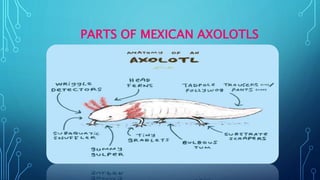
Pileated gibbons and Mexican axolotls are both endangered species. Pileated gibbons live in tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia and are threatened by habitat loss and hunting. They move through the trees and communicate with early morning songs. Mexican axolotls live in lakes in Mexico and face threats from pollution and introduced predators. They can regrow limbs multiple times and lay many eggs in protective coverings. Both species have unique locomotion and breeding behaviors that are threatened as their habitats decline.