Embed presentation
Download to read offline


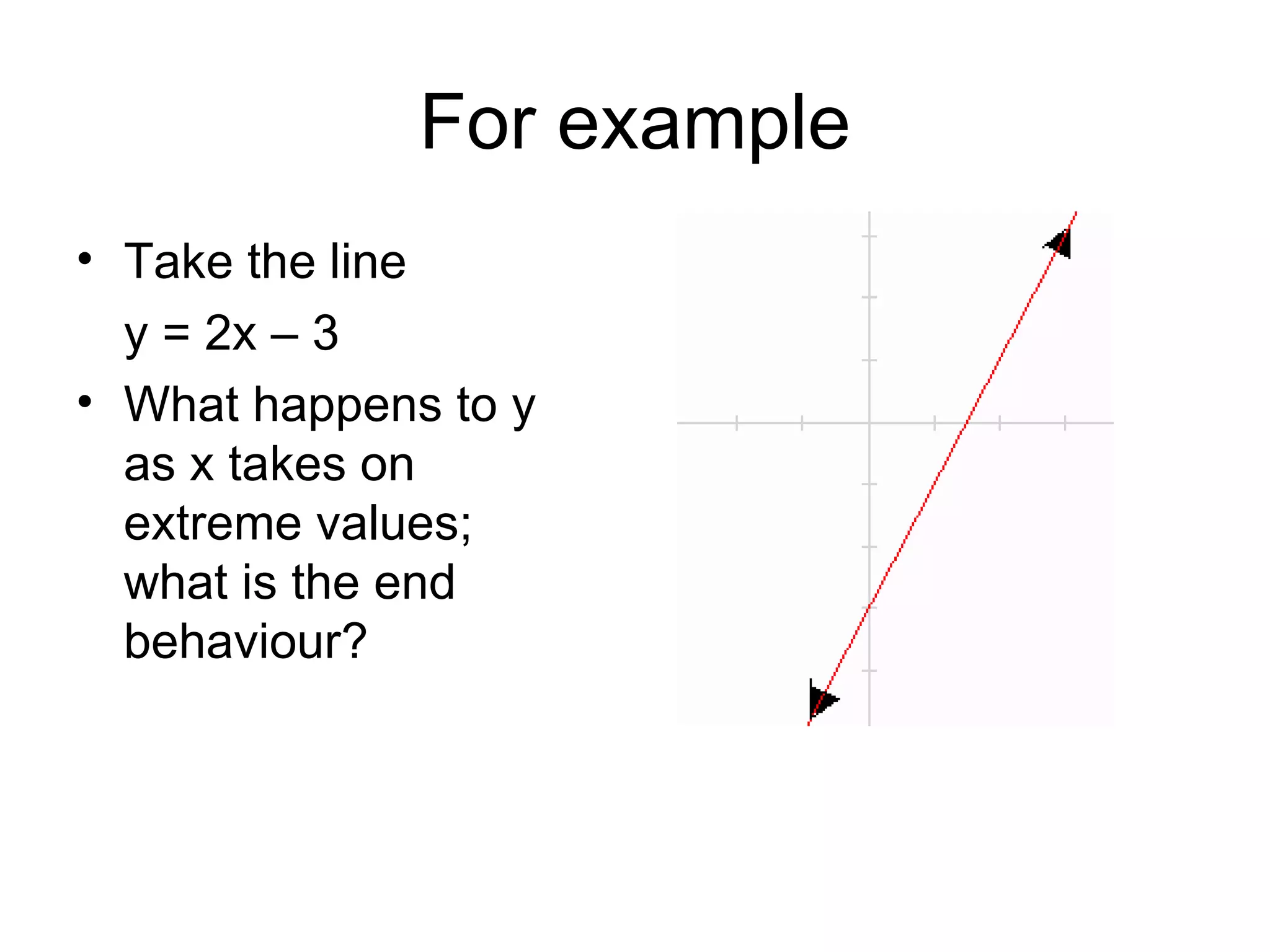


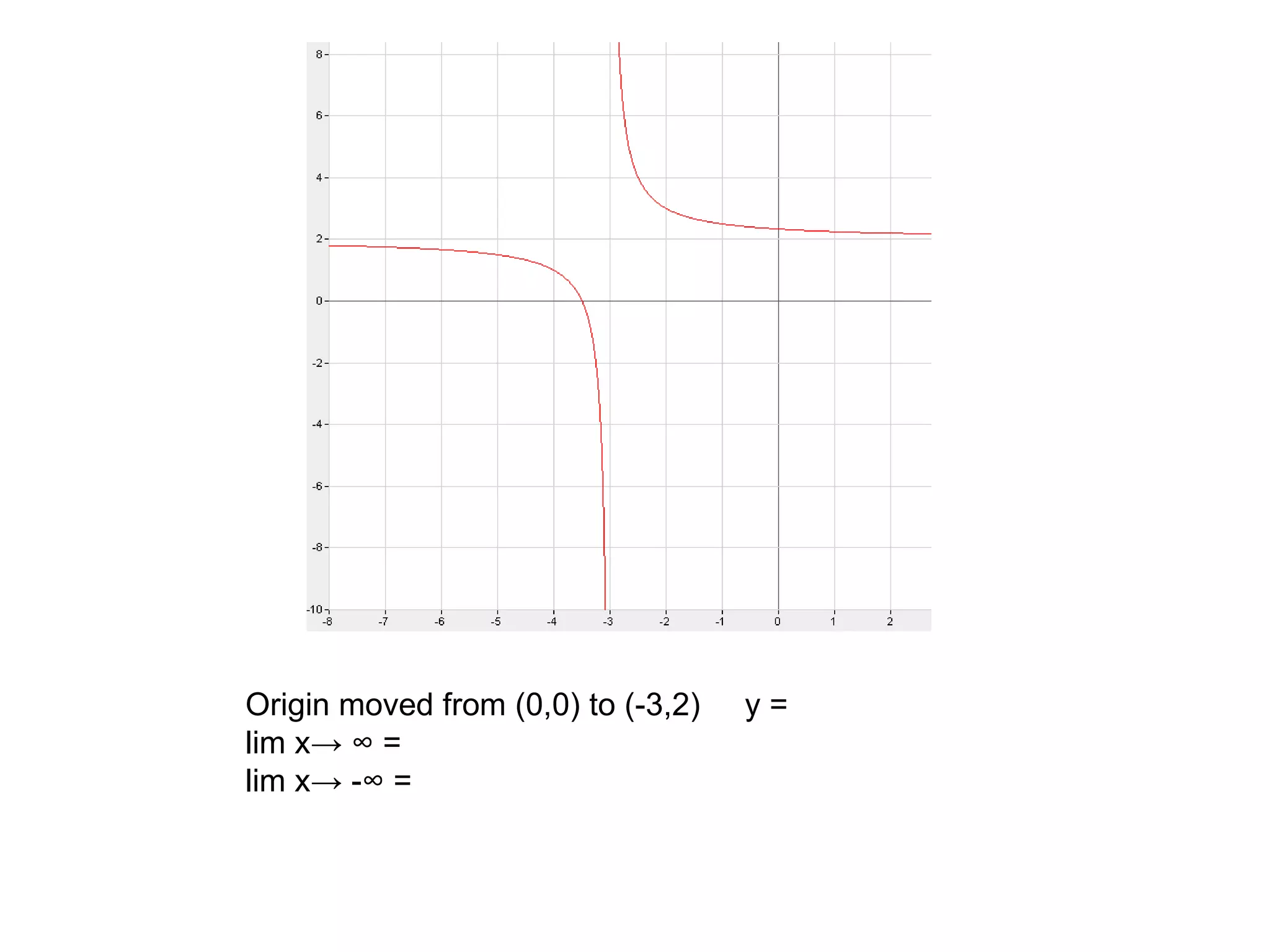
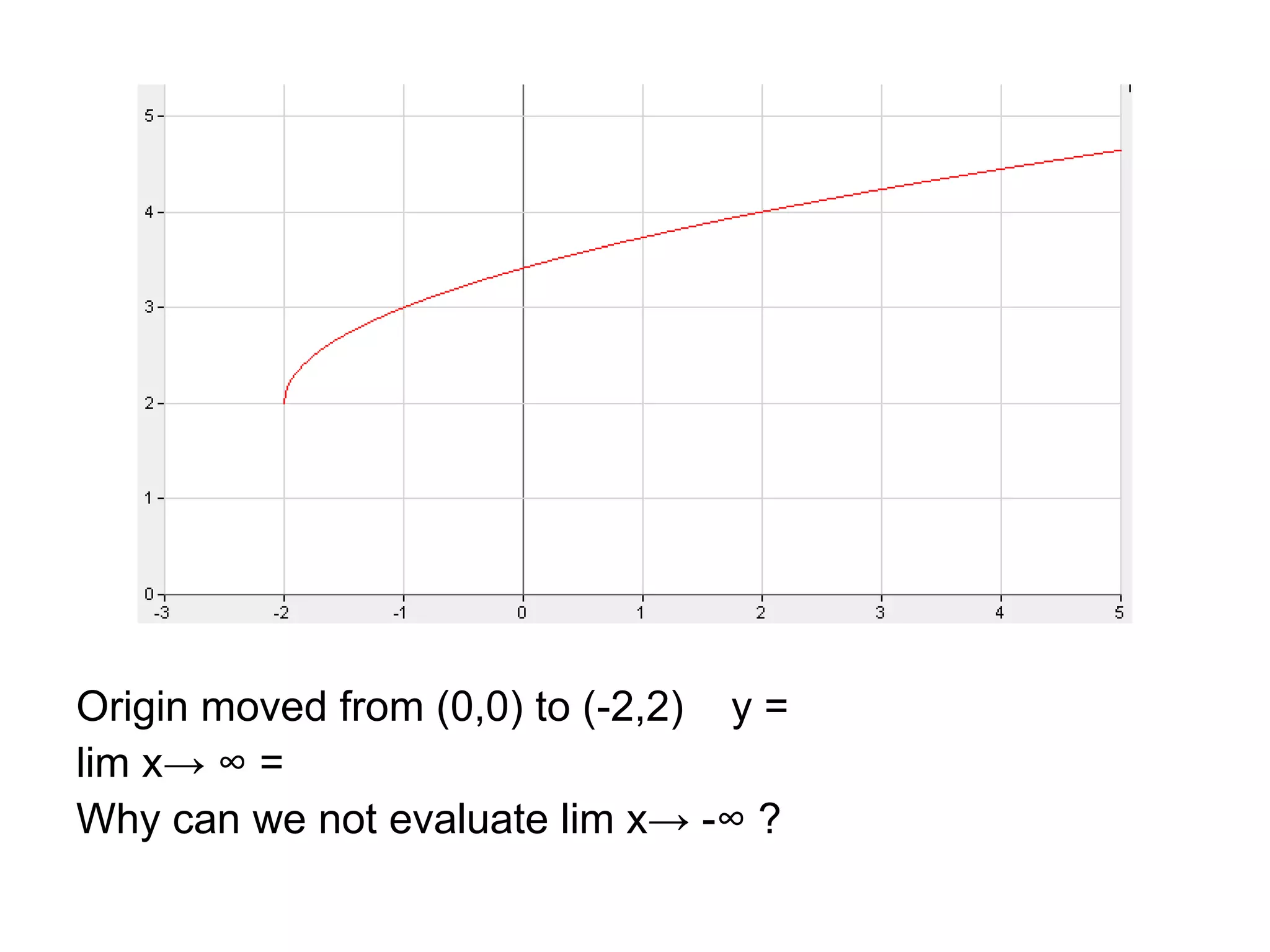


The document introduces the concept of end behavior of functions, which refers to the y-values as x takes on very large positive or negative values. This can be written using limit notation as x approaches infinity or negative infinity. For the linear function y=2x-3, the end behavior is positive infinity as x approaches positive infinity and negative infinity as x approaches negative infinity. Other functions are examined to determine their end behavior as x approaches positive or negative infinity based on transformations of the parent function y=2x.







