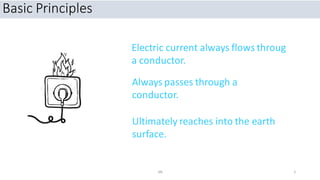
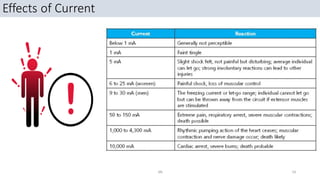
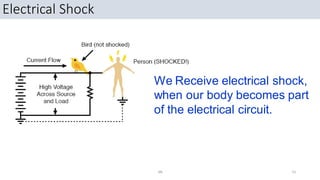
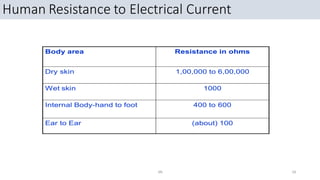
This document discusses electrical safety. It covers hazards of electricity like electrical shock, fire, and explosion. It defines terms like current, voltage, and resistance. It explains Ohm's law and the effects of electrical current. It discusses severity of electrical shock depending on path, voltage, and current type. It compares alternating and direct current. It covers shock protection devices and legal requirements from acts and rules. Finally, it discusses site practices to ensure electrical safety. The overall document provides an introduction to electrical safety, hazards, principles, definitions, effects, requirements, and practices.