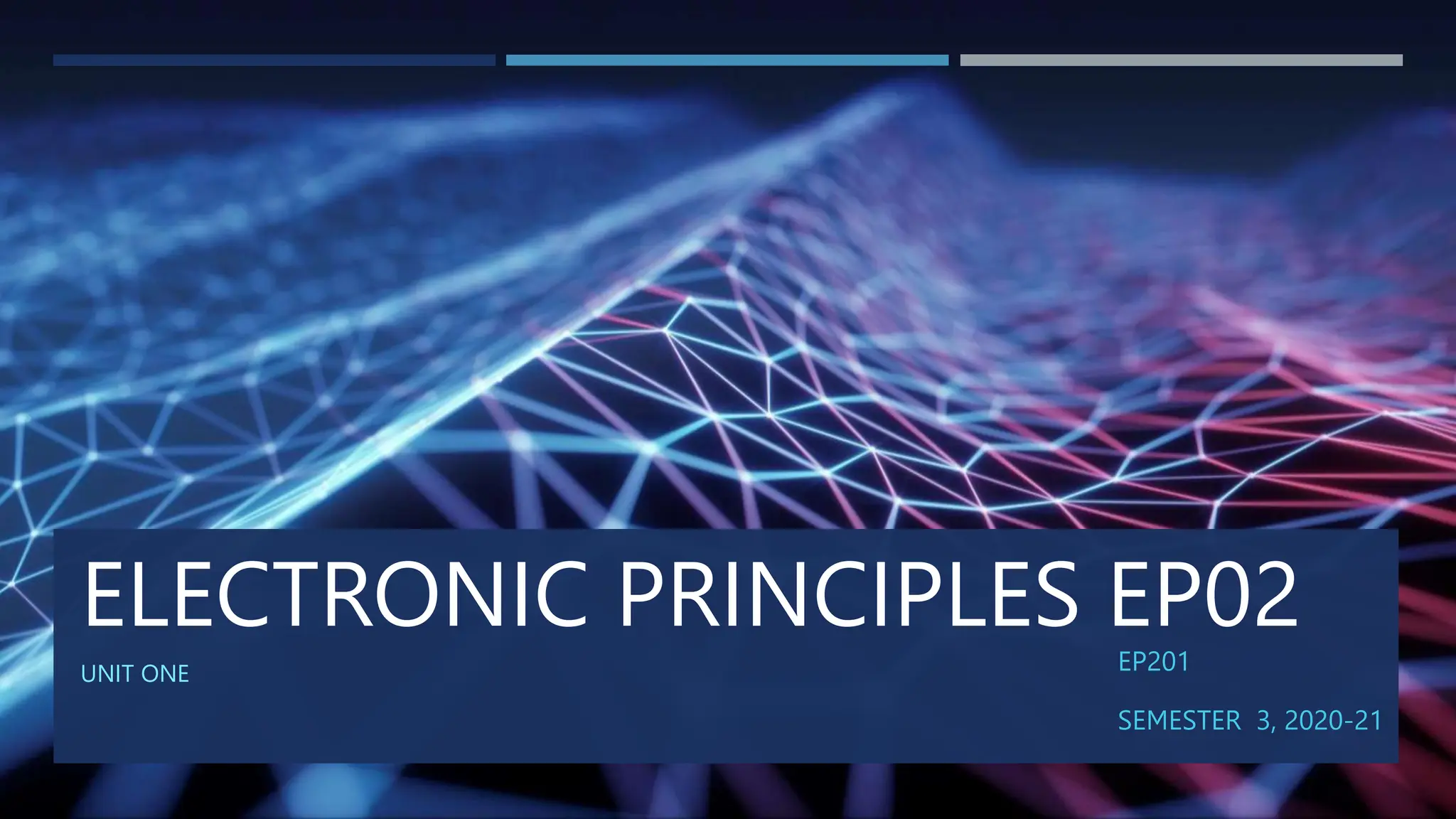
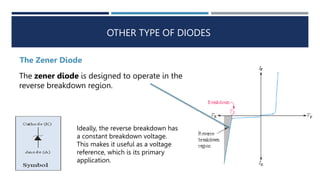
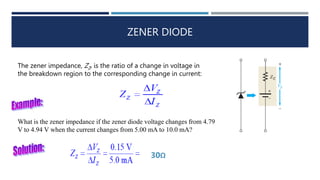
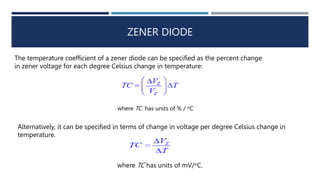
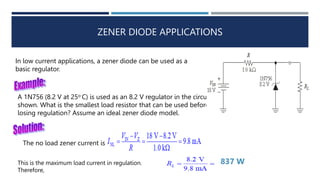
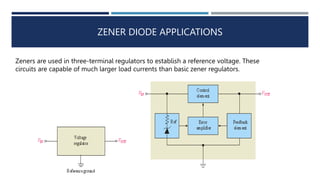
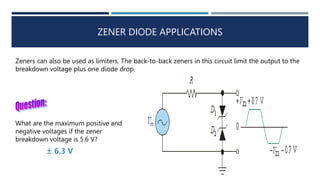
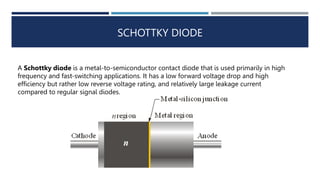
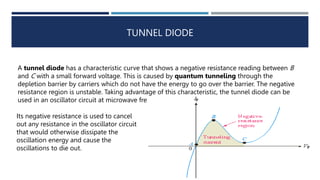
The document discusses different types of diodes, including Zener diodes, Schottky diodes, and tunnel diodes. It defines Zener diodes as diodes designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region and explains their use as voltage references. It also provides examples of calculating Zener impedance and the effects of temperature on Zener voltage. Schottky diodes are described as having low forward voltage drop and high efficiency but low reverse voltage rating. Tunnel diodes exhibit negative resistance due to quantum tunneling, which allows them to be used in oscillator circuits.