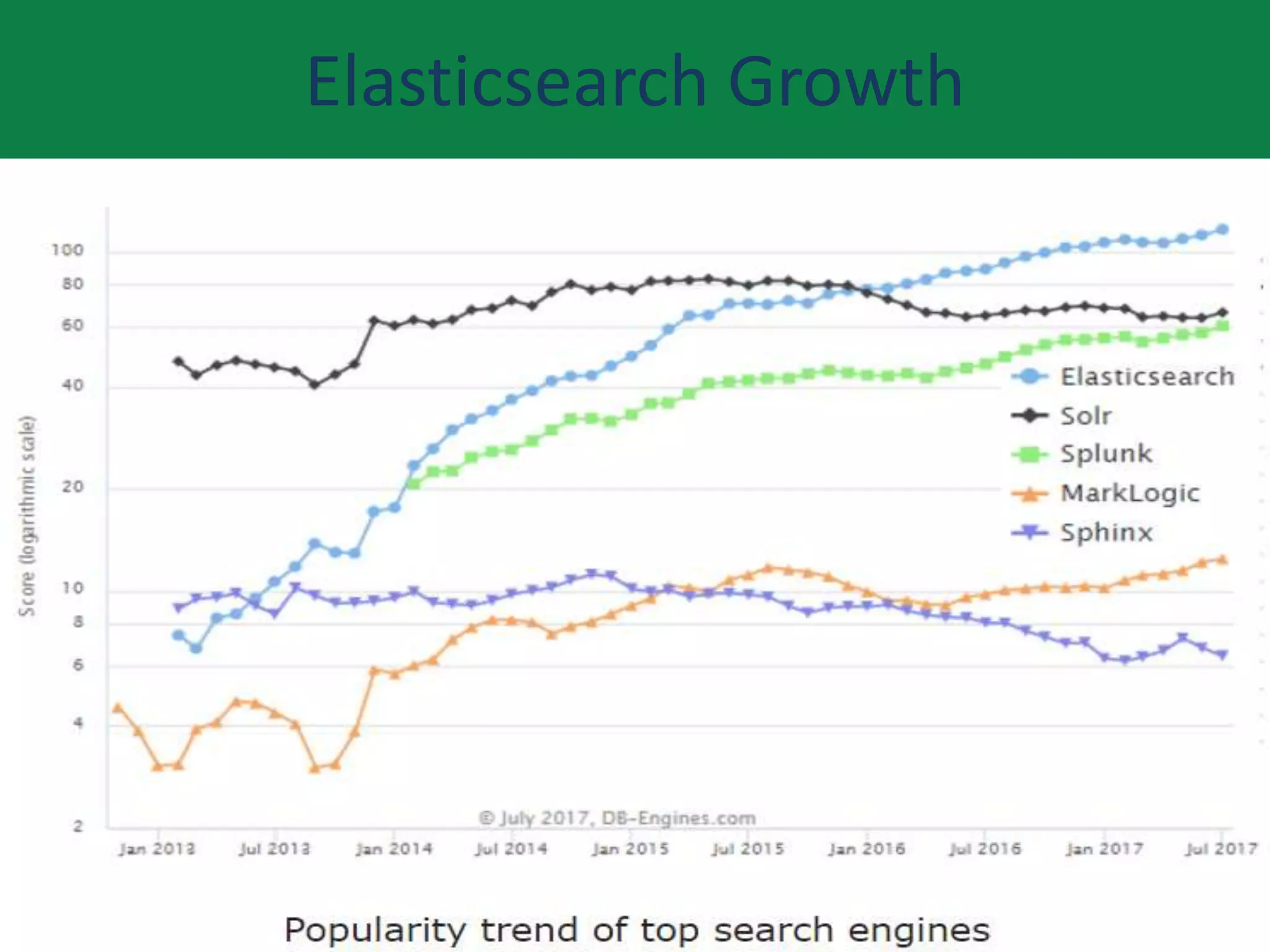
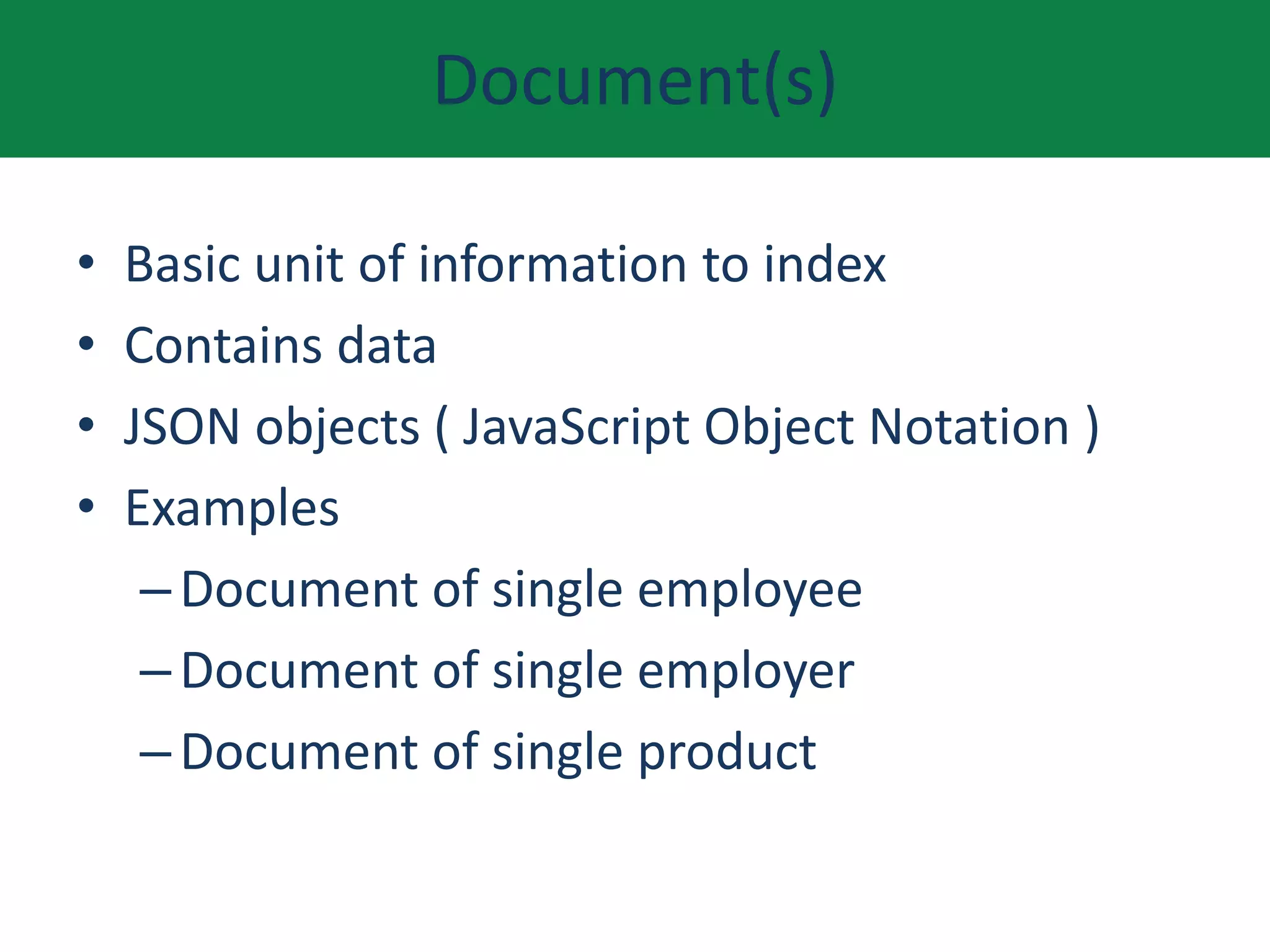
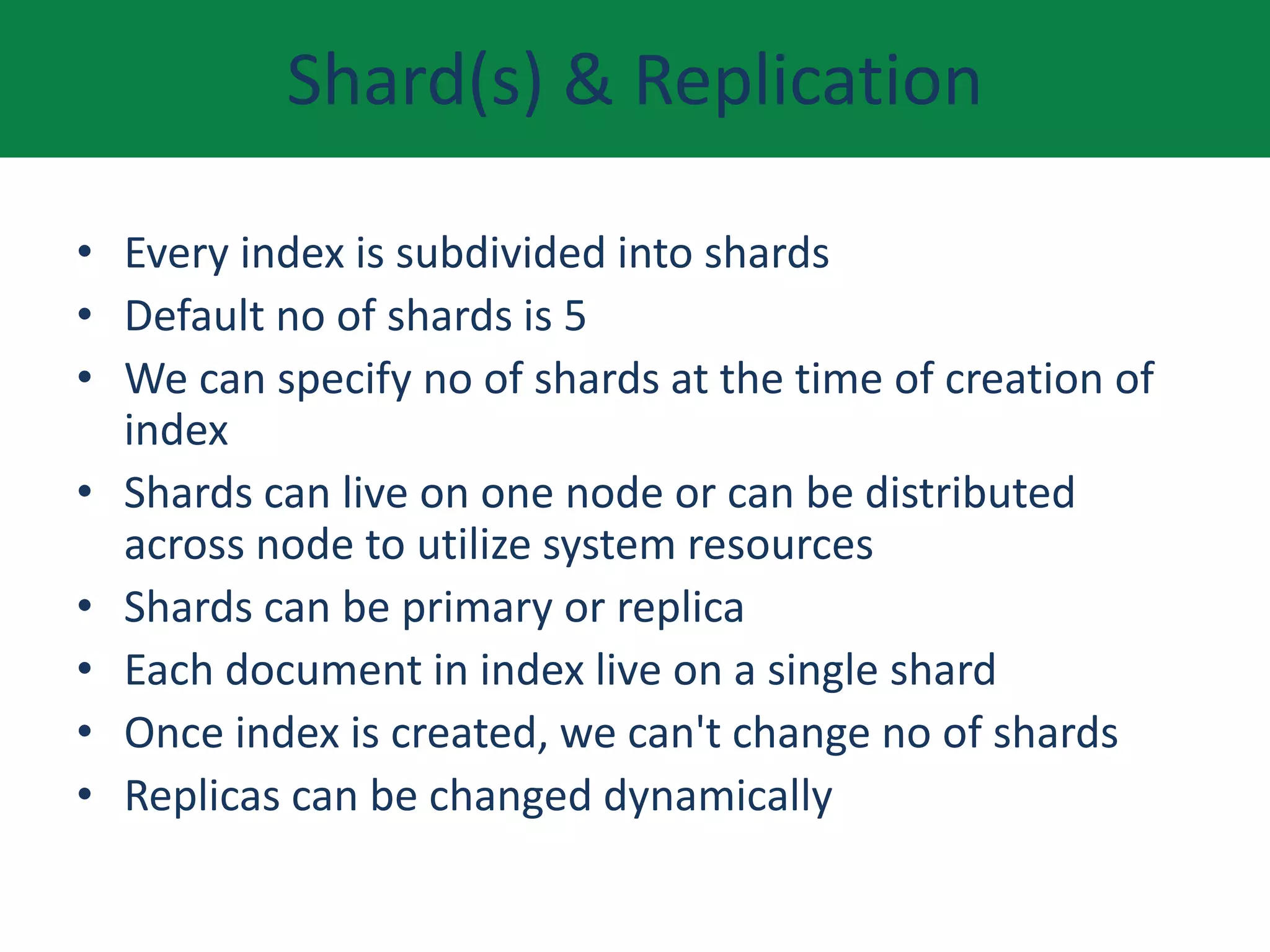
