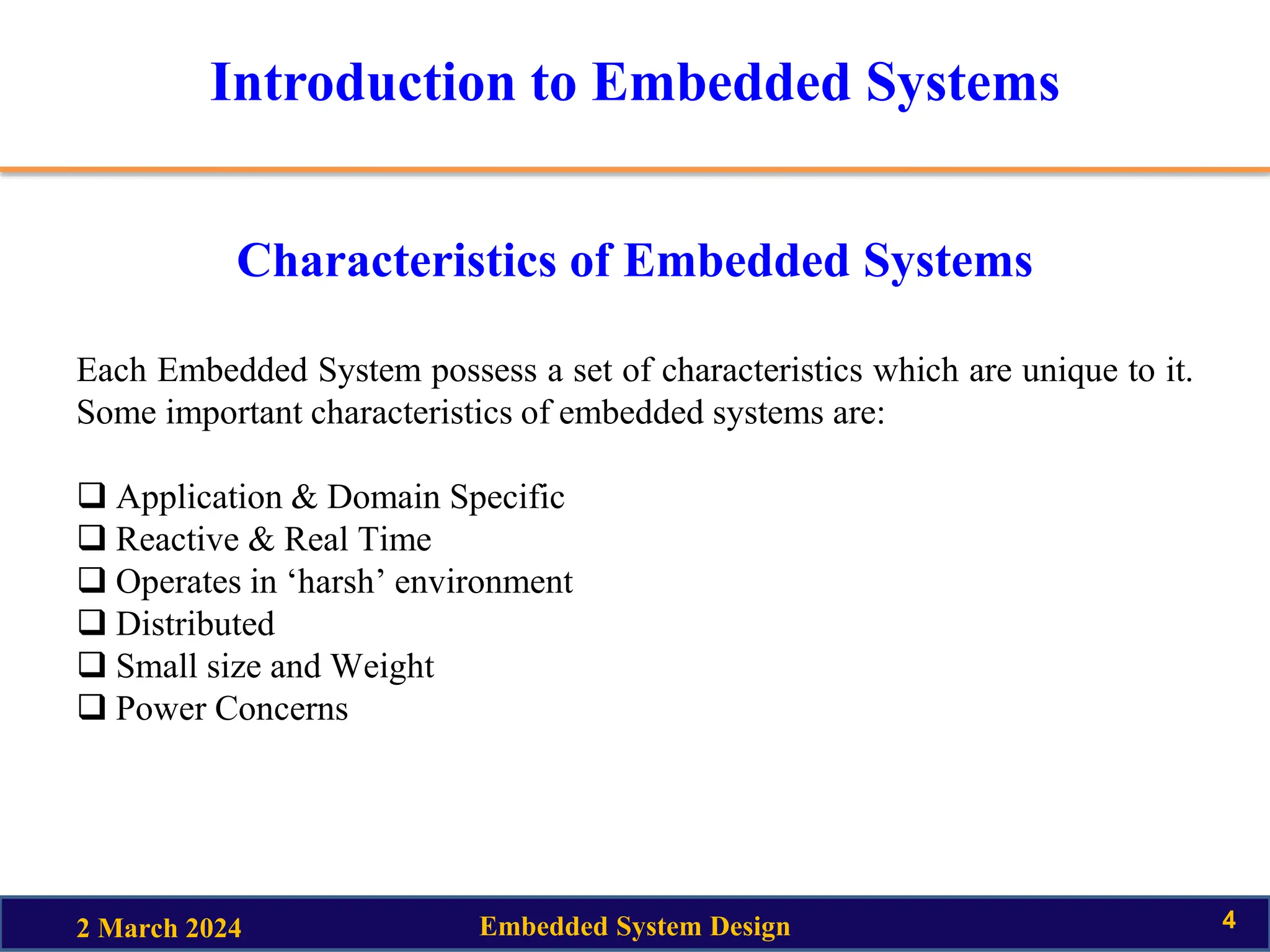
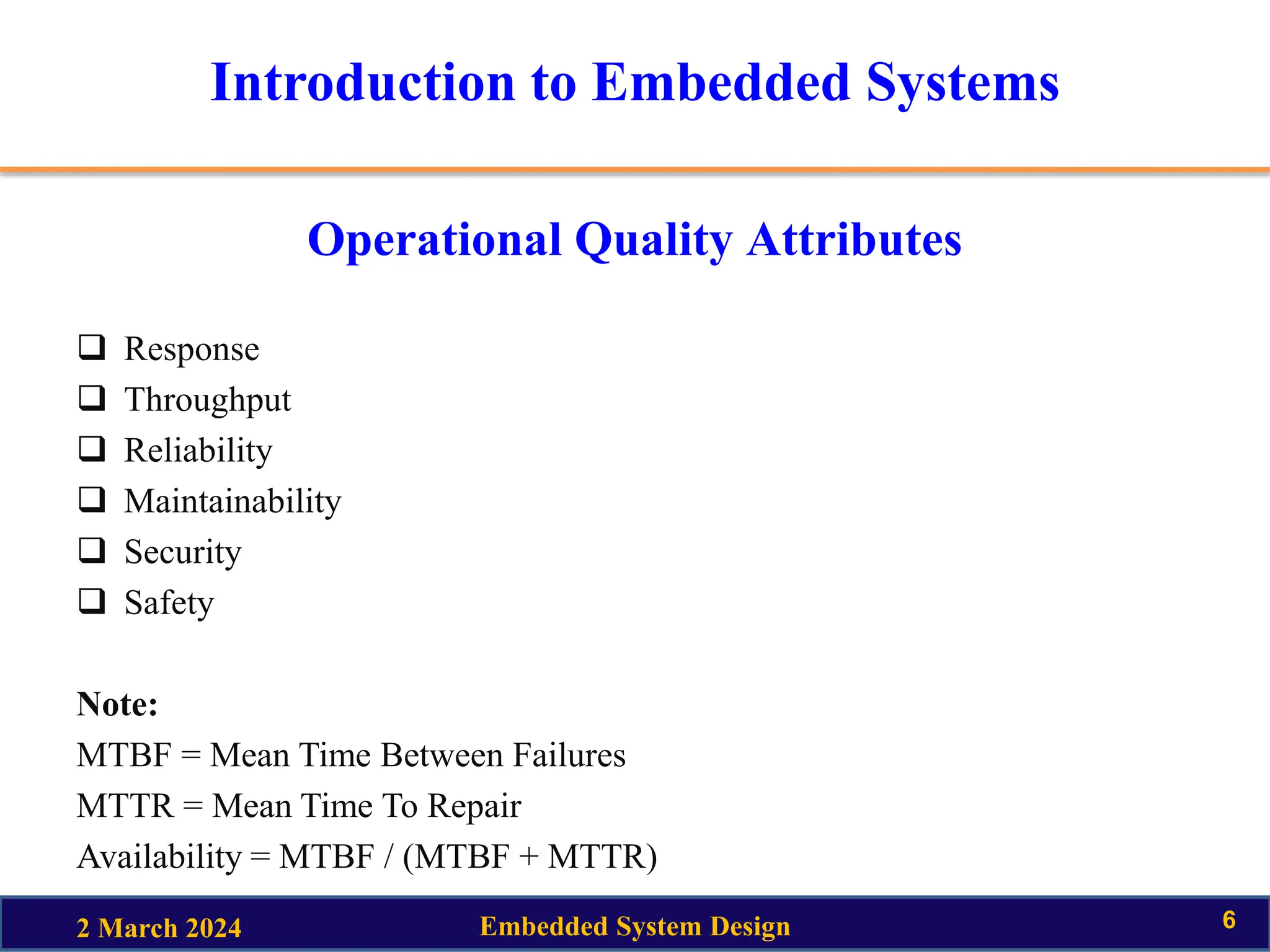
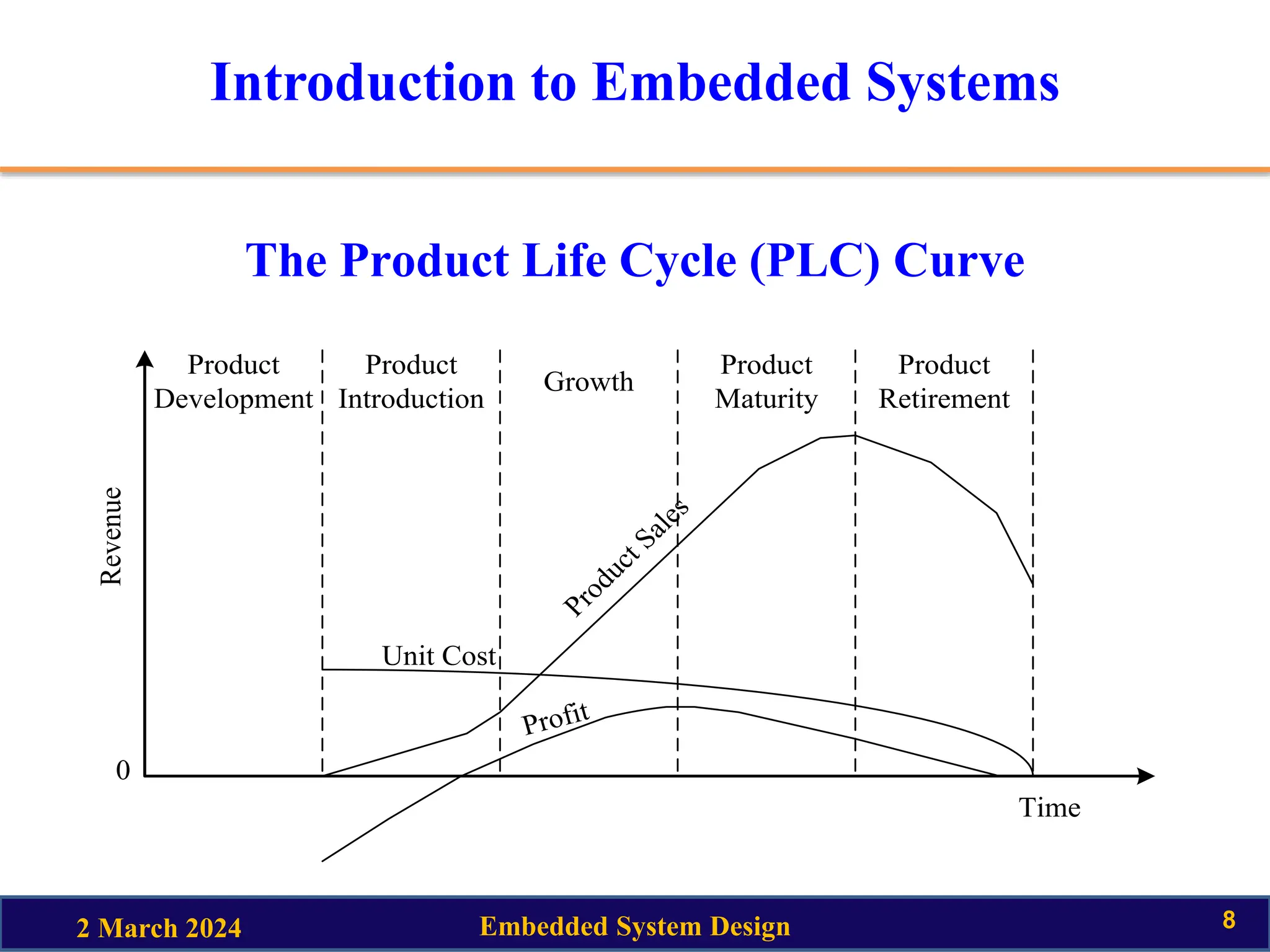
This document provides an introduction to embedded system design. It discusses key topics like the definition of embedded systems, their characteristics and quality attributes. Characteristics include being application specific, reactive, real-time, power-constrained and distributed. Quality attributes are classified as operational or non-operational. Operational attributes include response, throughput, reliability and safety. Non-operational attributes include testability, evolvability and portability. The document also provides an example of a smart running shoe from Adidas that uses sensors, actuators and a microprocessor to adapt shock absorption based on running style and conditions.