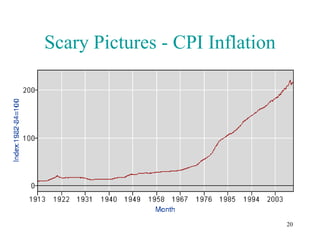
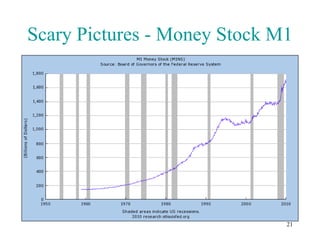
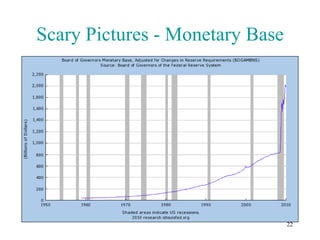
The document summarizes key points from a presentation about a book that takes a free-market perspective on the 2008 financial crisis. It defines relevant economic terms and outlines the book's argument that government intervention through low interest rates caused the boom, and bailouts will prolong the bust by preventing necessary market adjustments. The presentation questions some assumptions of free markets and identifies roles for government in addressing issues like natural monopolies and environmental protection. It also provides a deeper analysis of factors influencing the money supply and the impacts of fiat versus commodity-backed currencies.