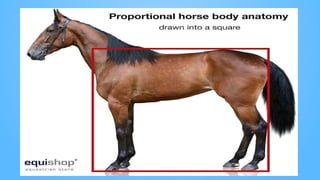
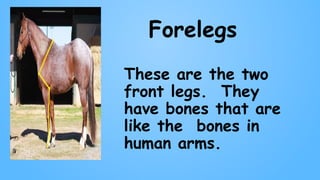
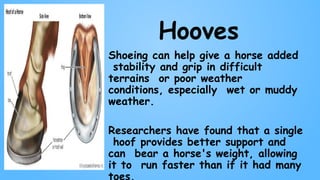
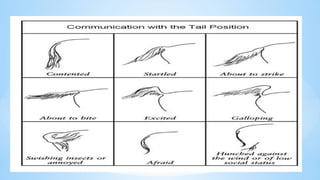
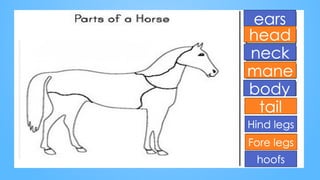
The document discusses the characteristics of mammals and details specific features of horses, highlighting their body types, sensory organs, and unique facts. Mammals share five key traits, including being warm-blooded and providing milk to their young. It also notes that horses cannot breathe through their mouths, can sleep standing, and possess exceptional reflexes and a wide field of vision.