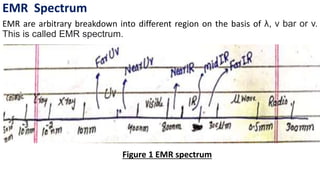
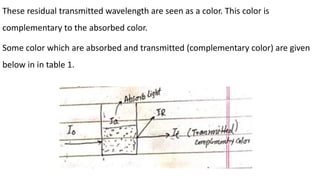
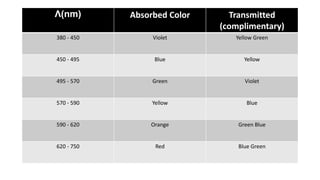
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is any form of radiant energy that propagates as a transverse wave, including visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays and radio waves. EMR is characterized by its wavelength or frequency. The EMR spectrum ranges from gamma rays to radio waves, divided into regions including infrared, visible light and ultraviolet. Visible light has wavelengths from 400-700 nm and is observed as different colors due to the wavelengths absorbed and transmitted by an object when illuminated with white light.