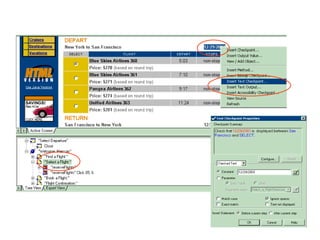
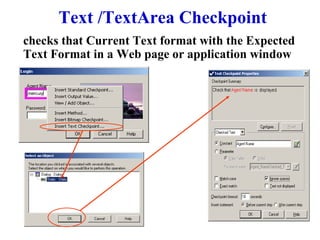
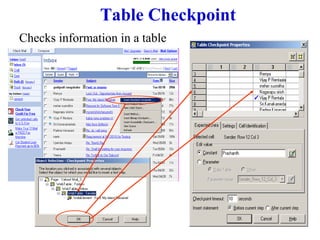
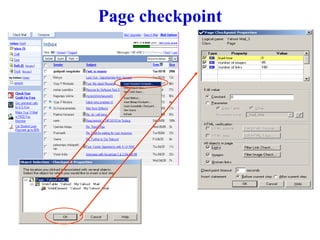
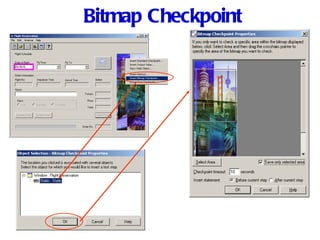
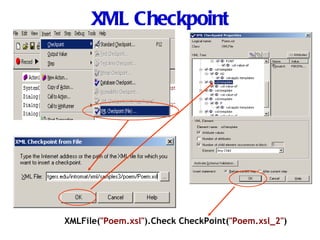
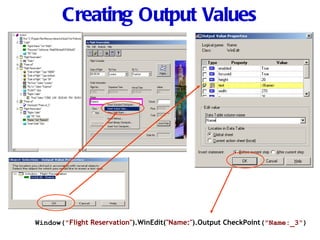
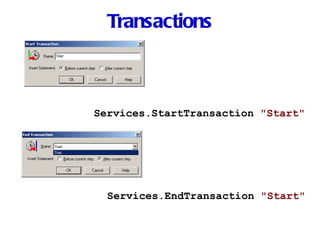
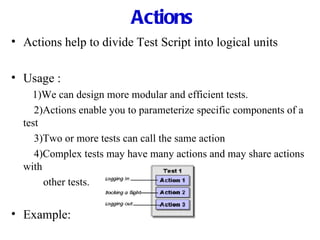
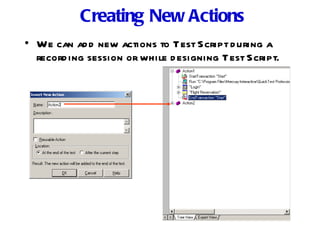
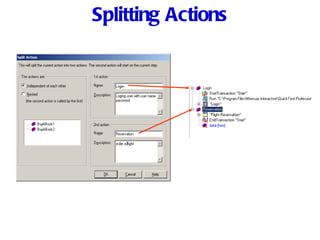
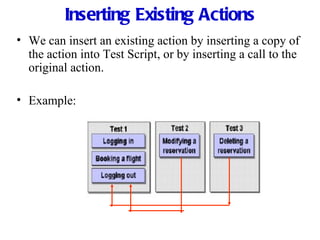
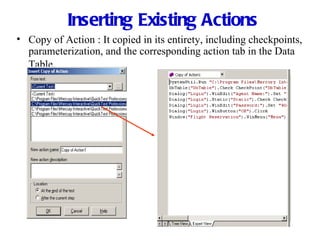
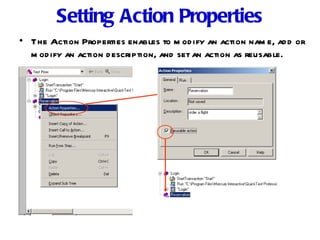
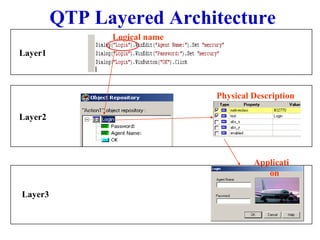
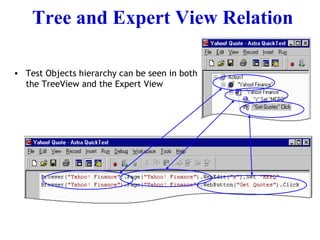
Automation testing involves recording user actions on an application and verifying its behavior. Quick Test Professional (QTP) is an automation testing tool that follows a 7 step process: 1) preparing the test environment; 2) recording user actions; 3) enhancing the test with checkpoints and parameters; 4) debugging the test; 5) running the test; 6) analyzing results; and 7) reporting defects. QTP allows dividing tests into logical units called actions to make tests more modular and reusable across multiple tests.







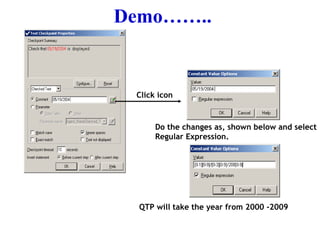
![Regular Expressions Regular expressions enable Quick Test to identify Objects and text strings with varying values. User has to identify the data projected to be change, like dates, so to accepts any dates, user can use regular expression. Example : Actual Date format : 05/19/2004 (mm/dd/yyyy) After Regular Expression: [0-1][0-9]/[0-3][0-9]/200[0-9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qtppresentation-13052882917668-phpapp01-110513070737-phpapp01/85/Qtp-Presentation-15-320.jpg)