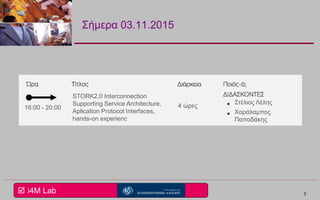
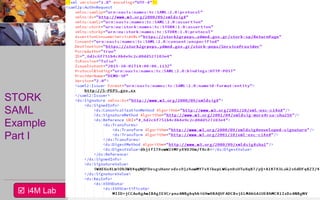
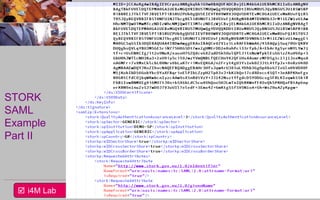
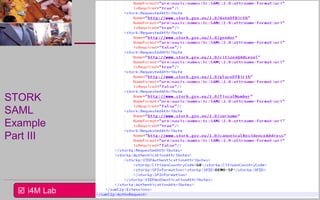
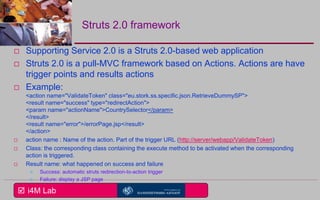
This document provides an overview of a seminar on e-identity and e-government hosted by the University of the Aegean. The agenda includes a discussion of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and its role in exchanging authentication data. It then outlines the architecture and APIs of the STORK2.0 Interconnection Supporting Service (ISS), including how it handles token validation, user selection validation, SAML processing, and attribute saving. The document concludes by inviting participants to a follow-up session for assignments presentations.