This study examined the relationship between emotional intelligence (EI) and well-being in 73 surgical residents. The study found that EI scores positively correlated with psychological well-being and negatively correlated with burnout and depression. Regression analyses controlling for demographics found that EI strongly predicted well-being, emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and depression among residents. The study concluded that EI is a strong predictor of resident well-being, and measuring EI could help identify residents most likely to thrive while interventions to increase EI may optimize resident wellness.


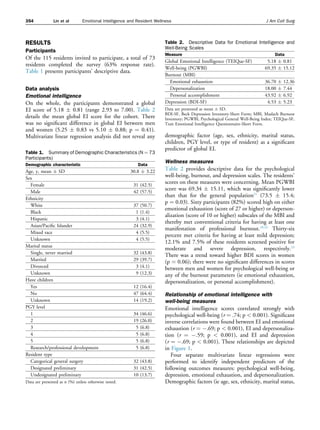

![combined with ours, suggest that interventions directed at
increasing or optimizing EI might, in turn, improve the
wellness of residents. It should be noted that Webb and
colleagues48
attempted to measure the effect of formal
EI coaching in family medicine residents by implement-
ing training sessions by a certified EI coach. This interven-
tion was unsuccessful due to a lack of protected time for
the residents, rendering the authors unable to assess its
effect. This example emphasizes the importance of
designing and implementing programs in such a way as
to ensure full participation of the residents to attain the
maximal effect.
This study has several limitations. One limitation is
the overall response rate of 63% and relatively small
sample size. As participation was voluntary, it is
possible that the results might be biased by self-
selection. Also limiting generalizability is that partici-
pants were recruited from a single academic surgical
training program; study findings might not be represen-
tative of trainees of other specialties or institutions.
Among the study cohort, junior residents well outnum-
bered senior residents, reflecting the PGY composition
of the program. There was, however, strong participa-
tion of the residents in PGY levels 3 to 5 with a survey
completion rate of 83% for each upper class.
It is imperative to address physician wellness, not
only for the sake of the individual practitioners, but
also for that of the health care organizations to which
they belong and the patients they serve. Our findings
suggest that interventions and curricula designed to in-
crease EI can help lessen the prevalence and degree of
burnout and depression among physicians. Future
research endeavors to better generalize our findings
could start with broadening the test population to
include attending surgeons and physicians from other
specialties. The relationship between physician EI and
clinical performance and patient outcomes should be
also more fully explored. Implementing and measuring
the effect of an EI intervention on individual EI score,
well-being parameters, and clinical outcomes can yield
justification for investing in initiatives that cultivate
the EI of physicians.
Author Contributions
Study conception and design: Lin, Liebert, Lau, Salles
Acquisition of data: Lin, Liebert, Tran, Salles
Analysis and interpretation of data: Lin, Tran, Lau, Salles
Drafting of manuscript: Lin, Lau, Salles
Critical revision: Lin, Liebert, Tran, Lau, Salles
Acknowledgment: The authors would like to acknowledge
Ralph Greco, MD, and Claudia Mueller, MD, for their
collaboration and support as faculty champions of the
Balance in Life program, which promotes wellness among
the general surgery residents at Stanford.
REFERENCES
1. West CP, Tan AD, Habermann TM, et al. Association of resi-
dent fatigue and distress with perceived medical errors. JAMA
2009;302:1294e1300.
2. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps G, et al. Burnout and
medical errors among American surgeons. Ann Surg 2010;
251:995e1000.
3. Wallace JE, Lemaire JB, Ghali WA. Physician wellness: a
missing quality indicator. Lancet 2009;374[9702]:
1714e1721.
4. Shanafelt TD, Bradley KA, Wipf JE, Back AL. Burnout and
self-reported patient care in an internal medicine residency
program. Ann Intern Med 2002;136:358e367.
5. Gelfand DV, Podnos YD, Carmichael JC, et al. Effect of the
80-hour workweek on resident burnout. Arch Surg 2004;
139:933e938; discussion 938e940.
6. Ishak WW, Lederer S, Mandili C, et al. Burnout during resi-
dency training: a literature review. J Grad Med Educ 2009;1:
236e242.
7. Dyrbye LN, West CP, Satele D, et al. Burnout among
US medical students, residents, and early career physicians
relative to the general U.S. population. Acad Med 2014;89:
443e451.
8. Rubin R. Recent suicides highlight need to address depression
in medical students and residents. JAMA 2014;312:
1725e1727.
9. Salles A, Liebert CA, Greco RS. Promoting balance in the lives
of resident physicians: a call to action. JAMA Surg 2015;150:
607e608.
10. OaklanderM.Doctorsonlifesupport.Time2015(September7):
44e50.
11. Salovey P, Mayer JD. Emotional intelligence. Imagin Cogn
Pers 1990;9:185e211.
12. Mikolajczak M, Petrides KV, Coumans N, Luminet O. The
moderating effect of trait emotional intelligence on mood
deterioration following laboratory-induced stress. Int J Clin
Hlth Psyc 2009;9:455e477.
13. Petrides KV, Furnham A. The role of trait emotional intelli-
gence in a gender-specific model of organizational variables.
J Appl Soc Psychol 2006;36:552e569.
14. Martins A, Ramalho N, Morin E. A comprehensive meta-
analysis of the relationship between emotional Intelligence
and health. Pers Indiv Differ 2010;49:554e564.
15. Revicki DA, Leidy NK, Howland L. Evaluating the psycho-
metric characteristics of the Psychological General Well-
Being Index with a new response scale. Qual Life Res 1996;
5:419e425.
16. Dupuy HJ. The Psychological General Well-Being (PGWD)
Index. In: Wenger NK, Mattson ME, Furburg CD,
Elinson J, eds. Assessment of Quality of Life in Clinical Trials
of Cardiovascular Therapies. New York: Le Jacq Publishing;
1984:170e183.
Vol. 223, No. 2, August 2016 Lin et al Emotional Intelligence and Resident Wellness 357](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/35a247f9-2cdf-4cff-8858-810d550995d7-160825170055/85/Emotional-Intelligence-6-320.jpg)
