkeley street, Boston, MA 02116: Houghton Mifflin.<br />Keat, P. G., & Young, P. K. (2006). Managerial Economics: Economic tools for today’s decision (5th ed.). Upper saddle river, New Jersey 07458: Pearson education,Inc. (Original work published 1996)<br />Kotler, P., & Lane, K. (2006). Marketing management (12th ed.). Upper saddle river, New Jersey 07458: Pearson education, Inc. (Original work published 1994)<br />Longenecker, J. G., Moore, C. W., & Petty, W. J. (2003). Small business management: an entrepreneurial emphasis. 5191 Natorp boulevard, Mason, : Thomson South-Western.<br />Mark, J. (2002, February 4). RS21135. In The Enron collapse: An overview of financial issues [Report]. Retrieved February 27, 2009, from http://fpc.state.gov/documents/organization/8038.pdf<br />Panda, R. K. (2005, December 19). Soft skills: the ultimate reality for corporate progress. Retrieved February 27, 2009, from http://searchwarp.com/swa29656.htm<br />Sanders, L. (2001, October 4). Attacks highlight Enron’s value [News]. Retrieved February 29, 2009, from http://www.marketwatch.com/news/story/attacks-highlight-strengths-enron/story.aspx?guid=%7B76418AE7-C15A-442C-B883-A6700C723722%7D<br />Wheelen, T. L., & Hunger, D. J. (2008). Strategic management and business policy (11th ed.). Upper saddle river, New Jersey 07458: Pearson education, Inc. (Original work published 2000)<br />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enron-swot-analysis-1292031468-phpapp02/75/Enron-SWOT-Analysis-1-2048.jpg)