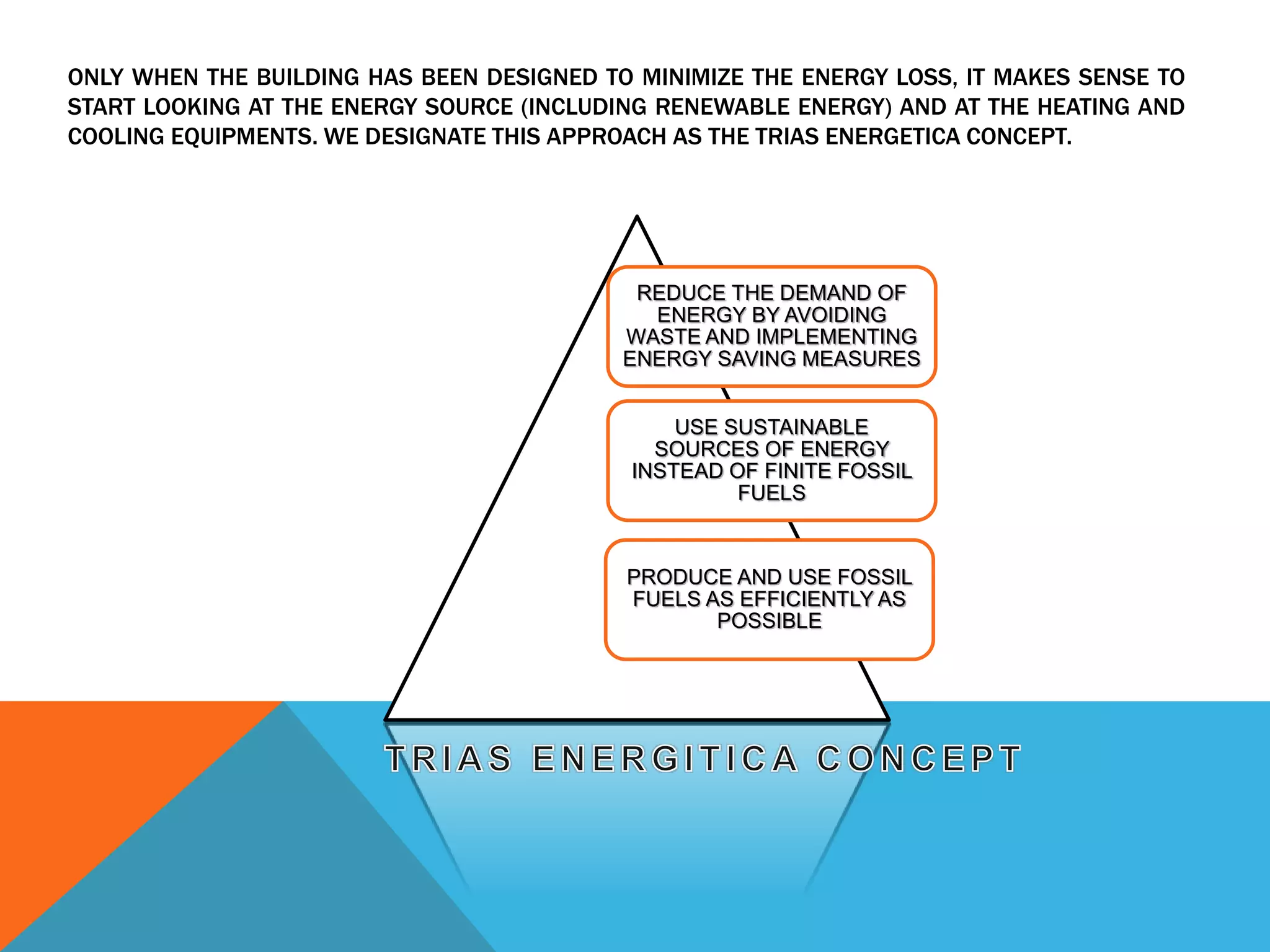
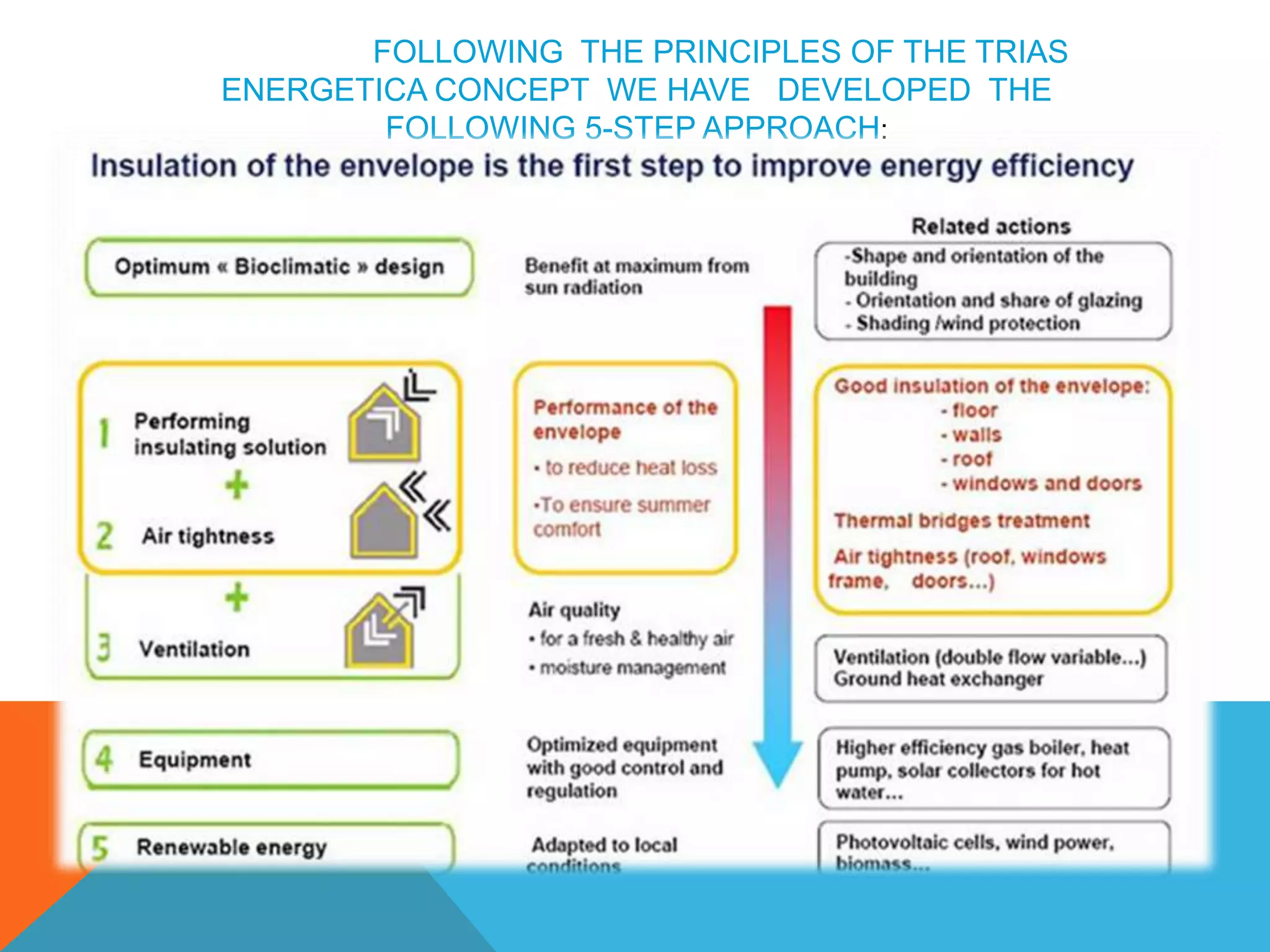
The document discusses elements of energy efficient buildings, including bioclimatic architecture, high performing building envelopes, and high performance controlled ventilation. It introduces the Trias Energetica concept of reducing energy demand through efficiency measures before considering energy sources and equipment. The concept advocates reducing waste, using sustainable energy sources over finite fossil fuels, and producing and using fossil fuels efficiently.
![ELEMENTS OF ENERGY EFFICIENT
BUILDINGS
B U I L D I N G S D E S I G N E D T O P R O V I D E A S I G N I F I C A N T
R E D U C T I O N O F T H E E N E R G Y N E E D F O R H E A T I N G ,
C O O L I N G , L I G H T E N I N G E T C . C A N B E A C H I E V E D
T H R O U G H F O L L O W I N G E L E M E N T S :
1]Bioclimatic architecture: shape and orientation of the building,
Solar protections, passive solar systems.
2]High performing building envelope: thorough insulation, high performing glazing
And windows, air-sealed construction, avoidance of thermal bridges.
3]High performance controlled ventilation: mechanical insulation, heat recovery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elementsofenergyefficientbuildings-180422110523/75/Elements-of-energy-efficient-buildings-1-2048.jpg)