Abstract:
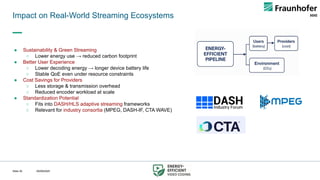
Video streaming today accounts for more than 80% of global internet traffic, with demands projected to rise further due to UHD, 8K, VR, and immersive media applications. While newer codecs like AV1 and VVC deliver better compression efficiency, their increased computational complexity significantly raises energy consumption in encoding, storage, transmission, and decoding. This creates a fundamental tension between maintaining high Quality of Experience (QoE) for users and ensuring sustainable, energy-efficient streaming.
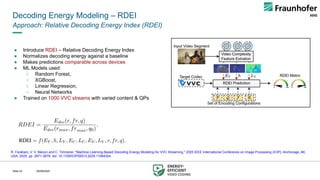
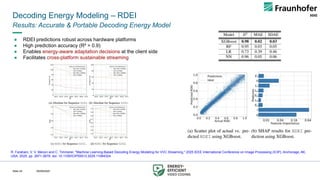
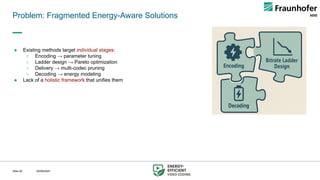
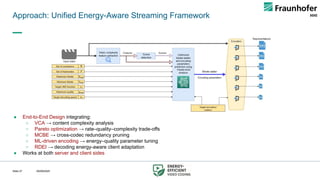
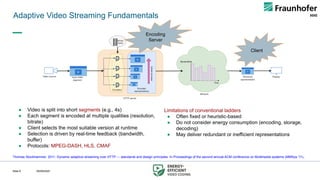
This talk presents a holistic framework for energy-aware adaptive streaming that addresses inefficiencies across the entire pipeline. First, a Video Complexity Analyzer (VCA) provides lightweight content features to guide efficient encoding. Second, convex-hull–based optimization enables Pareto-efficient bitrate ladder construction. Third, multi-codec bitrate ladder pruning (MCBE) reduces redundancy across AVC, HEVC, AV1, and VVC, achieving major savings in storage and transmission. Fourth, ML-driven encoding parameter selection balances quality and energy by predicting VMAF and power usage. Finally, a Relative Decoding Energy Index (RDEI) provides device-independent modeling of decoding costs, enabling client-side adaptation.
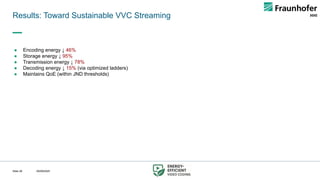
Together, these methods reduce encoding energy by 46%, storage by 95%, transmission by 78%, and decoding by 15%, all while maintaining QoE within just-noticeable-difference thresholds. The framework paves the way toward scalable, sustainable, and net-zero streaming ecosystems.



![MHV’24
Why Energy-Efficient Video Streaming?
Slide 4
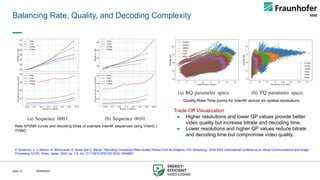
Video dominates internet usage
● Over 80% of global internet traffic is video (Cisco, Sandvine)
App category traffic share (2022)
● Video alone accounts for nearly 66% of total data volume
Bandwidth demands are growing
● Emerging applications (UHD, 8K, VR) need 100–500 Mbps
29/09/2025
[1] Cisco, “Cisco visual networking index: Forecast and methodology, 2017–2022 (White Paper),” 2019.
[2] Ericsson, Ericsson Mobility Report: November 2020, Nov. 2020. [Online]. Available:
https://www.ericsson.com/assets/local/reports-papers/mobility-report/documents/2020/november-2020-ericsson-mobility-report.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20250929ctsocpresentation-250929162808-68a1d68b/85/Energy-Efficient-Video-Coding-for-HTTP-Adaptive-Streaming-4-320.jpg)


