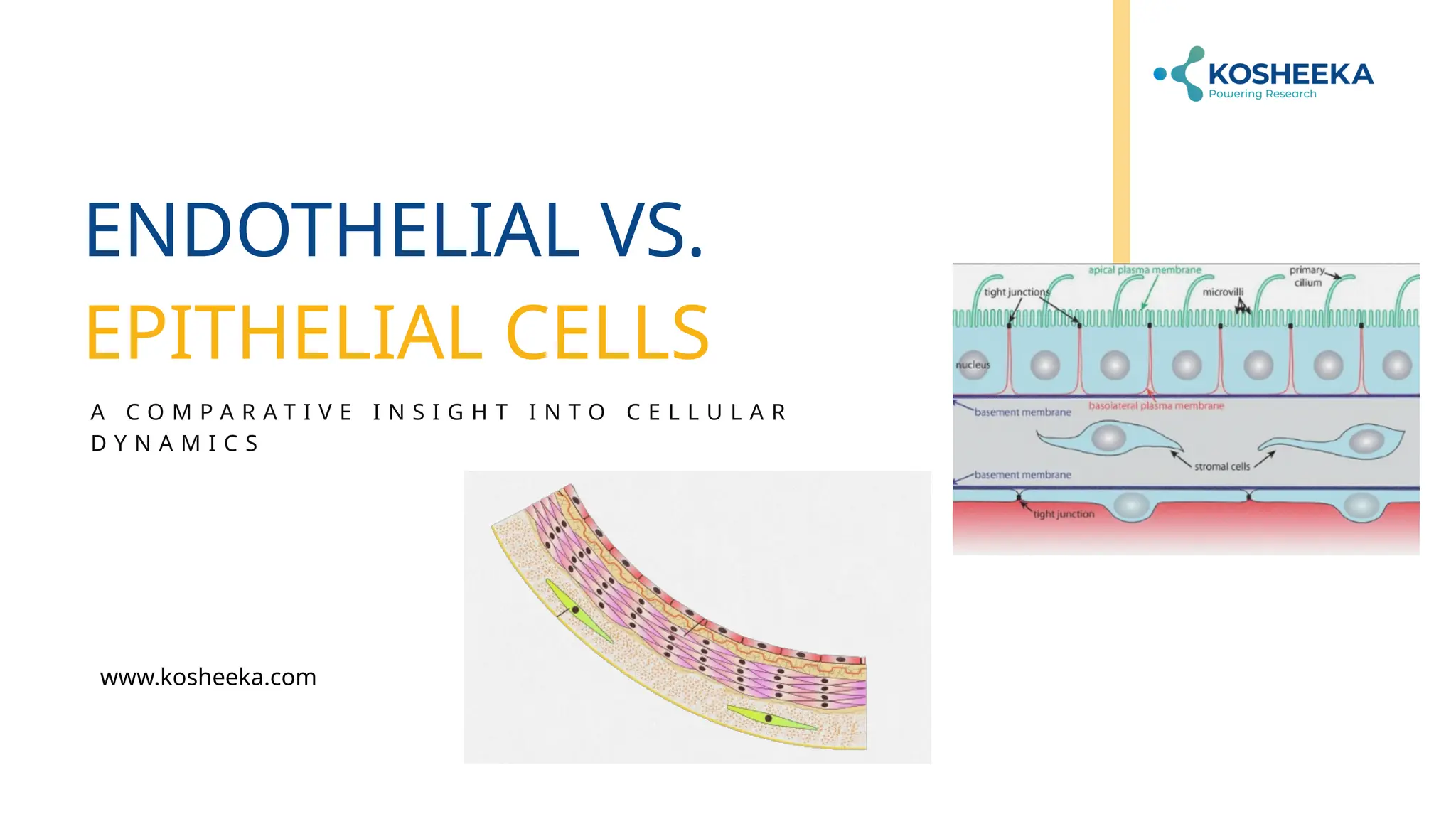
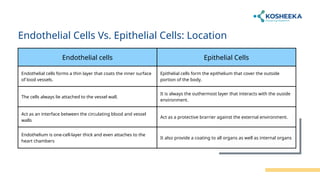
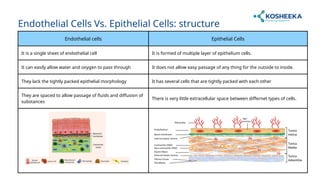
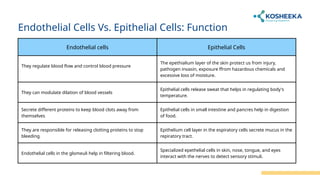
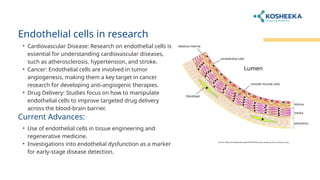
Endothelial cells line blood vessels and regulate blood flow, while epithelial cells cover body surfaces and perform various protective and absorptive functions. Both cell types share a common origin but differ significantly in location, structure, and function. Research on these cells is crucial for understanding various medical conditions, including cancer and cardiovascular diseases.