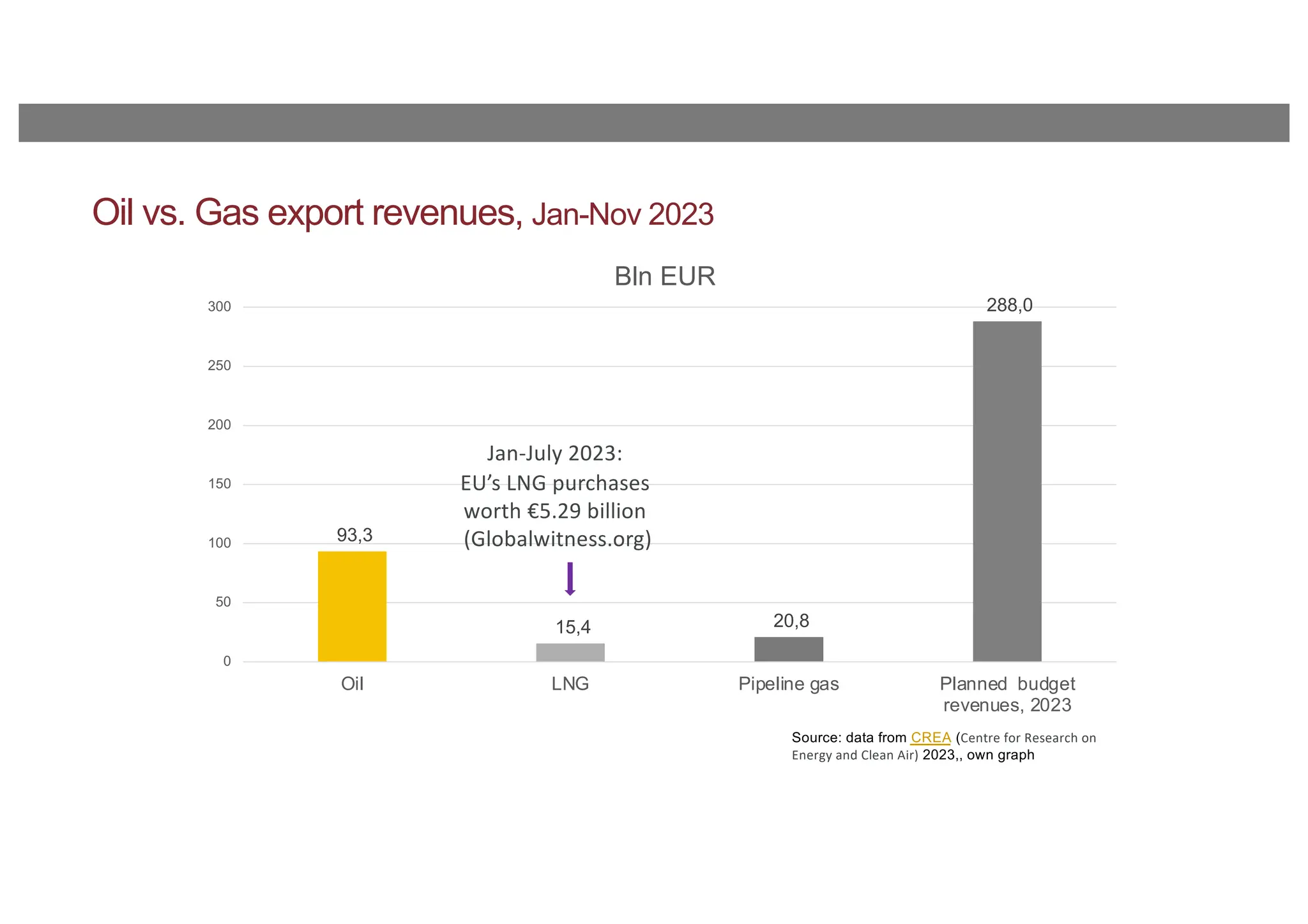
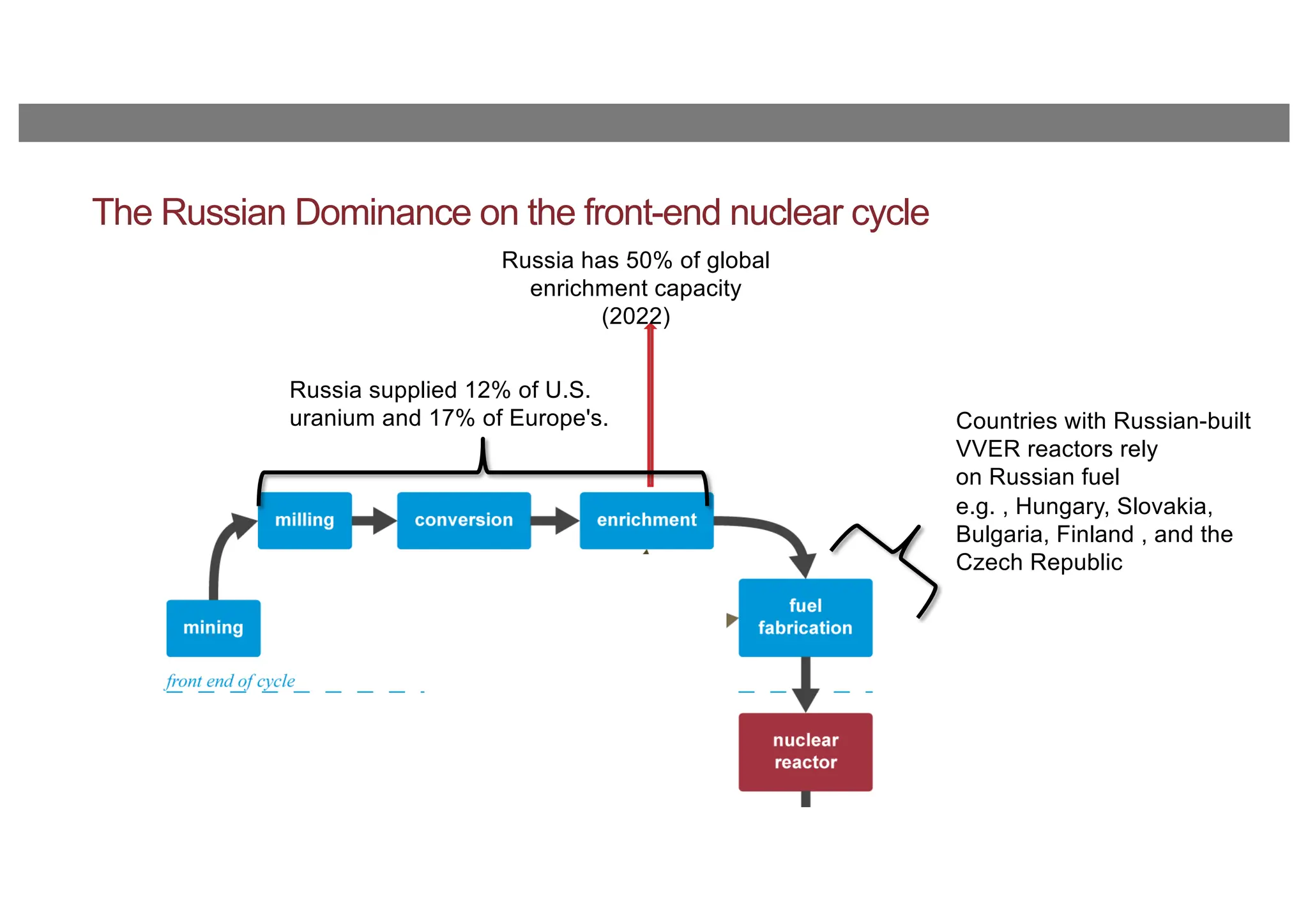
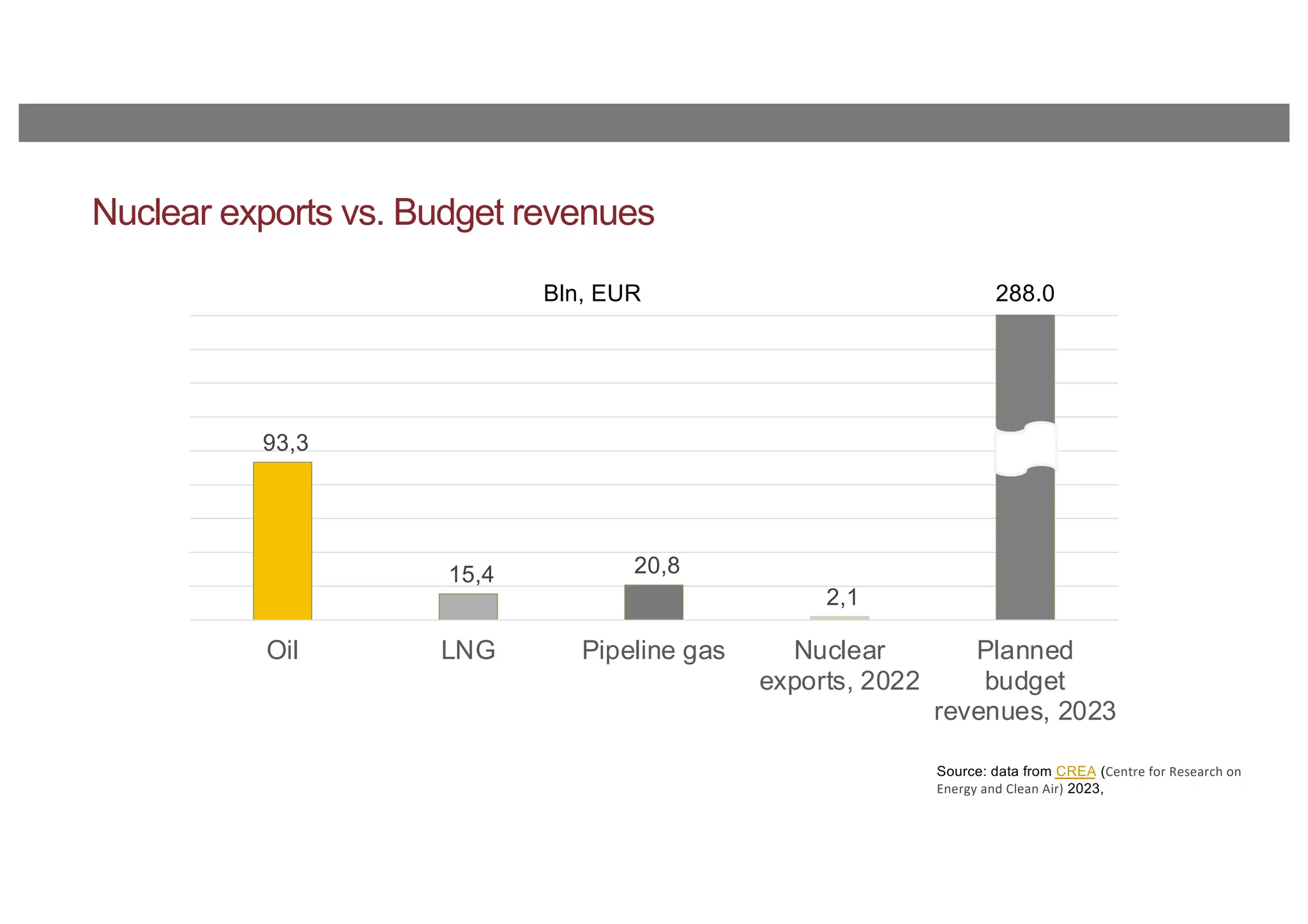
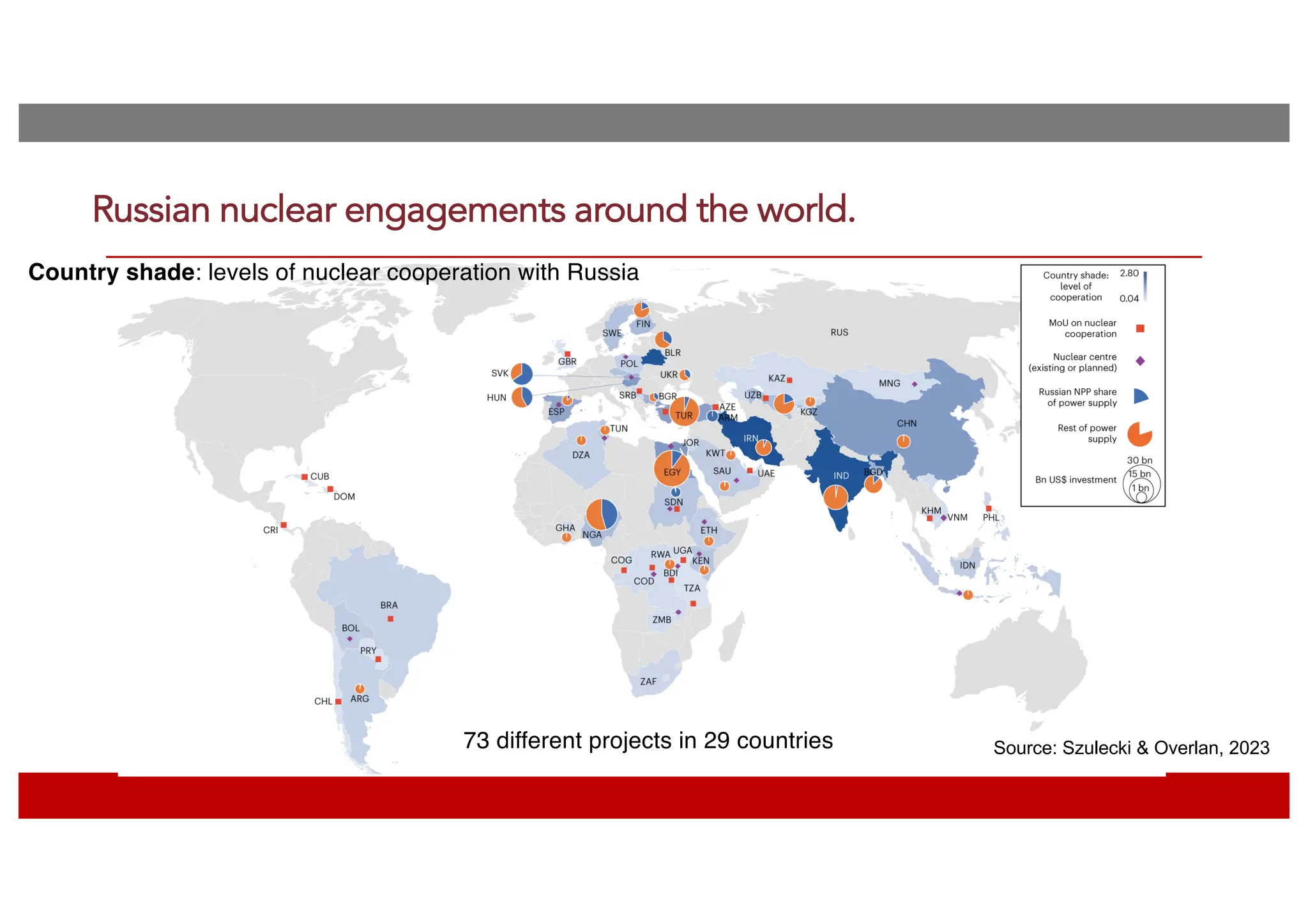
The document discusses the current energy sanctions against Russia, targeting crude oil, refined petroleum products, and coal, and considers expanding these sanctions to liquefied natural gas (LNG) and nuclear energy-related products. It emphasizes the importance of limiting Russia’s influence globally, not just reducing its government revenues, and highlights the EU's reliance on Russian LNG. The conclusion suggests developing credible and affordable alternatives to Russian energy to enhance energy security.