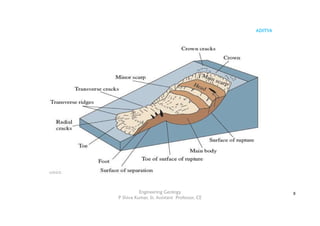
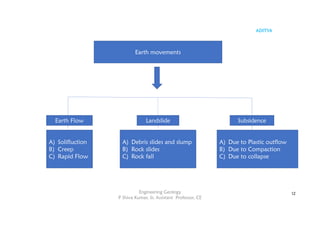
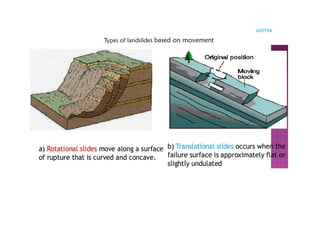
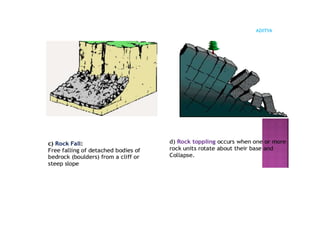
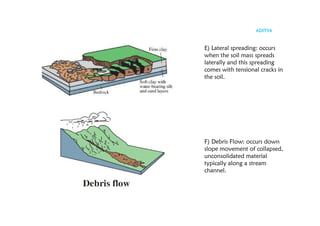
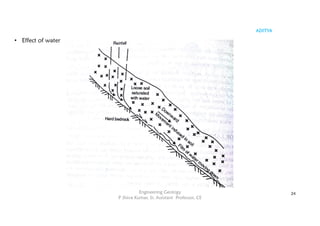
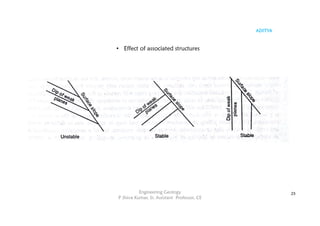
The document outlines the curriculum for a course in engineering geology, focusing on structural geology, landslides, and their impact on civil engineering. Key learning outcomes include understanding geological structures, mechanisms of folding and faulting, and the causes and types of landslides, as well as their implications for civil infrastructure. Preventive measures for managing landslide risks and the effects of landslides on transportation, communication, and construction are also discussed.