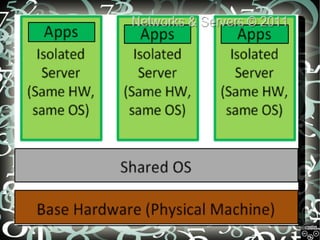
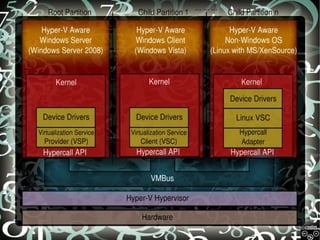
This document discusses virtualization techniques and cloud computing. It begins by defining virtualization as creating virtual versions of hardware platforms, operating systems, and other resources. Virtualization provides benefits like cost reduction, isolation, testing, and ease of duplication. The document then covers different virtualization types including full virtualization, OS-level virtualization, and hardware-assisted virtualization. The second part of the document defines cloud computing and discusses how it enables fast provisioning, easy scaling, and pay-as-you-go metering. It provides an overview of Amazon Web Services, including computing, storage, database and messaging services.