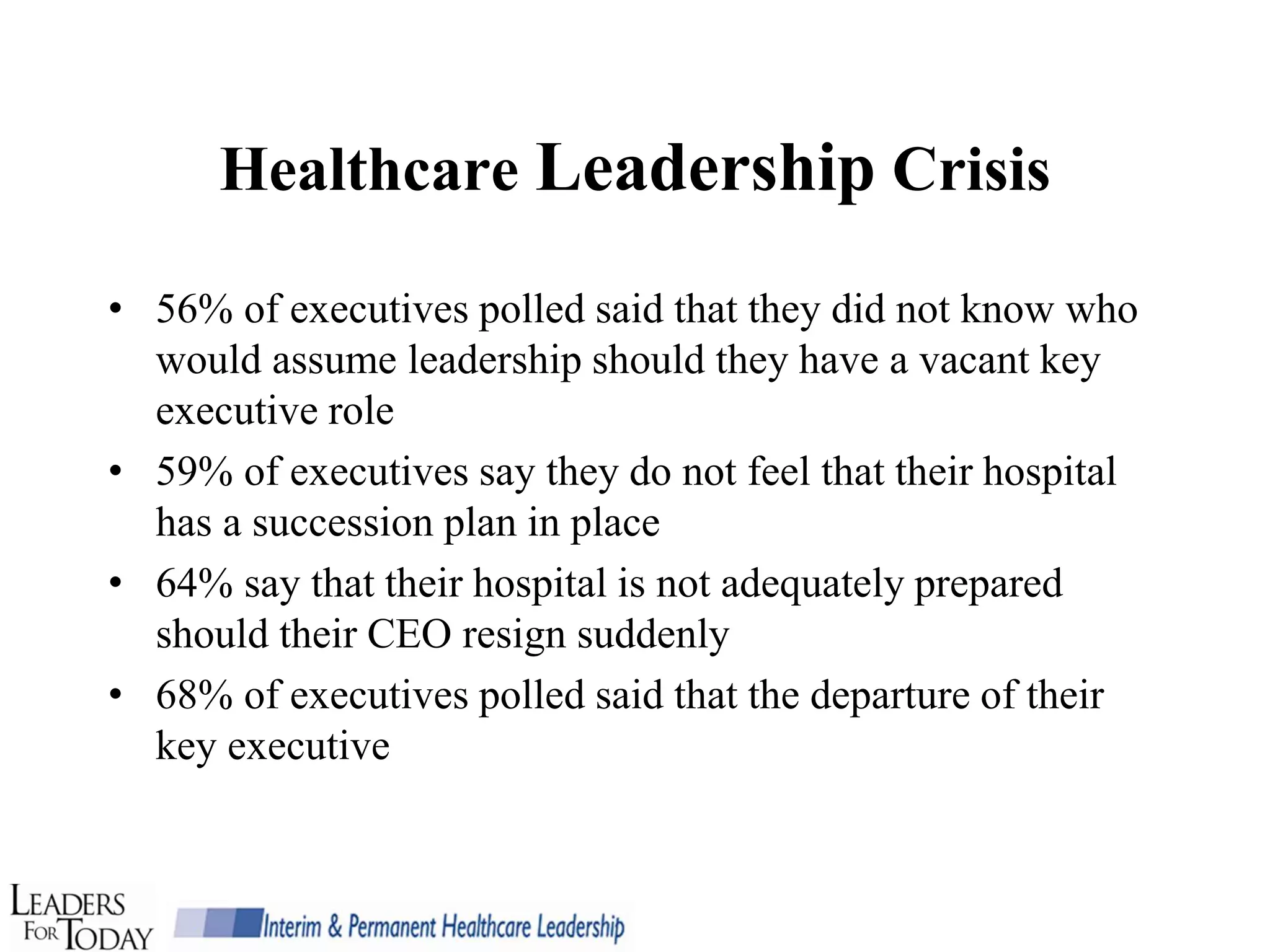
The document discusses the importance of succession planning for healthcare leadership. It notes that many healthcare organizations lack succession plans, despite projections that 50% of healthcare management could be lost in the next 5 years due to retirements. It then provides definitions and rationale for succession planning, including cost savings, continuity, and having a contingency plan. The document outlines best practices for developing a succession plan, including making a business case, identifying and developing high-potential leaders, and implementing leadership development programs. It discusses factors that can impede effective succession planning if not addressed.