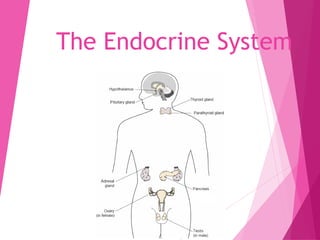
The document outlines the endocrine system, detailing its organs and how they communicate through hormones, which are produced and stored in specific glands. Key organs discussed include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, each playing a crucial role in regulating body functions such as metabolism and reproduction. It also provides a hands-on activity for students to create a model of the endocrine system to better understand hormone pathways and organ functions.