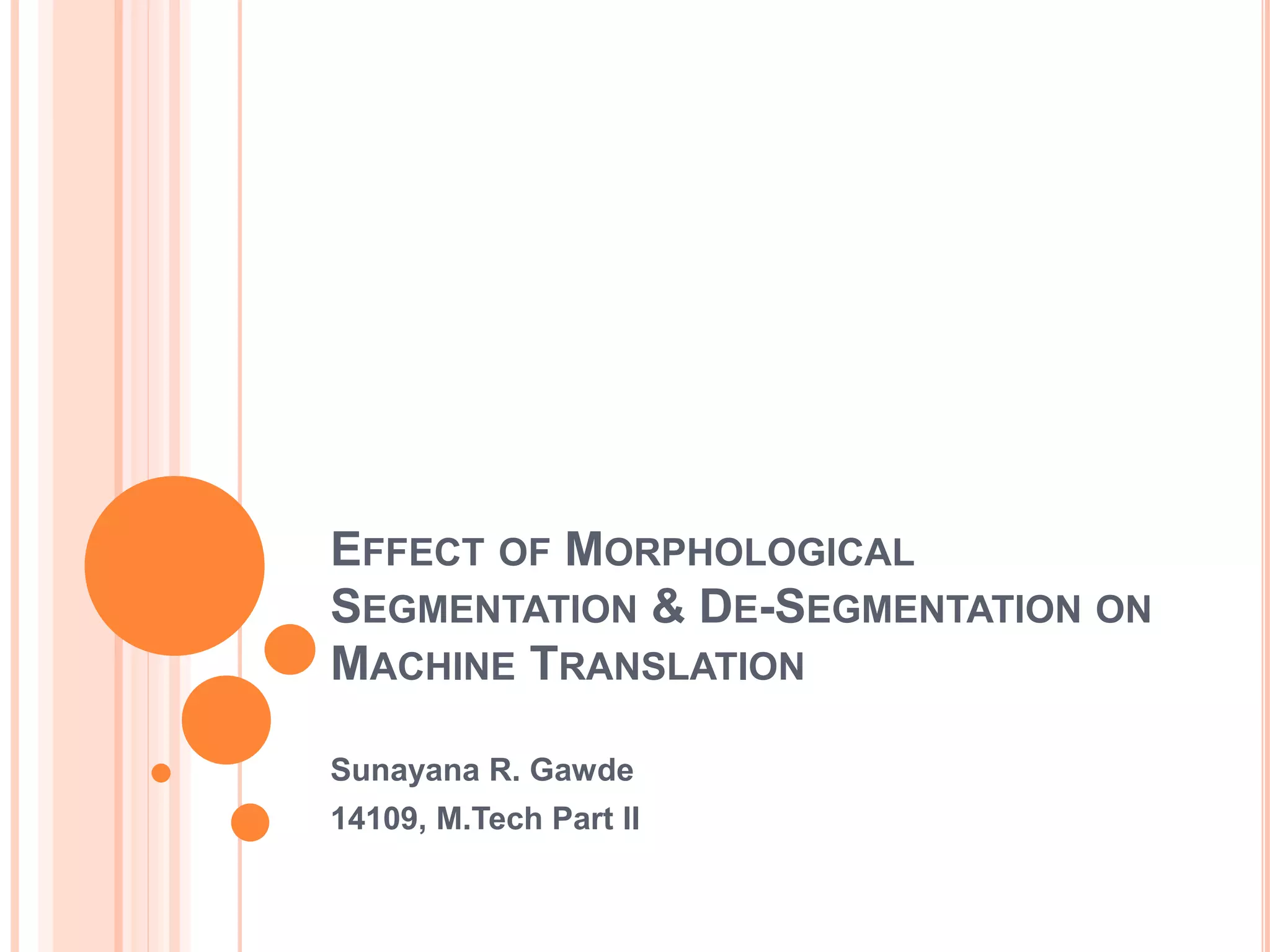
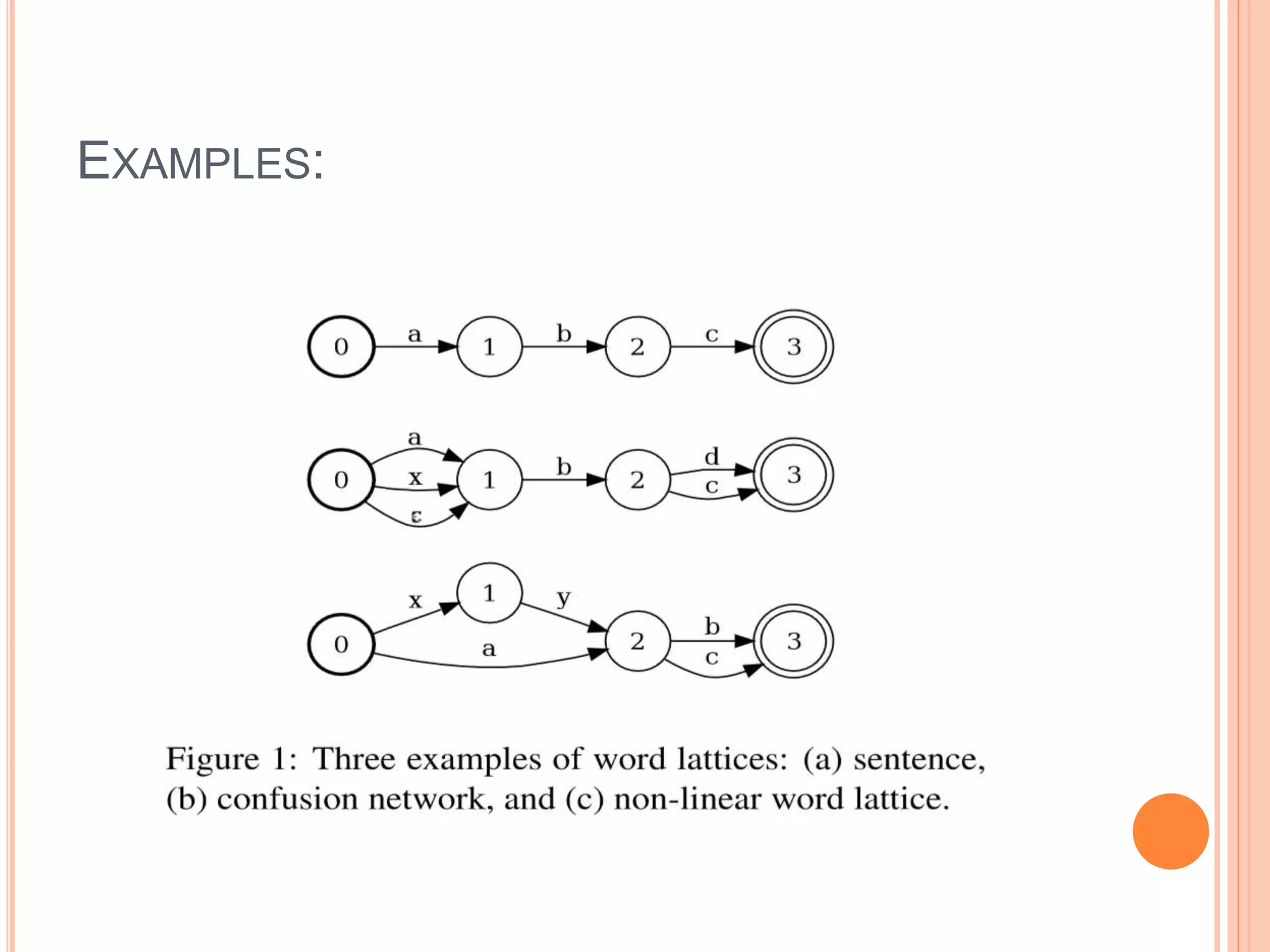
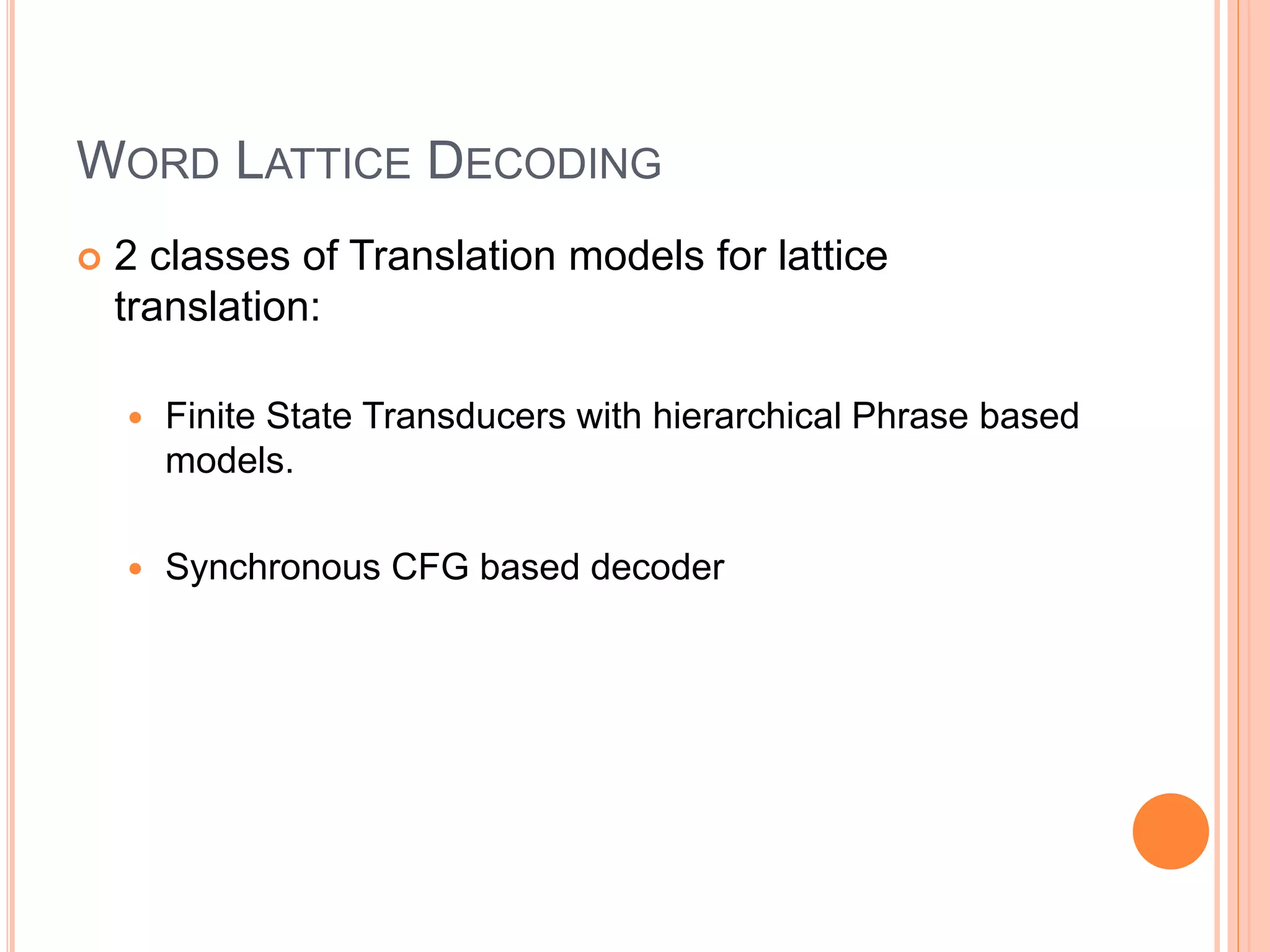
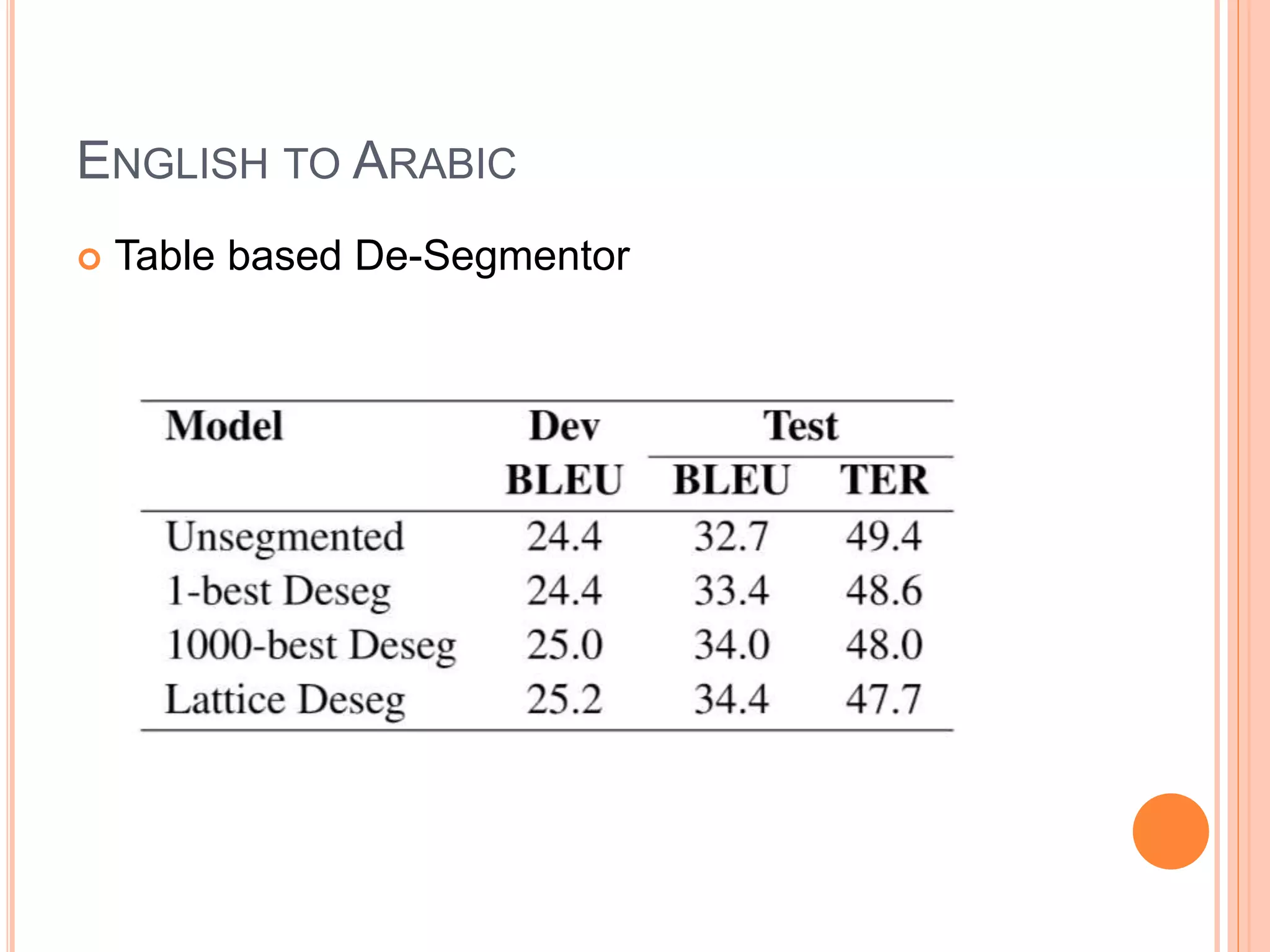