![MHV’24
Why Energy Efficiency is Critical in VVC
29/09/2025
Slide 8
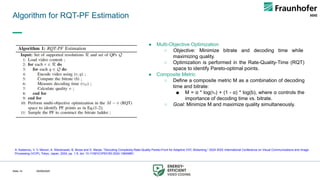
● Newer codec implementations are more efficient, but need more
CPU cycles to decode.
○ Higher computational load → thermal throttling, degraded QoE
○ Massive streaming demand → higher carbon footprint
● Energy-per-frame increases with complexity → direct impact on
battery.
● Alliance for Open Media Video 1 (AV1) and Versatile Video Coding
(VVC) offer better compression, but decoding cost can outweigh
savings in low-power devices.
● Need frameworks that optimize rate–quality–energy trade-offs.
Table: Averaged BD-BR savings depending on codec and resolution [1]. Table: Averaged BD-PSNR savings depending on codec and resolution [1].
[1] Uhrina, Miroslav, Lukas Sevcik, Juraj Bienik, and Lenka Smatanova. 2024. "Performance Comparison of VVC, AV1, HEVC, and AVC for High Resolutions" Electronics 13, no. 5: 953.
https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050953](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20250929ctsocpresentation-250929162808-68a1d68b/85/Energy-Efficient-Video-Coding-for-HTTP-Adaptive-Streaming-8-320.jpg)

![MHV’24
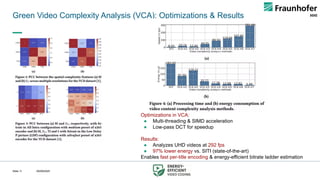
Green Video Complexity Analysis (VCA): Features
29/09/2025
Slide 10
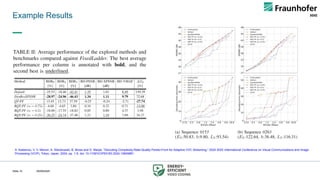
Goal: Low-complexity, accurate features for real-time
streaming decisions
We use seven DCT-energy-based features extracted
using Video Complexity Analyzer (VCA) [1,2]:
● average texture energy (EY),
● average gradient of the luma texture energy (h)
● average luma brightness (LY),
● average chroma texture energy of U and V
channels (EU and EV)
● average chroma brightness of U and V channels
(LU and LV) .
1. V. V. Menon, C. Feldmann, K. Schoeffmann, M. Ghanbari, and C. Timmerer. 2023. Green Video Complexity Analysis for Efficient Encoding in Adaptive Video Streaming. In Proceedings of the First International ACM
Green Multimedia Systems Workshop (GMSys 2023). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1145/3593908.3593942
2. V. V. Menon, C. Feldmann, H. Amirpour, M. Ghanbari, and C. Timmerer. 2022. VCA: video complexity analyzer. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference (MMSys '22). Association for
Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1145/3524273.3532896
https://github.com/cd-athena/VCA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20250929ctsocpresentation-250929162808-68a1d68b/85/Energy-Efficient-Video-Coding-for-HTTP-Adaptive-Streaming-10-320.jpg)
![MHV’24
Motivation for convex-hull estimation
29/09/2025
Slide 12
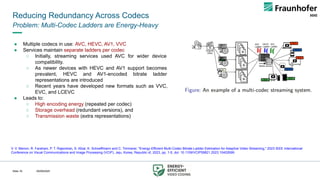
● The convex hull is where the encoding point achieves “Pareto efficiency”.
● Convex-hull estimation provide a dynamic and adaptive means to optimize
(bitrate/ resolution/ framerate…) selections.
● By dynamically adjusting the bitrate-resolution pairs in response to the
video content complexity and coding algorithms, these methods achieve
an optimal trade-off between computational efficiency and visual fidelity in
the face of the increased intricacies associated with advanced codecs like
VVC [1,2].
Figure: Conceptual plot to depict the bitrate-quality relationship for
any video source encoded at different resolutions. Source: [3]
[1] B. Bross, Y. Wang, Y. Ye, S. Liu, J. Chen, G. Sullivan, and J. Ohm. (2021). Overview of the Versatile Video Coding (VVC) Standard and its Applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology. 31. 3736-3764. 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3101953.
[2] R. Kaafarani et al., “Evaluation Of Bitrate Ladders For Versatile Video Coder,” in 2021 International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), 2021, pp. 1–5.
[3] A. Aaron, Z. Li, M. Manohara, J.D. Cock, D. Ronca, "Per-title encode optimization." The Netflix Techblog (2015).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20250929ctsocpresentation-250929162808-68a1d68b/85/Energy-Efficient-Video-Coding-for-HTTP-Adaptive-Streaming-12-320.jpg)