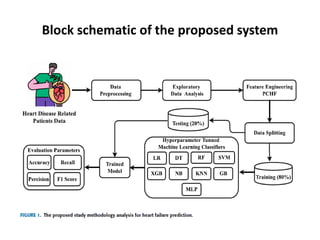
The document discusses heart disease, its early detection significance, and the study's objective to investigate machine learning methods for predicting heart disease. It evaluates various algorithms like decision trees, naive bayes, and k-nearest neighbors, comparing their performance in terms of accuracy and effectiveness. The study concludes that while multiple machine learning techniques show promise, each has unique strengths and limitations relevant to clinical applications.