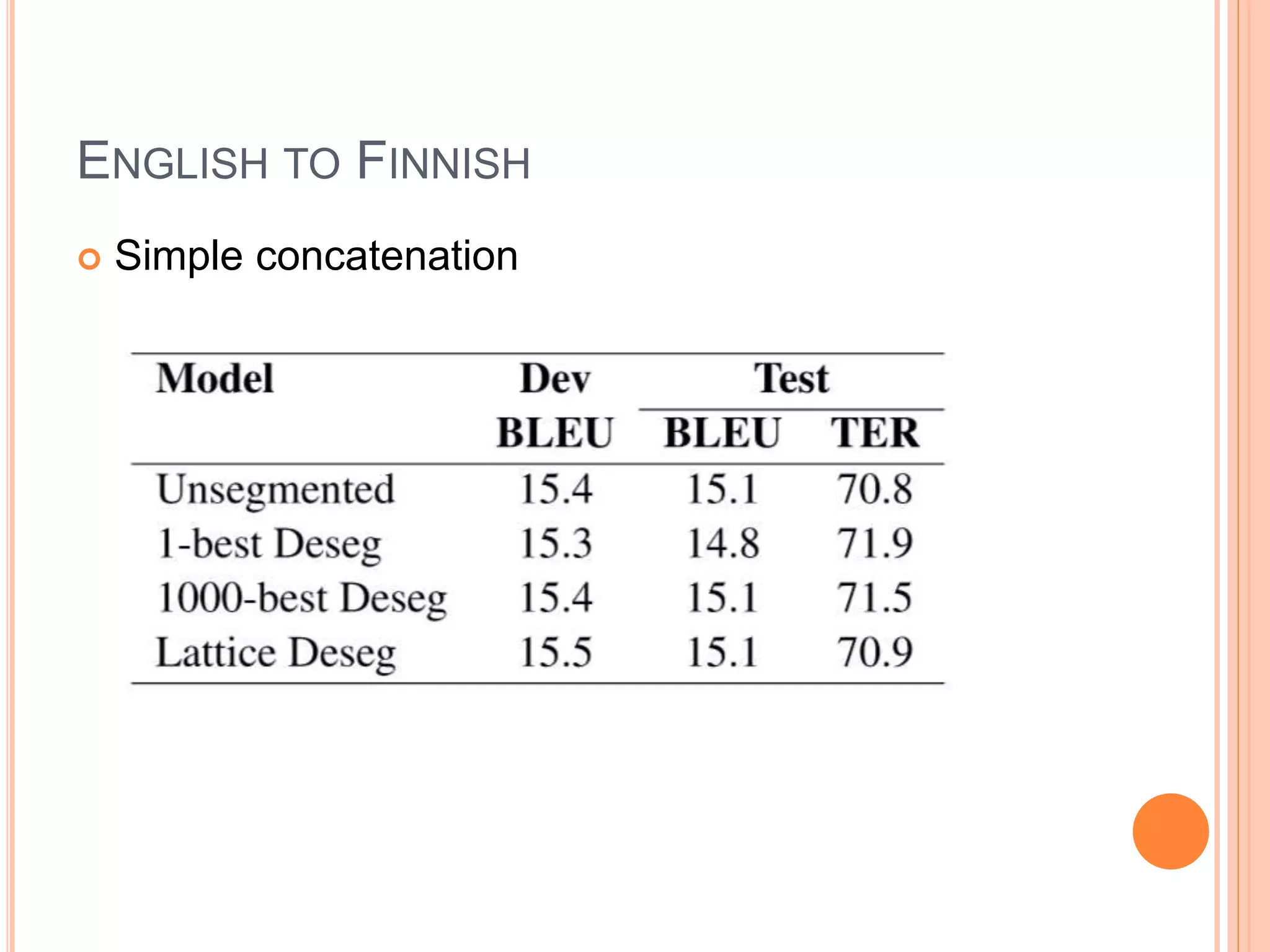
The document discusses the impact of morphological segmentation and de-segmentation on machine translation, highlighting their roles in reducing data sparsity for English-to-Hindi, English-to-Arabic, and English-to-Finnish translations. Key methods include lattice de-segmentation, where word lattices are used for translation with various models such as finite state transducers and phrase-based models, leading to improved BLEU scores. The proposed work aims to implement these techniques in English to Konkani and Hindi to Konkani translation systems, emphasizing the need for morphological analysis and evaluation.