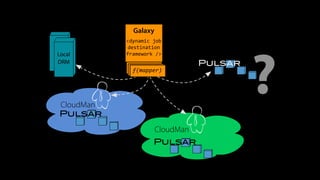
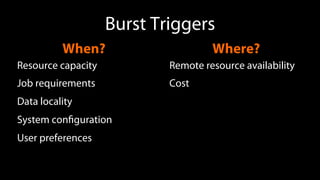
The document outlines the implementation of cloud bursting for life sciences using the Galaxy data analysis framework, which integrates various tools and resources to facilitate data analysis. It discusses the mechanics of cloud bursting, user configurations, job destination management, and the role of pulsar in handling job execution and data staging. Additionally, it provides insights into job performance metrics and resource utilization within the Galaxy environment.





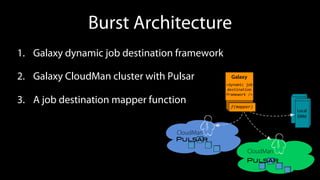


![3. Job mapper function
Determine job destination at runtime
import pyslurm
def cloud_burst():
n = pyslurm.node()
nodes_state = n.get()
available_nodes = []
for node in nodes_state.itervalues():
if node['total_cpus'] > 0:
available_nodes.append(node)
if not available_nodes:
return 'pulsar_nectar_galaxy'
return 'drmaa_runner’
job destination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burstingpresentation-150213085810-conversion-gate02/85/Enabling-Cloud-Bursting-for-Life-Sciences-within-Galaxy-12-320.jpg)