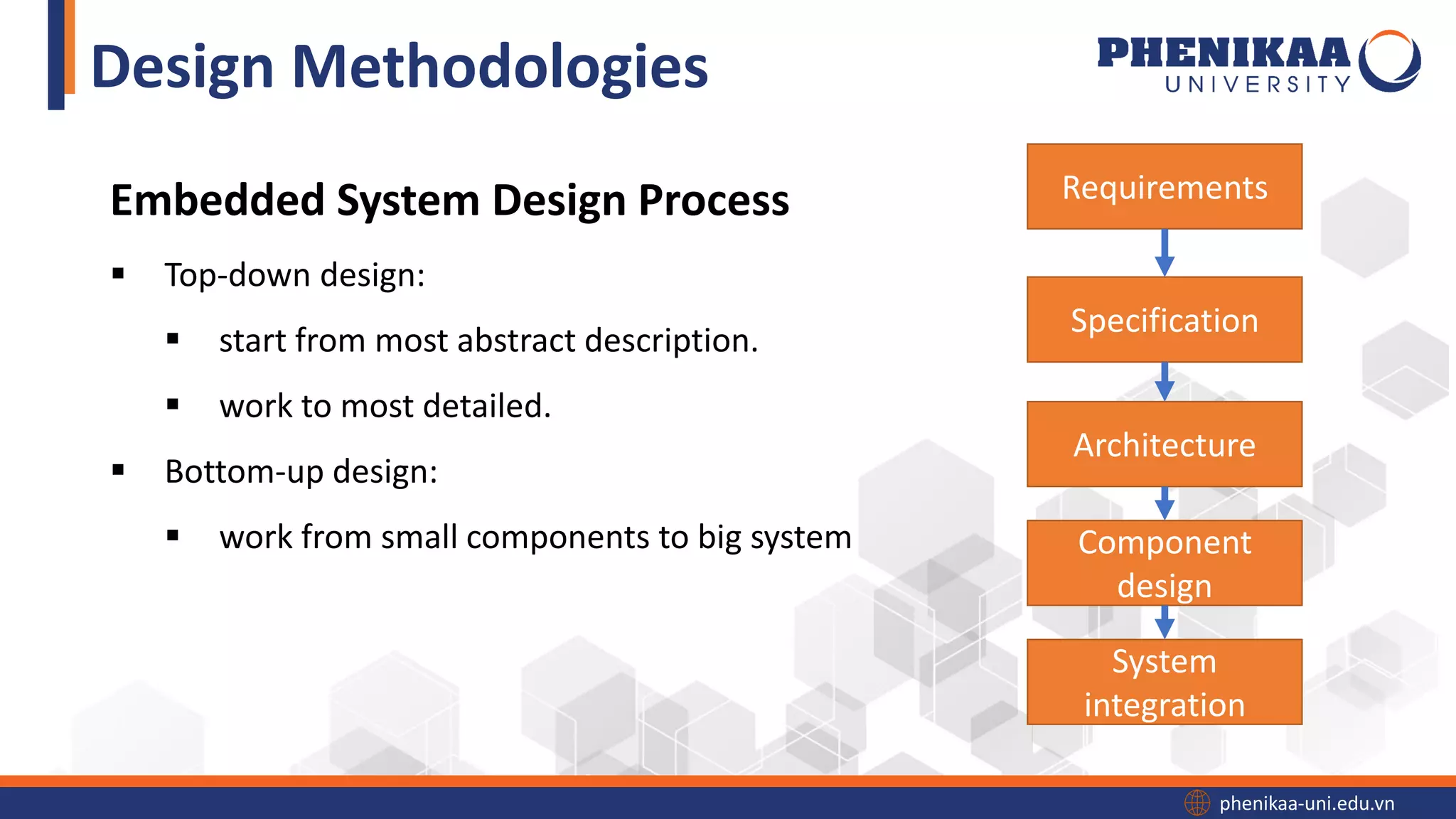
The document discusses embedded system design processes and methodologies. It describes the typical steps in an embedded system design process as requirements specification, architecture design, component design, and system integration. It also outlines recent trends in embedded systems such as increased processor speed and reduced size and power consumption. Finally, it lists some major application areas for embedded systems like consumer electronics, industrial automation, biomedical systems, and telecommunications.