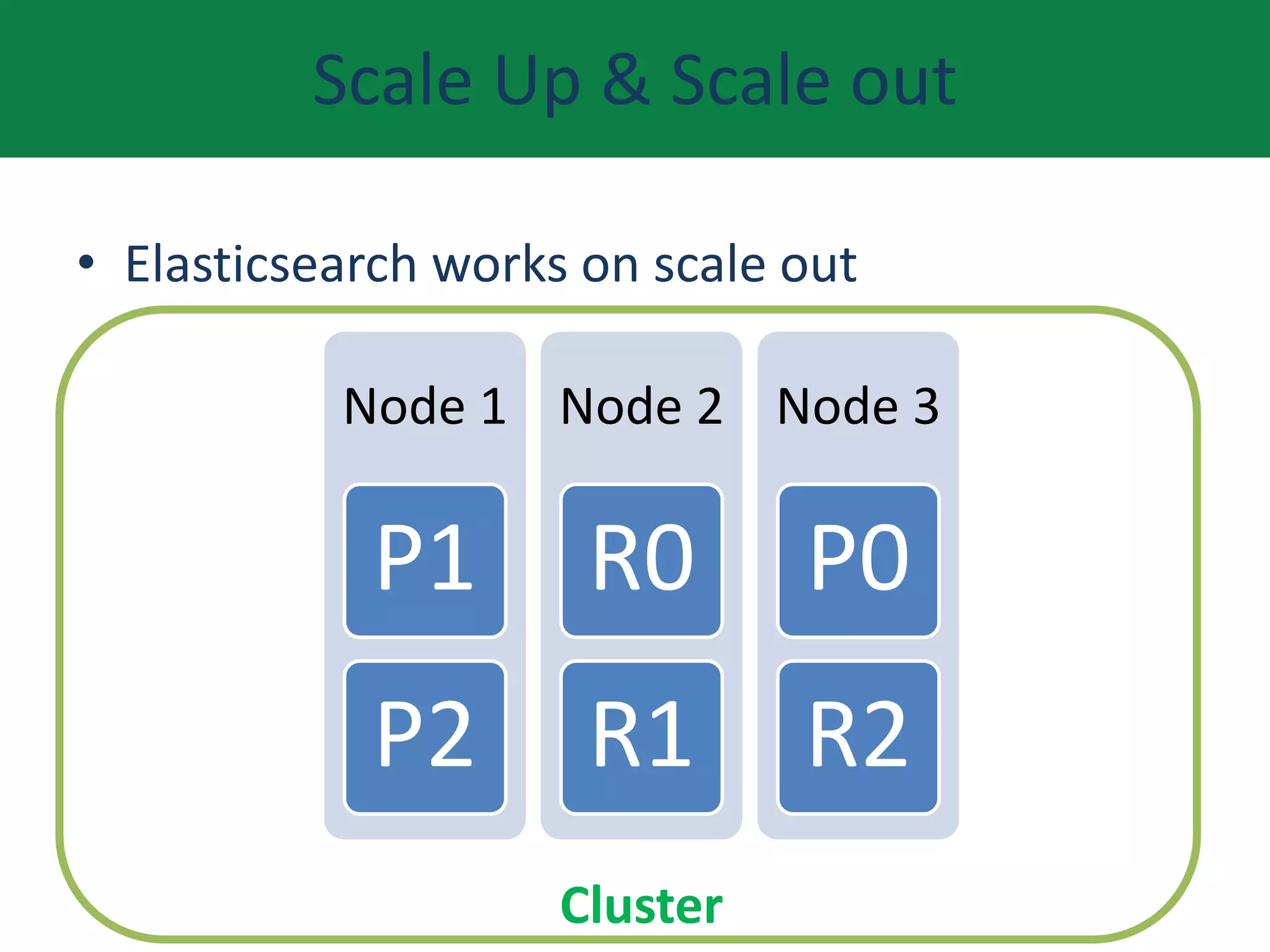
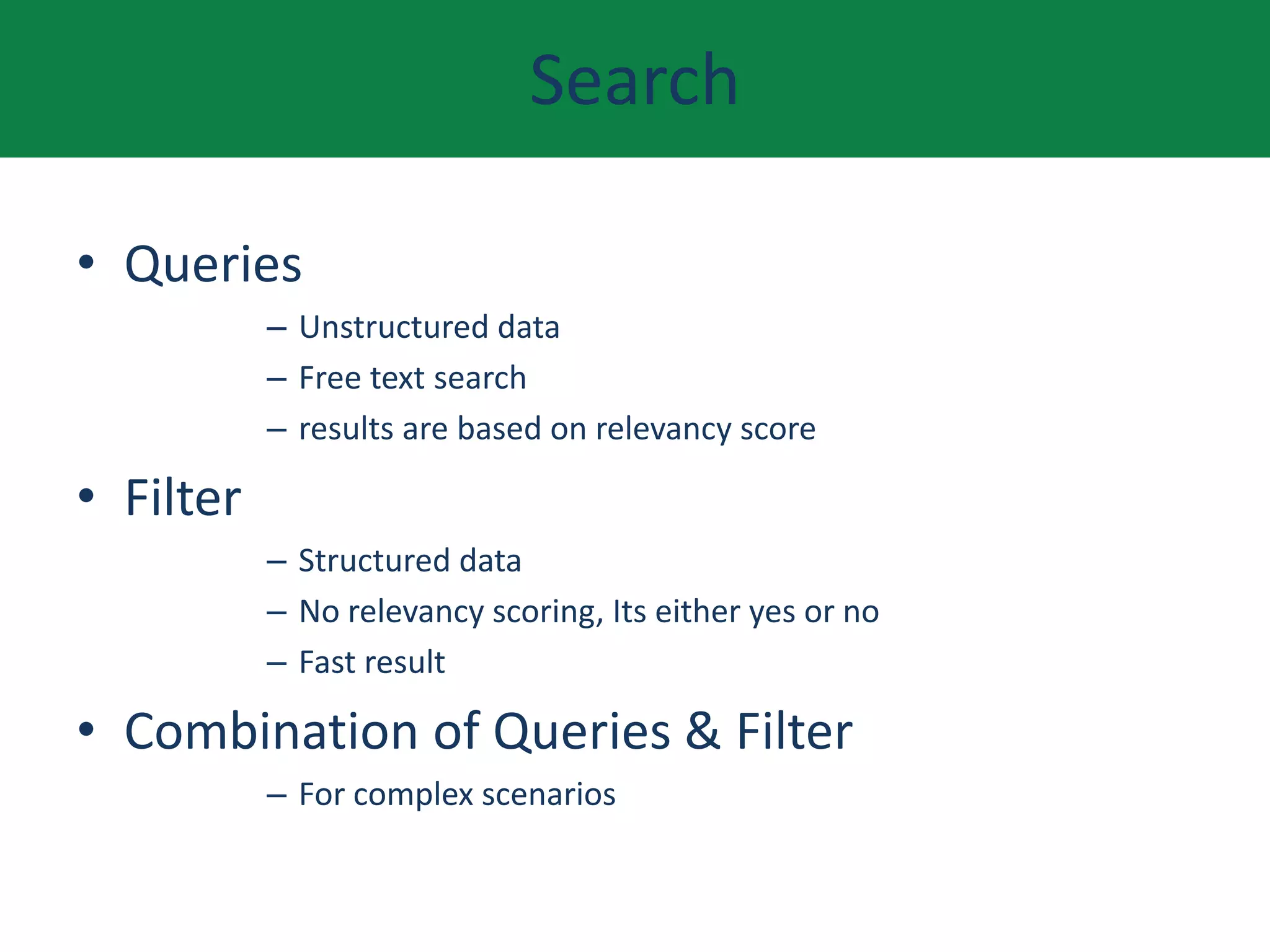
This document provides an overview of Elasticsearch including what it does, use cases, its history and growth. It describes the Elastic Stack and components like Logstash, Kibana, and Beats. It explains key Elasticsearch concepts such as clusters, nodes, indexes, types, documents, shards, and replication. It also covers search, aggregations, and how to install Elasticsearch on AWS.